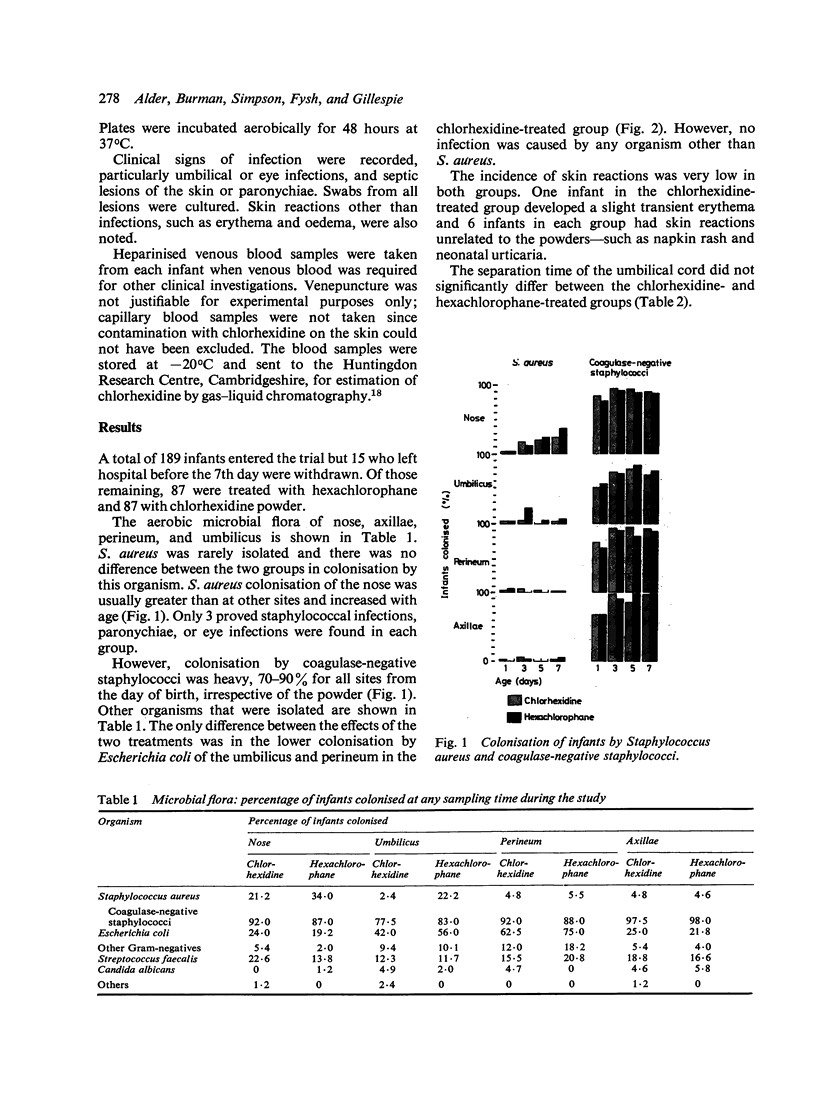
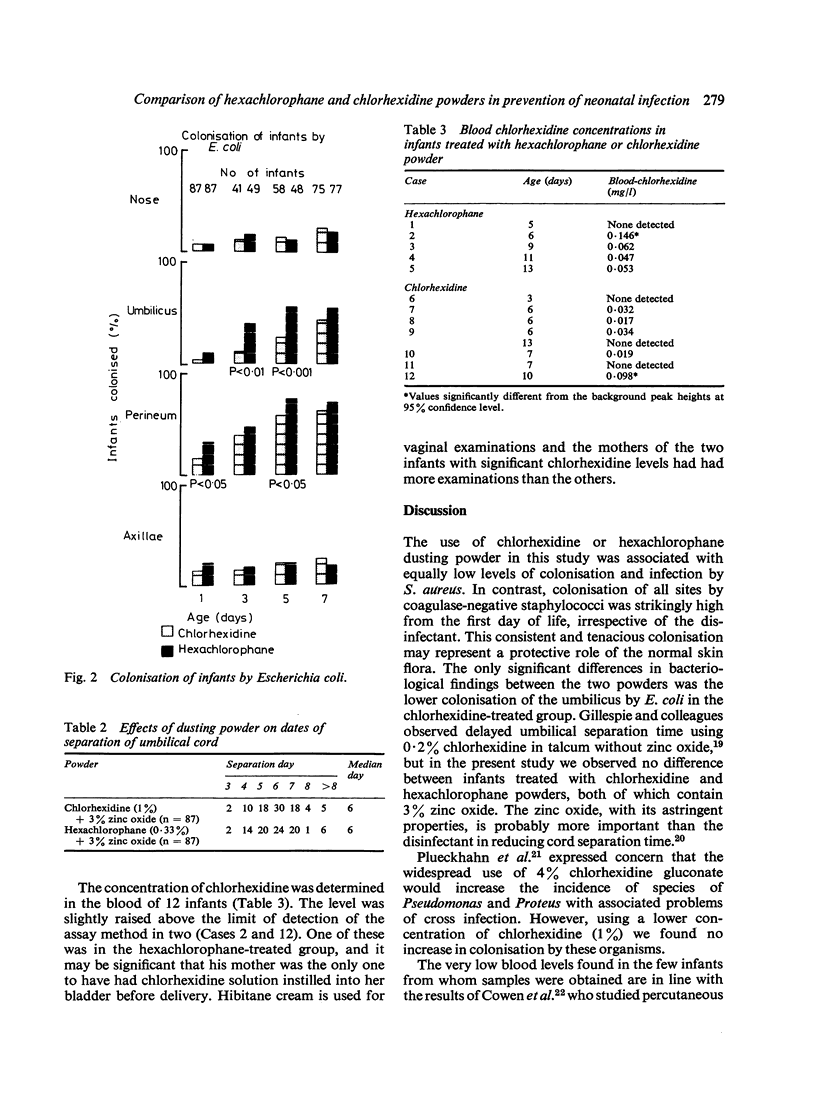
Abstract
The protective effect of treating the skin of newborn infants with powders containing 1% chlorhexidine or 0.33% hexachlorophane was compared. Each was equally effective in preventing colonisation and infection by Staphylococcus aureus. In contrast, the skin became profusely colonised by coagulase-negative staphylococci, irrespective of the powder used. Venous blood concentrations of chlorhexidine were low or undetectable in the few infants whose blood was analysed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alder V. G., Burman D., Corner B. D., Gillespie W. A. Absorption of hexachlorophane from infants' skin. Lancet. 1972 Aug 19;2(7773):384–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91780-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayliffe G. A., Brightwell K. M., Ball P. M., Derrington M. M. Staphylococcal infection in cervical glands of infants. Lancet. 1972 Sep 2;2(7775):479–480. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91868-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNER B. D., CROWTHER S. T., EADES S. M. Control of staphylococcal infection in a maternity hospital; clinical survey of the prophylactic use of hexachlorophane. Br Med J. 1960 Jun 25;1(5190):1927–1929. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5190.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. G., Pitkewicz J. S. The incidence of infections in nurseries since the discontinuation of hexachlorophene bathing. Pediatrics. 1973 Feb;51(2):360–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen J., Ellis S. H., McAinsh J. Absorption of chlorhexidine from the intact skin of newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1979 May;54(5):379–383. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.5.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curley A., Kimbrough R. D., Hawk R. E., Nathenson G., Finberg L. Dermal absorption of hexochlorophane in infants. Lancet. 1971 Aug 7;2(7719):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewar J., Porter I. A., Smylie H. G. Staphylococcal infection in cervical glands of infants. Lancet. 1972 Sep 30;2(7779):712–712. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. E., Kaslow R. A., Mallison G. F., Bennett J. V. Staphylococcal disease outbreaks in hospital nurseries in the United States--December 1971 through March 1972. Pediatrics. 1973 Feb;51(2):413–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE W. A., SIMPSON K., TOZER R. C. Staphylococcal infection in a maternity hospital; epidemiology and control. Lancet. 1958 Nov 22;2(7056):1075–1080. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)92462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie W. A., Corner B. D., Burman D., Alder V. G. Absorption of hexachlorophane from dusting powder on newborn infant's skin. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Oct;73(2):311–315. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutières F., Aicardi J. Accidental percutaneous hexachlorophane intoxication in children. Br Med J. 1977 Sep 10;2(6088):663–665. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6088.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopelman A. E. Cutaneous absorption of hexachlorophene in low-birth-weight infants. J Pediatr. 1973 Jun;82(6):972–975. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plueckhahn V. D., Ballard B. A., Banks J. M., Collins R. B., Flett P. T. Hexachlorophene preparations in infant antiseptic skin care: benefits, risks, and the future. Med J Aust. 1978 Dec 2;2(12):555-6, 558-60. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1978.tb131725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plueckhahn V. D. Infant antiseptic skin care and hexachlorophene. Med J Aust. 1973 Jan 20;1(3):93–100. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1973.tb119650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON K., TOZER R. C., GILLESPIE W. A. Prevention of staphylococcal sepsis in a maternity hospital by means of hexachlorophane. Br Med J. 1960 Jan 30;1(5169):315–317. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5169.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes J. W., Eykyn S., Phillips I. Letter: Staphylococcal infection in the newborn. Lancet. 1974 Dec 7;2(7893):1392–1392. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman R. M., Leech R. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Neurotoxicity of hexachlorophene in the human: I. A clinicopathologic study of 248 children. Pediatrics. 1974 Dec;54(6):689–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


