Abstract
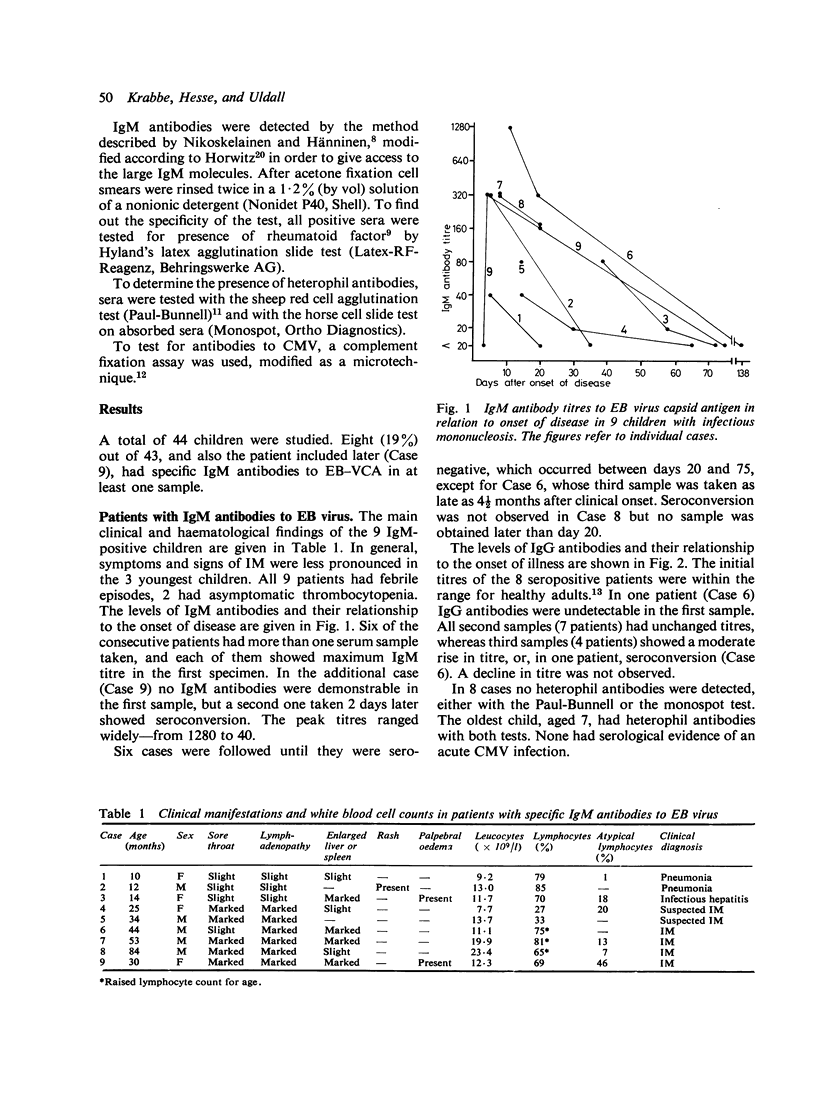
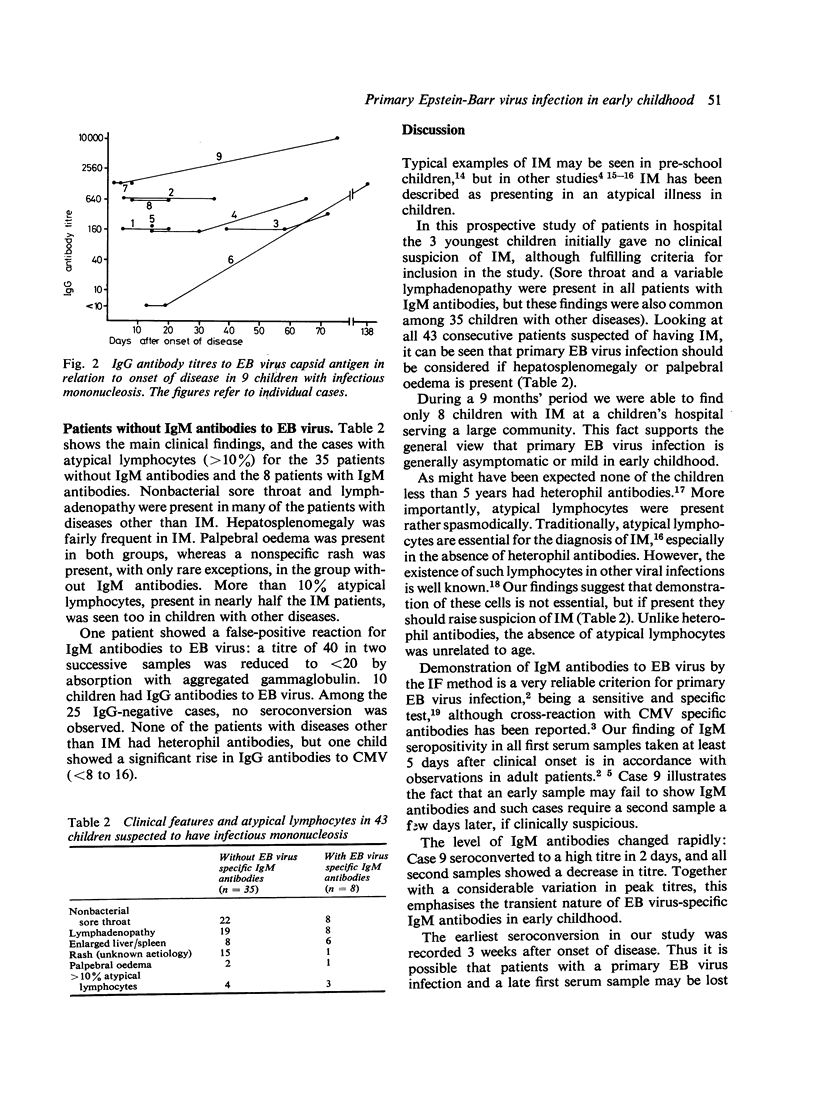
In a prospective study 43 consecutive children in hospital, aged between 6 months and 7 years and displaying at least one of the clinical signs of infectious mononucleosis (IM), were investigated for Epstein-Barr (EB) virus-specific IgM antibodies by an indirect immunofluorescence test. On this basis EB virus infection was considered confirmed in 8 patients, each of whom had IgM antibodies in the initial serum sample. In one additional patient, IgM antibodies were only detected in a second sample. The IgM antibodies disappeared with 3-11 weeks. Assessment of IgG antibodies had no diagnostic value in the acute phase of IM. Clinically the 3 youngest children, about 1 year of age, were diagnosed as having pneumonia or hepatitis, the 5 other consecutive patients as having IM. Hepatosplenomegaly was fairly frequently associated with IM, while sore throat, lymphadenopathy, and rash were often signs of other diseases. Only the oldest child had heterophil antibodies. Atypical lymphocytes (greater than 10%) were present in 4 of the 9 IM cases and were seen in children with other diseases as well. Our data stress the importance of measuring EB virus-specific IgM antibodies in order to diagnose IM in early childhood.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIDSOHN I., LEE C. L. SEROLOGIC DIAGNOSIS OF INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FIVE TESTS. Am J Clin Pathol. 1964 Feb;41:115–125. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/41.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S., Niederman J. C., Cenabre L. C., West B., Richards V. A. A prospective evaluation of heterophile and Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgM antibody tests in clinical and subclinical infectious mononucleosis: Specificity and sensitivity of the tests and persistence of antibody. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):546–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser K. B., Shirodaria P. V., Stanford C. F. Fluorescent staining and human IgM. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 18;3(5776):707–707. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5776.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg C. M., Henle W., Henle G., Horwitz C. A. Infectious mononucleosis in children. Evaluation of Epstein-Barr virus-specific serological data. JAMA. 1977 Feb 21;237(8):781–785. doi: 10.1001/jama.237.8.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Observations on childhood infections with the Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):303–310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. E., Horwitz C. A. Epstein-Barr virus specific diagnostic tests in infectious mononucleosis. Hum Pathol. 1974 Sep;5(5):551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G. Epstein-Barr virus and infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):263–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J., Levine P. H., Ebbesen P., Connelly R. R., Mordhorst C. H. A case control study on immunity to two Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens, and to herpes simplex virus and adenovirus in a population-based group of patients with Hodgkin's disease in Denmark, 1971-73. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jan;19(1):49–58. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz C. A., Henle W., Henle G., Schmitz H. Clinical evaluation of patients with infectious mononucleosis and development of antibodies to the R component of the Epstein-Barr virus-induced early antigen complex. Am J Med. 1975 Mar;58(3):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90599-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen J., Hänninen P. Antibody response to Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.42-51.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen J., Leikola J., Klemola E. IgM antibodies specific for Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis without heterophil antibodies. Br Med J. 1974 Oct 12;4(5936):72–75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5936.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Scherer M. IgM antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in infectious mononucleosis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(4):332–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01241456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling K. A., Fernbach D. J. Infectious mononucleosis in the preschool child. JAMA. 1968 Feb 26;203(9):810–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumaya C. V. Primary Epstein-Barr virus infections in children. Pediatrics. 1977 Jan;59(1):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamir D., Benderly A., Levy J., Ben-Porath E., Vonsover A. Infectious mononucleosis and Epstein-Barr virus in childhood. Pediatrics. 1974 Mar;53(3):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischendorf P., Shramek G. J., Balagtas R. C., Deinhardt F., Knospe W. H., Noble G. R., Maynard J. E. Development and persistence of immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):401–409. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAHLQUIST B., EKELUND H., TVETRAS E. Infectious mononucleosis and pseudo-mononucleosis in childhood. Acta Paediatr. 1958 Mar;47(2):120–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1958.tb07867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. A., Frenkel E. P. The atypical lymphocyte. Am J Med. 1967 Jun;42(6):923–936. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


