Abstract
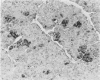
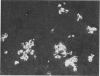
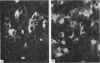
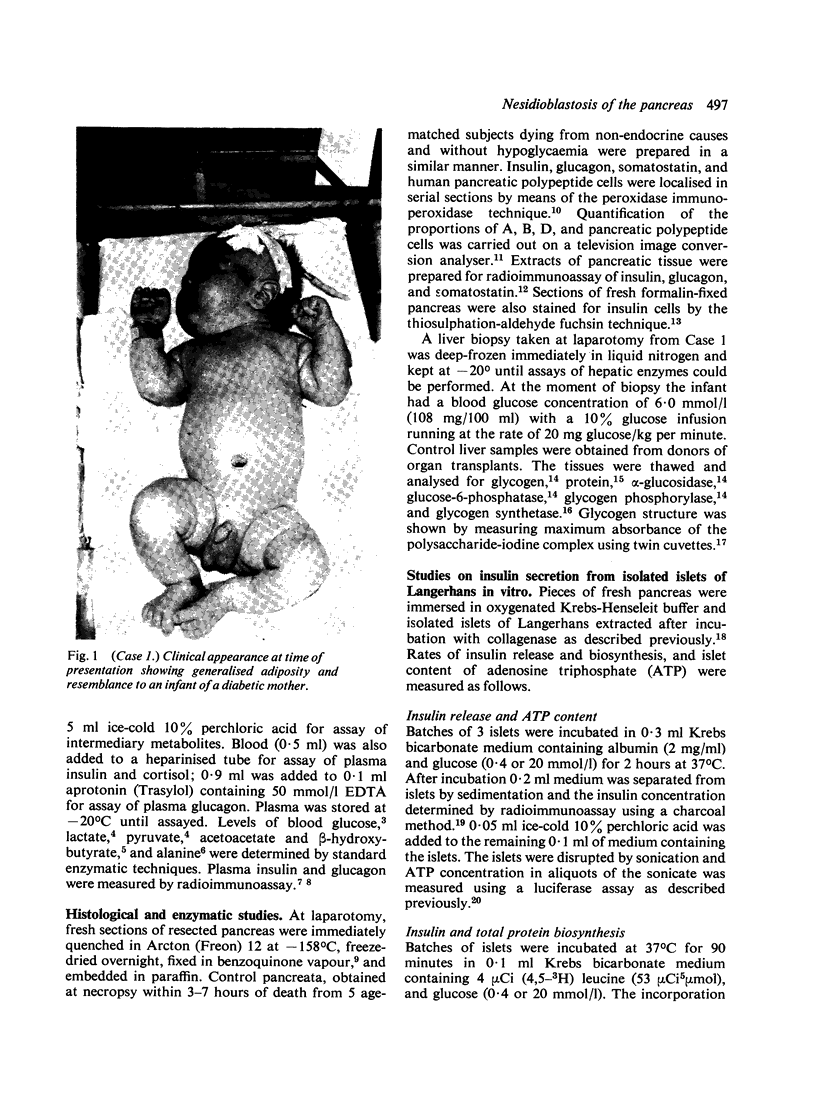
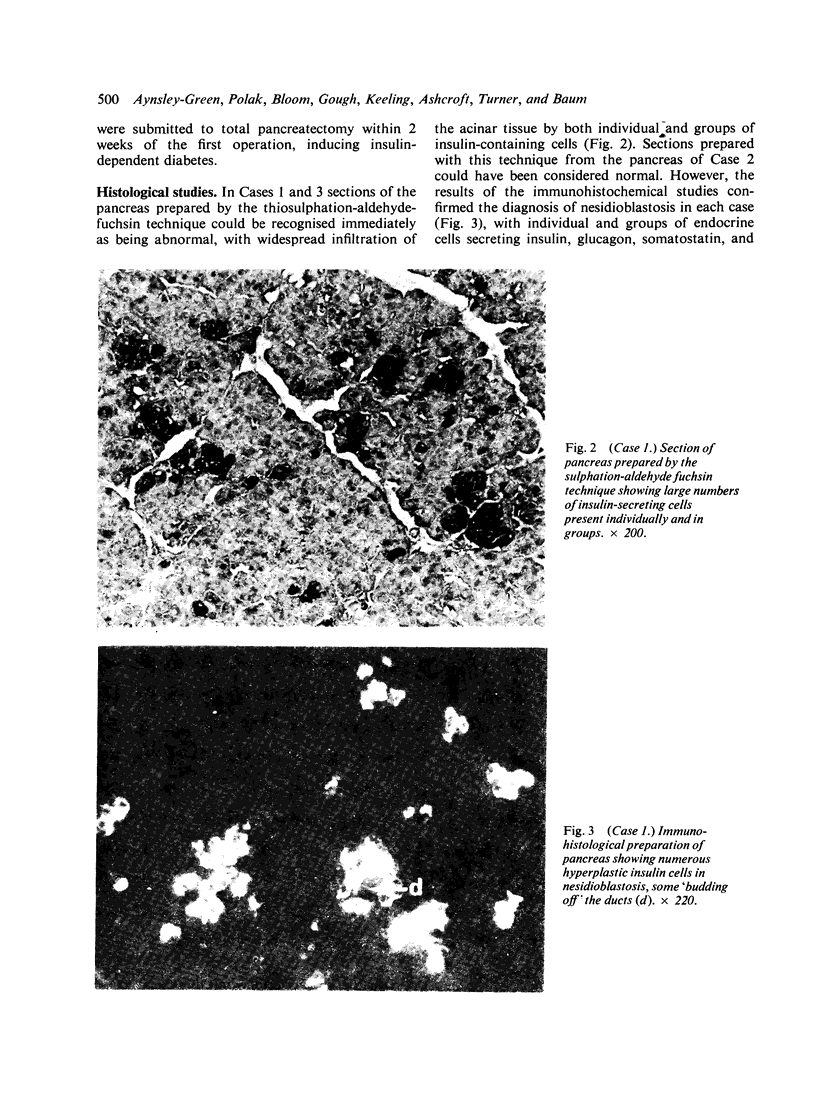
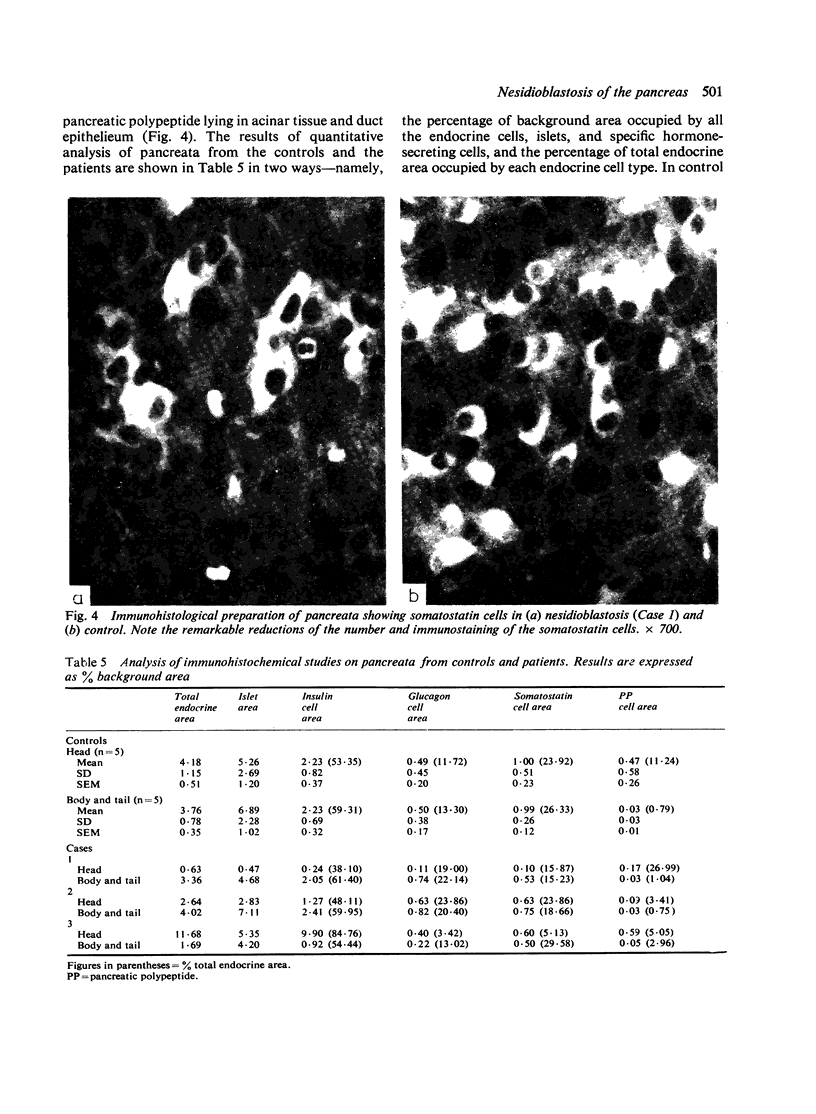
Three newborn infants are reported who developed severe non-ketotic hypoglycaemia (blood glucose less than 1.1 mmol/l; 19.8 mg/100 ml) within 6 hours of birth. All had inappropriately raised plasma insulin concentrations for the level of glycaemia, and required high rates of glucose infusion (less than 15 mg glucose/kg per minute) to prevent symptoms of hypoglycaemia. Medical treatment (hydrocortisone, diazoxide, chlorothiazide, phenytoin, propranolol, and depot glucagon) was ineffective in preventing hypoglycaemia and all 3 infants were subjected to partial and then total pancreatectomy. The pathological features of nesidioblastosis are reported from quantitative immunohistochemical studies on the pancreata. These results together with those from metabolic and endocrine studies performed on the 3 infants during the investigation of the cause of the hypoglycaemia and during the preoperative and postoperative period are presented in detail in order to define a practical approach to the management of this difficult clinical problem in the neonate.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberti K. G., Christensen N. J., Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Iversen J., Lundbaek K., Seyer-Hansen K., Orskov H. Inhibition of insulin secretion by somatostatin. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1299–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A., Borg H., Groth C. G., Gunnarsson R., Hellerström C., Lundgren G., Westman J., Ostman J. Survival of isolated human islets of Langerhans maintained in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1295–1301. doi: 10.1172/JCI108397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Bassett J. M., Randle P. J. Isolation of human pancreatic islets capable of releasing insulin and metabolising glucose in vitro. Lancet. 1971 May 1;1(7705):888–889. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92445-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Bunce J., Lowry M., Hansen S. E., Hedeskov C. J. The effect of sugars on (pro)insulin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):517–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1740517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Crossley J. R., Crossley P. C. The effect of N-acylglucosamines on the biosynthesis and secretion of insulin in the rat. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):701–707. doi: 10.1042/bj1540701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Crossley J. R. The effects of glucose, N-acetylglucosamine, glyceraldehyde and other sugars on insulin release in vivo. Diabetologia. 1975 Aug;11(4):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00422392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Nino S. Effects of phloretin and dextran-linked phloretin on pancreatic islet metabolism and insulin release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 18;538(2):334–342. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J. The control of insulin release by sugars. Ciba Found Symp. 1976;41:117–139. doi: 10.1002/9780470720233.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Randle P. J. Interrelationship of islet metabolism, adenosine triphosphate content and insulin release. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):223–231. doi: 10.1042/bj1320223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley-Green A., Bloom S. R., Williamson D. H., Turner R. C. Endocrine and metabolic response in the human newborn to first feed of breast milk. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Apr;52(4):291–295. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley-Green A., Illig R. Letter: Enhancement by chlorpromazine of hyperglycaemic action of diazoxide. Lancet. 1975 Oct 4;2(7936):658–659. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aynsley-Green A., Polak J. M., Keeling J., Gough M. H., Baum J. D. Averted sudden neonatal death due to pancreatic nesidioblastosis. Lancet. 1978 Mar 11;1(8063):550–551. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier D. M., Leake R. D., Haymond M. W., Arnold K. J., Gruenke L. D., Sperling M. A., Kipnis D. M. Measurement of "true" glucose production rates in infancy and childhood with 6,6-dideuteroglucose. Diabetes. 1977 Nov;26(11):1016–1023. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.11.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R. Hormones of the gastrointestinal tract. Br Med Bull. 1974 Jan;30(1):62–67. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum I., Doron M., Laron Z., Atsmon A., Tiqva P. Prevention of hypoglycemic attacks by propranolol in a patient suffering from insulinoma. Diabetes. 1975 Jun;24(6):535–537. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.6.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder L. E., Carter S. K. Pancreatic islet cell carcinoma. II. Results of therapy with streptozotocin in 52 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jul;79(1):108–118. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-1-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodows R. G., Campbell R. G. Control of refractory fasting hypoglycemia in a patient with suspected insulinoma with diphenylhydantoin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jan;38(1):159–162. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. E., Young R. B. A possible role for the exocrine pancreas in the pathogenesis of neonatal leucine-sensitive hypoglycemia. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Jan;15(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02239348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buist N. R., Campbell J. R., Castro A. Congenital islet cell adenoma causing hypoglycemia in a newborn. Pediatrics. 1971 Mar;47(3):605–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolati G., Bassa T. Thiosulfation aldehyde fuchsin (TAF) procedure for the staining of pancreatic B cells. Stain Technol. 1974 Sep;49(5):313–315. doi: 10.3109/10520297409117001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Lundbaek K., Orskov H., Seyer-Hansen K. Letter: Somatostatin and insulinoma. Lancet. 1975 Jun 28;1(7922):1426–1426. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92640-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Bower R. H., Fidler S. M., Johnsonbaugh R. E., Sode J. Inhibition of insulin release by diphenylhydantoin and diazoxide in a patient with benign insulinoma. Lancet. 1973 Jan 6;1(7793):40–41. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll-Garcia E., Gill J. R. Insulin release by isolated pancreatic islets of the mouse incubated in vitro. Diabetologia. 1969 Apr;5(2):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01211999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Randle P. J. Regulation of insulin secretion studied with pieces of rabbit pancreas incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):66–78. doi: 10.1042/bj0930066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. N., Guelpa G., Terrapon M. Islet-cell hyperplasia and sudden infant death. Lancet. 1976 Oct 2;2(7988):739–740. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder W. L., Maclaren N. K., Gutberlet R. L., Frost J. L., Mason G. R., Cornblath M. Neonatal pancreatic beta-cell hyperplasia: report of a case with failure of diazoxide and benefit of early subtotal pancreatectomy. Pediatrics. 1976 Jun;57(6):897–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERNESTI M., MITCHELL M. L., RABEN M. S., GILBOA Y. CONTROL OF HYPOGLYCAEMIA WITH DIAZOXIDE AND HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE. Lancet. 1965 Mar 20;1(7386):628–630. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91716-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garces L. Y., Drash A., Kenny F. M. Islet cell tumor in the neonate. Studies in carbohydrate metabolism and therapeutic response. Pediatrics. 1968 Apr;41(4):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. B., Barbor P. R. Islet-cell tumour causing hypoglycaemia in a newborn infant. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Jun;45(241):434–436. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.241.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOHORST H. J., KREUTZ F. H., BUECHER T. [On the metabolite content and the metabolite concentration in the liver of the rat]. Biochem Z. 1959;332:18–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz P. U., Klöppel G., Häcki W. H., Polak J. M., Pearse A. G. Nesidioblastosis: the pathologic basis of persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in infants. Morphologic and quantitative analysis of seven cases based on specific immunostaining and electron microscopy. Diabetes. 1977 Jul;26(7):632–642. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.7.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. J., Loo S., Evans N., Crigler J. F., Filler R. M., Gabbay K. H. Hypoglycemia of infancy and nesidioblastosis. Studies with somatostatin. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 9;296(23):1323–1326. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706092962305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttenlocher P. R. Ketonemia and seizures: metabolic and anticonvulsant effects of two ketogenic diets in childhood epilepsy. Pediatr Res. 1976 May;10(5):536–540. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197605000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISMAN C. R. A method for the colorimetric estimation of glycogen with iodine. Anal Biochem. 1962 Jul;4:17–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laidlaw G. F. Nesidioblastoma, the islet tumor of the pancreas. Am J Pathol. 1938 Mar;14(2):125–134.5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misugi K., Misugi N., Sotos J., Smith B. The pancreatic islet of infants with severe hypoglycemia. Arch Pathol. 1970 Mar;89(3):208–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESS P. REMARQUES SUR L''EVOLUTION DE LA SARCIUIDOSE PULMONAIRE. A PROPOS DE 50 CAS. Med Thorac. 1963;20:SUPPL–SUPPL:117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. A., Williamson D. H. Enzymes of ketone-body utilisation in human brain. Lancet. 1971 Jul 10;2(7715):66–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M. Bifunctional reagents as vapour- and liquid-phase fixatives for immunohistochemistry. Histochem J. 1975 Mar;7(2):179–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01004561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Wigglesworth J. S. Letter: Islet-cell hyperplasia and sudden infant death. Lancet. 1976 Sep 11;2(7985):570–571. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91814-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Graber A. L., Kuzuya T., Williams R. H. The effect of epinephrine on immunoreactive insulin levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI105335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinas E. D., Jr, Mangurten H. H., Roberts S. S., Simon W. H., Cornblath M. Functioning islet cell adenoma in the newborn. Report of a case with failure of diazoxide. Pediatrics. 1968 Mar;41(3):646–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. A., Baker L. Hyperinsulinism in infancy: diagnosis by demonstration of abnormal response to fasting hypoglycemia. Pediatrics. 1976 May;57(5):702–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Schlender K. K., Larner J. A rapid filter paper assay for UDPglucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase, including an improved biosynthesis of UDP-14C-glucose. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. C., Heding L. G. Plasma proinsulin, C-peptide and insulin in diagnostic suppression tests for insulinomas. Diabetologia. 1977 Dec;13(6):571–577. doi: 10.1007/BF01236309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. E., Stoll R. W., Kitabchi A. E., Williams R. H., Wood F. C., Jr Nesidioblastosis in familial endocrine adenomatosis. JAMA. 1969 Mar 3;207(9):1679–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo D., Scopes J. W., Polak J. M. Idiopathic hypoglycaemia in sibs with morphological evidence of nesidioblastosis of the pancreas. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Jul;51(7):528–531. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.7.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakovac W. C., Baker L., Hummeler K. Beta cell nesidioblastosis in idiopathic hypoglycemia of infancy. J Pediatr. 1971 Aug;79(2):226–231. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]