Abstract
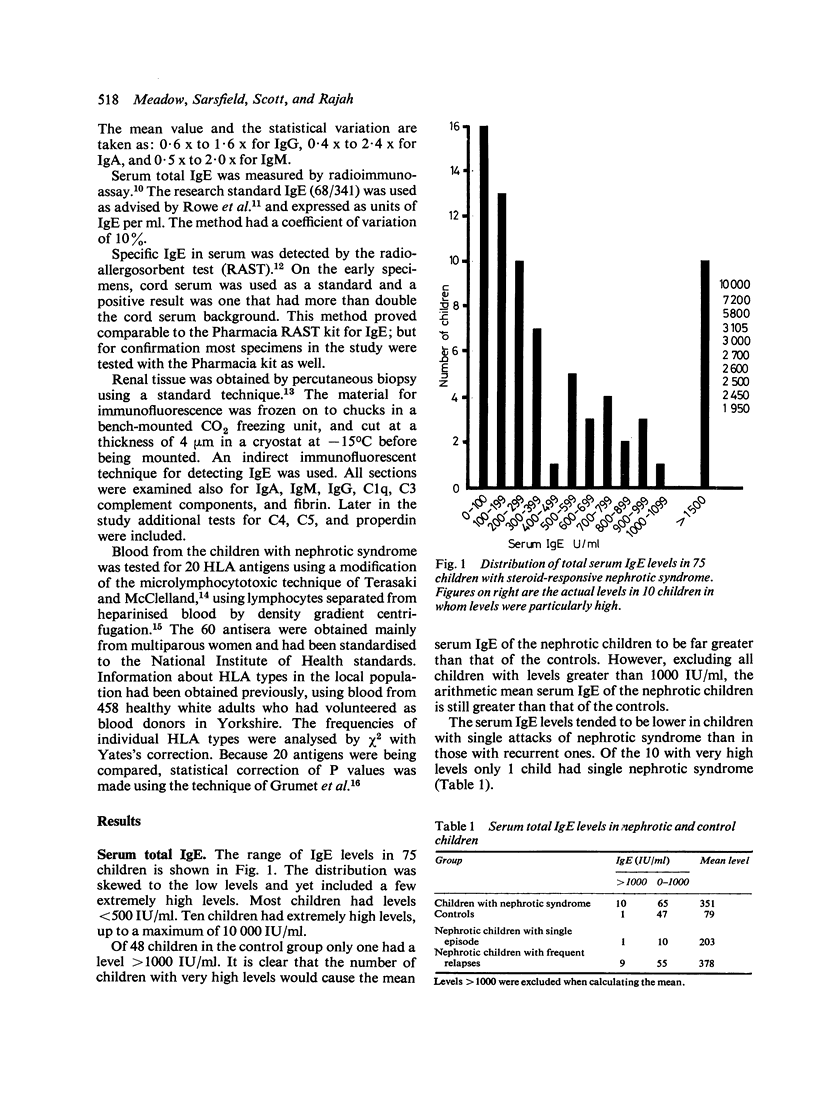
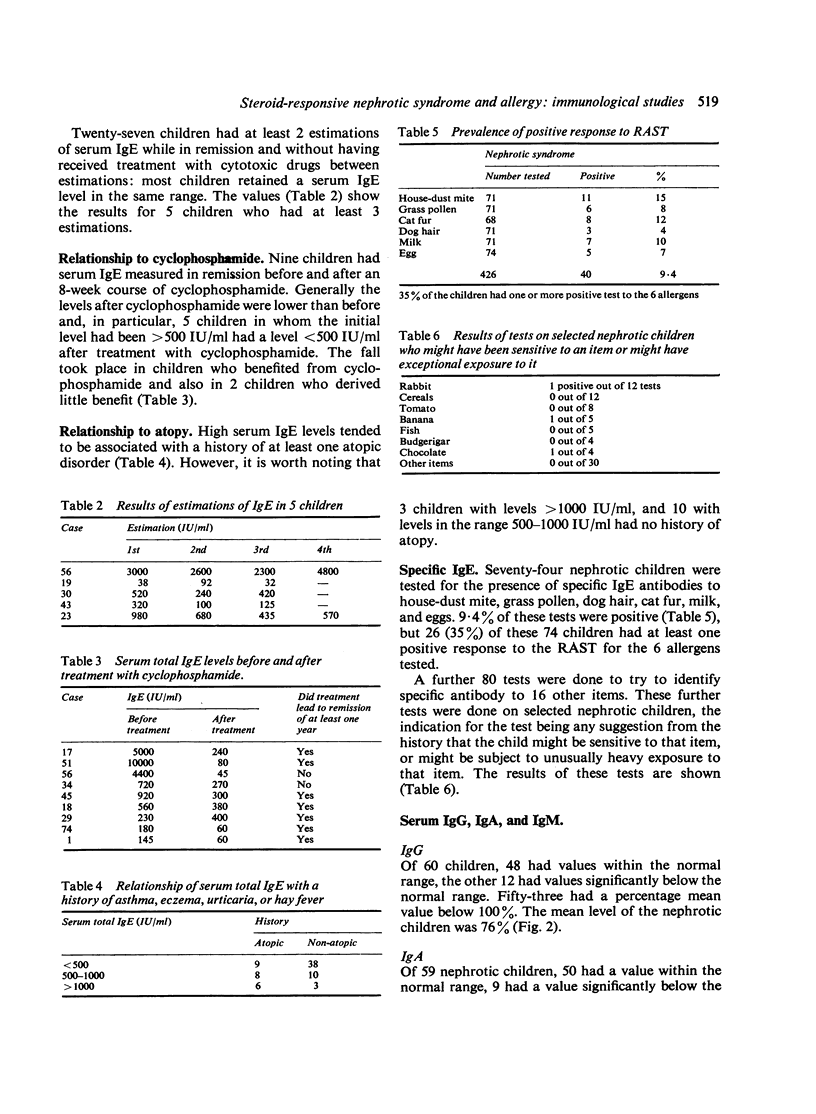
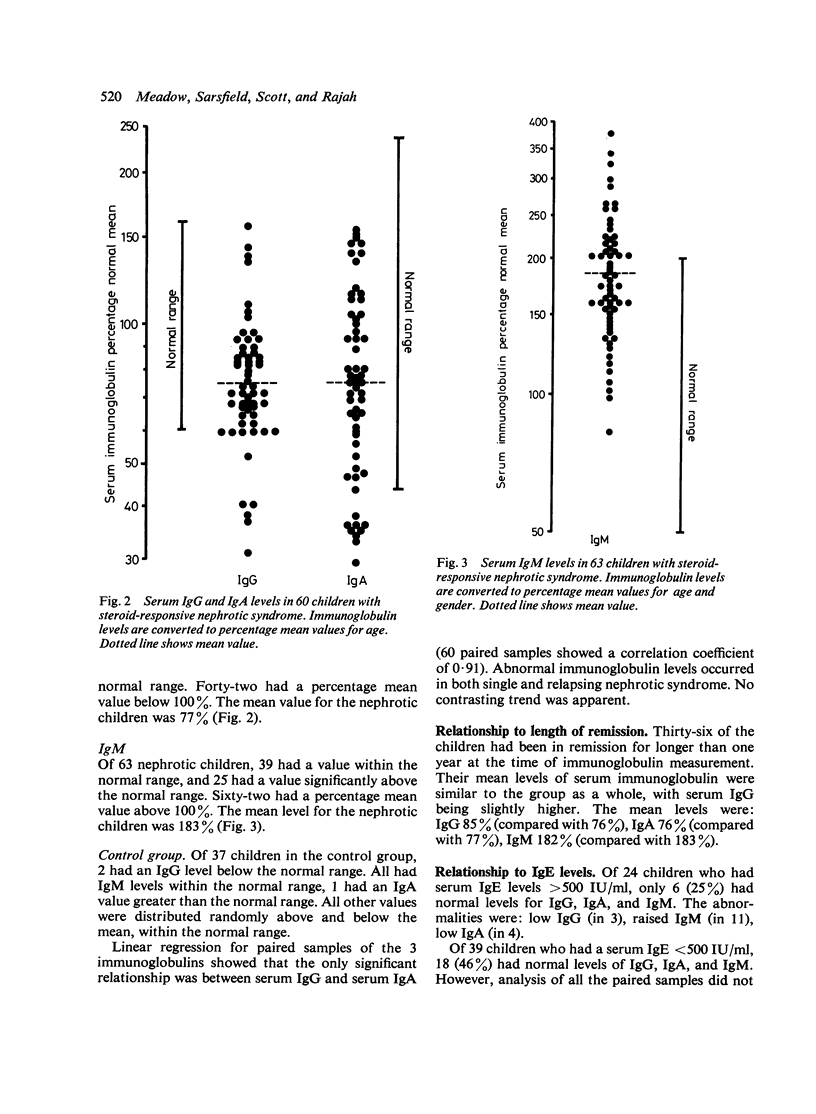
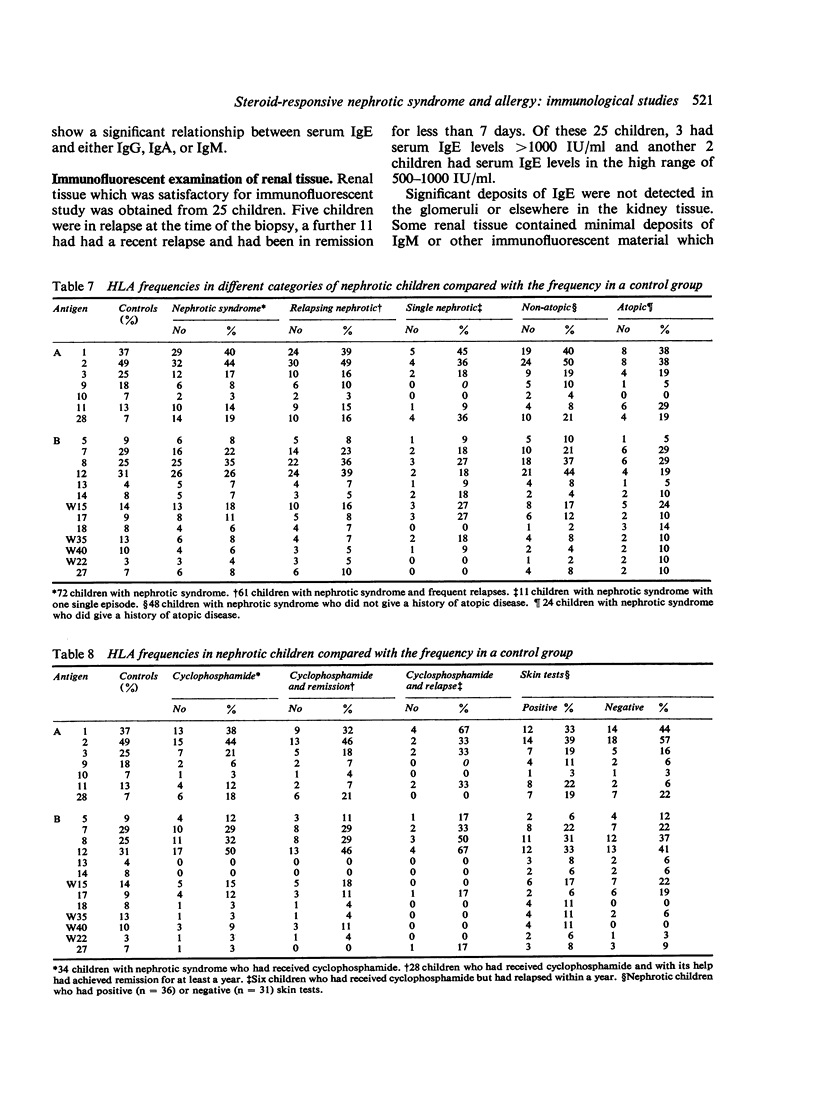
Immunological studies were performed on 84 children with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome as part of an investigation of the relationship between steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome and allergy. Serum total IgE levels tended to be raised, particularly in children who had frequent relapses of nephrotic syndrome. Ten children had extremely high levels (greater than 1500 IU/ml) and several of them had neither a history of atopy nor any other identifiable cause. 25% of the children had at least one positive test for specific IgE antibody. IgE was not detected by immunofluorescence in renal biopsy tissue from 25 children, regardless of whether the child was in remission or relapse at the time of biopsy. Serum IgG and IgA levels were depressed particularly at the time of a relapse. Serum IgM tended to be raised and to remain so, even in children who had been in remission for more than a year. No clinically useful relationship was found between the frequency of HLA antigens and the occurrence or course of the syndrome, whether or not accompanied by atopy. Clinical and immunological features of atopy are more common in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. This may be a causal or non-causal association. Pollen sensitivity is a rare cause of nephrotic syndrome; careful search for provocative agents may show other causes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allansmith M., McClellan B. H., Butterworth M., Maloney J. R. The development of immunoglobulin levels in man. J Pediatr. 1968 Feb;72(2):276–290. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennich H., Rowe D. S., Tackett L., Ishizaka K., Johansson S. G., Anderson S. G. A research standard for human serum immunoglobulin E. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(4):609–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T. L., Johansson S. G. Allergy diagnosis with the radioallergosorbent test: A comparison with the results of skin and provocation tests in an unselected group of children with asthma and hay fever. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1974 Oct;54(4):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(74)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Dees S. C., O'Fallon W. M. Serum immunoglobulins. I. Levels in normal children and in uncomplicated childhood allergy. Pediatrics. 1968 Mar;41(3):600–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Lundkvist U. A new and simple radioimmunoassay method for the determination of IgE. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):1021–1030. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Paronetto F. IgE in glomeruli of patients with nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1097–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91838-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Paronetto F. New patterns of immunoglobulin deposition in the lesions of malignant nephrosclerosis, with special reference to IgE. Am J Pathol. 1971 Dec;65(3):535–542. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giangiacomo J., Cleary T. G., Cole B. R., Hoffsten P., Robson A. M. Serum immunoglobulins in the nephrotic syndrome. A possible cause of minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 3;293(1):8–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507032930103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groshong T., Mendelson L., Mendoza S., Bazaral M., Hamburger R., Tune B. Serum IgE in patients with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. J Pediatr. 1973 Nov;83(5):767–771. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet F. C., Coukell A., Bodmer J. G., Bodmer W. F., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. A possible genetic predisposition to disease. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 22;285(4):193–196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107222850403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G., Berg T. Immunoglobulin levels in healthy children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967 Nov;56(6):572–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb15982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman H. S., Hobbs J. R. Immunoglobulin deficiencies in an atopic population. Lancet. 1970 Nov 21;2(7682):1061–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90288-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman N. I. Predictive value of high IgE levels in children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Jul;65(4):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman N. M., Johansson S. G., Roth A. Serum IgE levels in healthy children quantified by a sandwich technique (PRIST). Clin Allergy. 1976 Jan;6(1):51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: Serum immunoglobulins in idiopathic minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 1;294(1):50–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601012940117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow S. R., Sarsfield J. K. Steroid-responsive and nephrotic syndrome and allergy: clinical studies. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Jul;56(7):509–516. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.7.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. G., Cameron J. S., Johansson S. G., Ogg C. S., Peters D. K., Weller R. O. Seasonal nephrotic syndrome. Description and immunological findings. Clin Allergy. 1975 Jun;5(2):121–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. R., Potter E. V., Roberts M. L., Patterson R. Immunoglobulin E in renal disease. Nephron. 1976;16(4):256–271. doi: 10.1159/000180610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stege N., Gugler E. Die quantitative Bestimmung der Immunglobulinreifung mit Hilfe der einfachen radialen Immundiffusionsmethode. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1968 Jun;23(3):242–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Serum levels of immune globulins in health and disease: a survey. Pediatrics. 1966 May;37(5):715–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoop J. W., Zegers B. J., Sander P. C., Ballieux R. E. Serum immunoglobulin levels in healthy children and adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):101–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson P. D., Stokes C. R., Barratt T. M., Turner M. W., Soothill J. F. HLA antigens and atopic features in steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Lancet. 1976 Oct 9;2(7989):765–768. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90600-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE R. H. Observations on percutaneous renal biopsy in children. Arch Dis Child. 1963 Jun;38:260–266. doi: 10.1136/adc.38.199.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wide L., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Diagnosis of allergy by an in-vitro test for allergen antibodies. Lancet. 1967 Nov 25;2(7526):1105–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90615-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


