Abstract
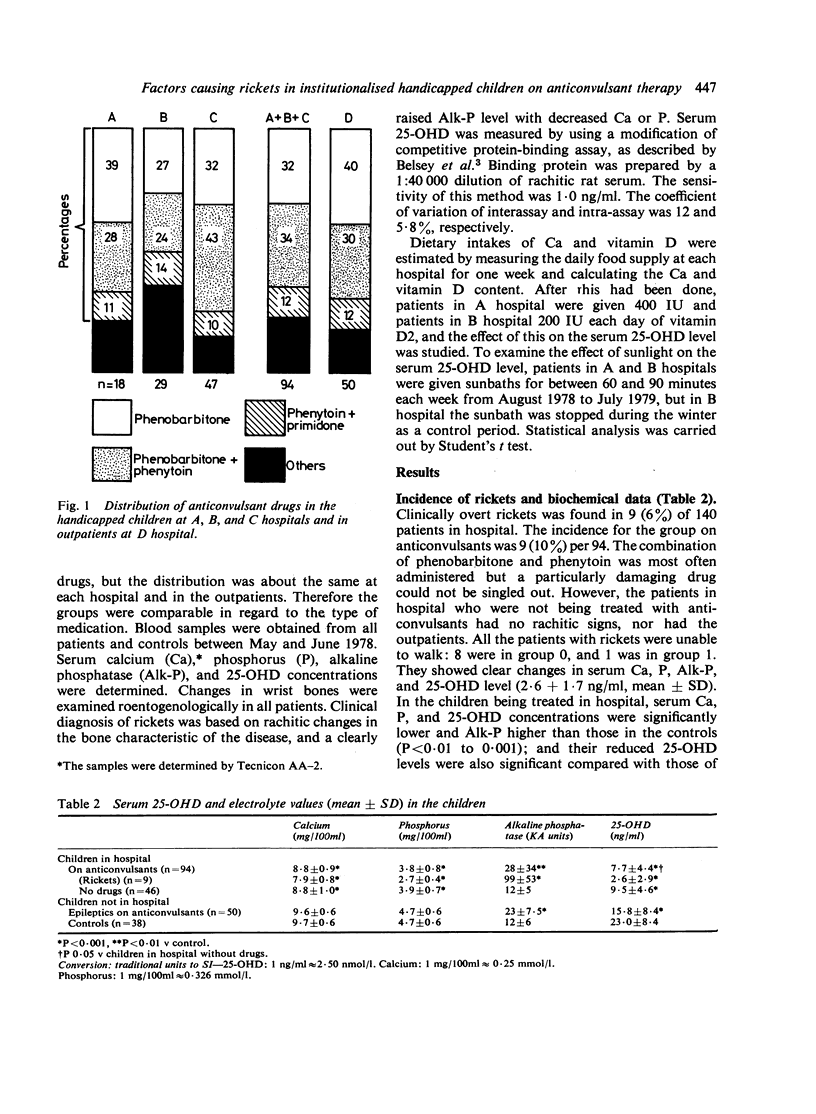
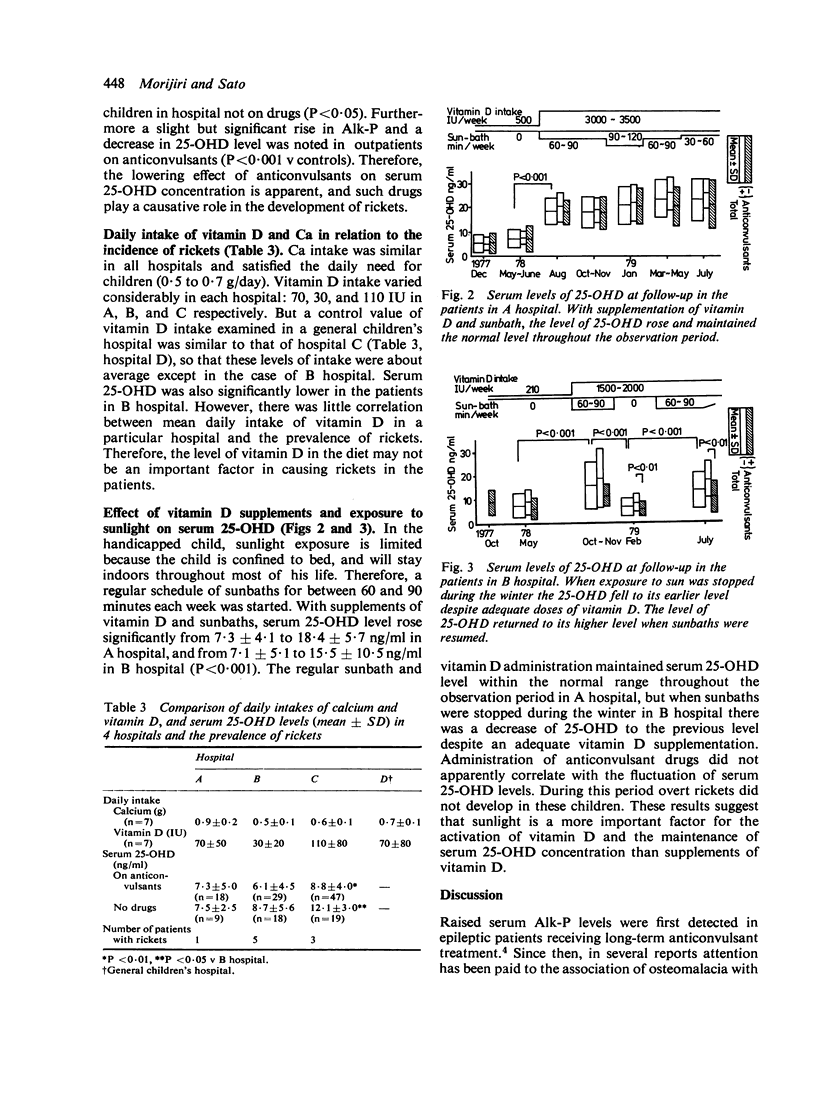
An epidemiological study on vitamin D-dependent rickets was carried out in severely handicapped institutionalised children on long-term anticonvulsant therapy. Nine (10%) of 94 patients had overt rickets on the basis of roentgenological bone changes and biochemical indices, but 46 patients in hospital without medication, and 50 epileptic patients attending an outpatient clinic and taking anticonvulsants had no sign of rickets. Causative factors for the development of rickets were evaluated. Administration of anticonvulsive drugs depressed the serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) level, but this was not the major factor in the development of rickets. Vitamin D intake seemed to be about average in these patients and its supplementation increased their serum 25-OHD level. This serum 25-OHD level was not maintained by supplemental vitamin D, unless the children were exposed to sunlight. These results indicate that although several factors--such as anticonvulsants, low vitamin D intake, and inactivity--are concerned in the development of rickets, the main cause is lack of sun in institutionalised handicapped children.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belsey R. E., DeLuca H. F., Potts J. T., Jr A rapid assay for 25-OH-vitamin D3 without preparative chromatography. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jun;38(6):1046–1051. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-6-1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon R., Reynaert J., Claes J. H., Lissens W., De Moor P. The effect of anticonvulsant therapy on serum levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D, calcium, and parathyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Dec;41(06):1130–1135. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-6-1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Birge S. J., Scharp C. R., Avioli L. V. Phenobarbital-induced alterations in vitamin D metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):741–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI106868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Hendin B. A., Scharp C. R., Haddad J. G., Jr Effect of chronic anticonvulsant therapy on serum 25-hydroxycalciferol levels in adults. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 2;287(18):900–904. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211022871803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz F., Maclaren N. K. Vitamin D-dependent rickets in institutionalized, mentally retarded children receiving long-term anticonvulsant therapy. I. A survey of 288 patients. J Pediatr. 1973 Oct;83(4):612–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston S., Berman W., Pauli L. L. Anticonvulsant drugs and vitamin D metabolism. JAMA. 1973 Jun 18;224(12):1634–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richens A., Rowe D. J. Anticonvulsant osteomalacia. Br Med J. 1971 Dec 11;4(5788):684–684. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5788.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamp T. C., Haddad J. G., Twigg C. A. Comparison of oral 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, vitamin D, and ultraviolet light as determinants of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Lancet. 1977 Jun 25;1(8026):1341–1343. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamp T. C., Round J. M. Seasonal changes in human plasma levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Nature. 1974 Feb 22;247(5442):563–565. doi: 10.1038/247563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolman K. G., Jubiz W., Sannella J. J., Madsen J. A., Belsey R. E., Goldsmith R. S., Freston J. W. Osteomalacia associated with anticonvulsant drug therapy in mentally retarded children. Pediatrics. 1975 Jul;56(1):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT J. A. TRINURIDE IN THE TREATMENT OF MAJOR EPILEPSY. Epilepsia. 1965 Mar;6:67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1965.tb03352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman Y., Fattal A., Eisenberg Z., Harel S., Spirer Z., Harell A. Decreased serum 24,25-dihydroxy vitamin D concentrations in children receiving chronic anticonvulsant therapy. Br Med J. 1979 Sep 1;2(6189):521–523. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6189.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winnacker J. L., Yeager H., Saunders J. A., Russell B., Anast C. S. Rickets in children receiving anticonvulsant drugs. Biochemical and hormonal markers. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Mar;131(3):286–290. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120160040005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


