Abstract
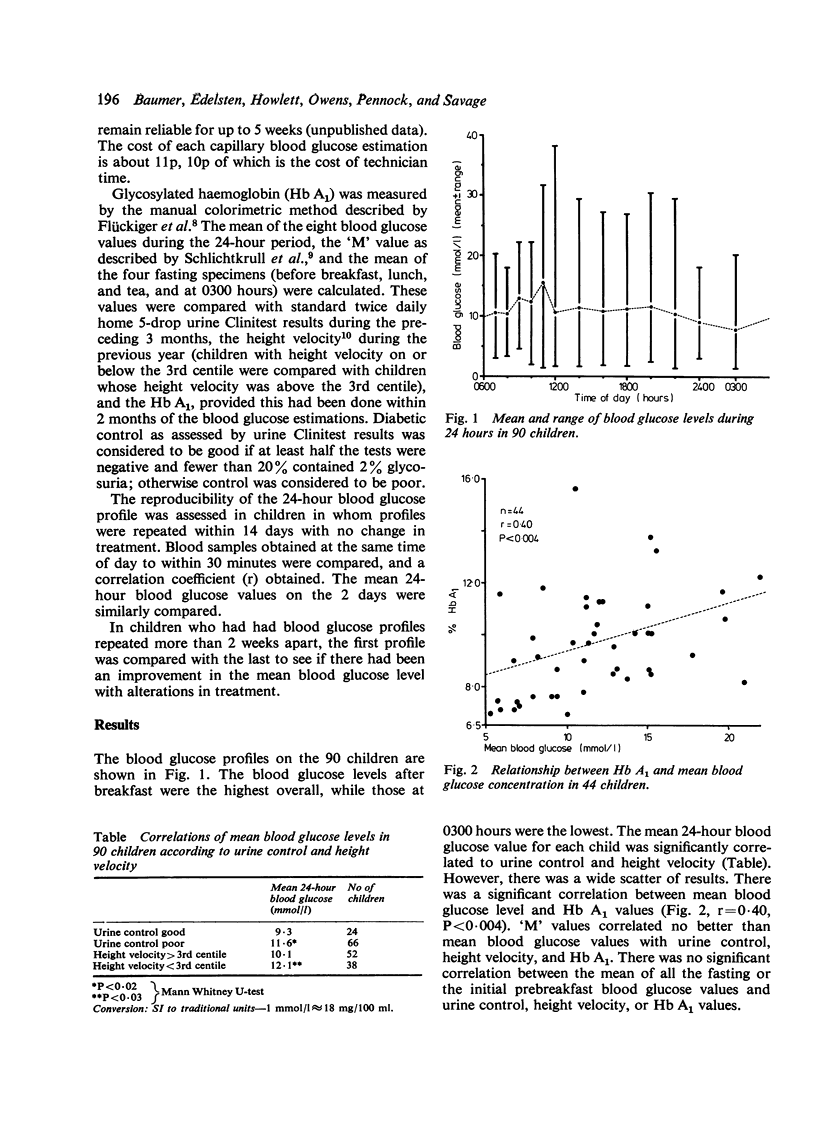
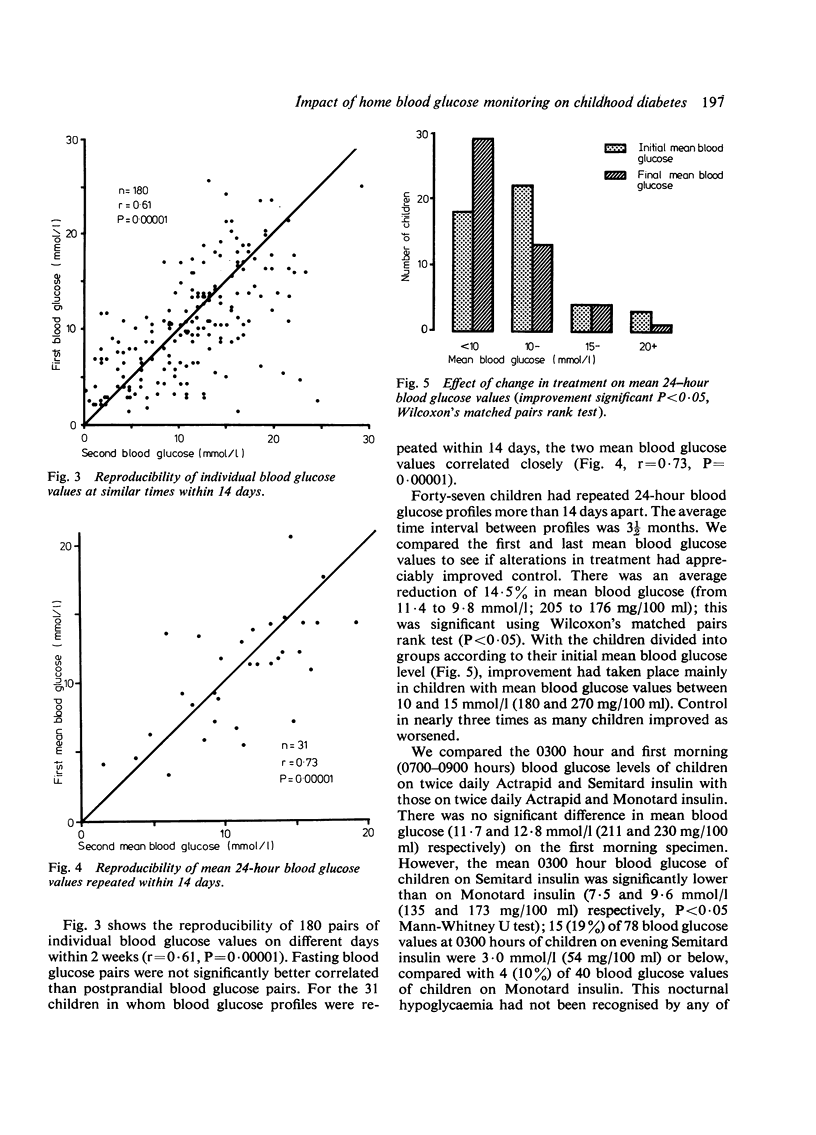
Ninety diabetic children each provided at least one 24-hour blood glucose profile at home using an impregnated filter paper strip. The mean 24-hour blood glucose level correlated significantly with urine control, height velocity, and Hb A1. The correlation coefficient for individual blood glucose values (r = 0.61) and for mean 24-hour blood glucose values (r = 0.73) repeated within 14 days showed an acceptable degree of reproducibility for the blood glucose profiles. Mean 24-hour blood glucose values fell significantly overall (11.4 to 9.8 mmol/l; 205 to 176 mg/100 ml) in 47 children who had repeated profiles more than 2 weeks apart. Unrecognised nocturnal hypoglycaemia (less than 3.0 mmol/l; 54 mg/100 ml) was found in 19% of children on twice-daily Semitard insulin. The study shows that children over age 7 years manage home blood glucose monitoring without difficulty. It shows that the results are reproducible and correlate with other indices of control, and that it provides a practical basis for the improvement of diabetic control.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumer J. H., Savage D. C. Are reflectance meters necessary for home blood glucose monitoring? Br Med J. 1980 Nov 8;281(6250):1286–1286. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6250.1286-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earis J. E., Greenway M. W., Macaulay M. B. Blood glucose monitoring without a meter. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):823–824. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. D., Prosser R. Are reflectance meters necessary for home blood glucose monitoring? Br Med J. 1980 Oct 4;281(6245):912–912. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6245.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. A., Kurtz A. B., Tattersall R. B. In search of the Somogyi effect. Lancet. 1980 Aug 9;2(8189):279–282. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. A., Tattersall R. B. Unrecognised nocturnal hypoglycaemia in insulin-treated diabetics. Lancet. 1979 May 19;1(8125):1049–1052. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92950-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Peterson C. M., Jones R. L., Saudek C., Lehrman M., Cerami A. Correlation of glucose regulation and hemoglobin AIc in diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):417–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone J. I., Hellrung J. M., Malphus E. W., Rosenbloom A. L., Grgic A., Weber F. T. Good diabetic control - a study in mass delusion. J Pediatr. 1976 Jun;88(6):943–947. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paisey R., Bradshaw P., Hartog M., West P. Home monitoring of blood glucose using filter paper strips. Br Med J. 1979 Dec 8;2(6203):1509–1509. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6203.1509-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLICHTKRULL J., MUNCK O., JERSILD M. THE M-VALVE, AN INDEX OF BLOOD-SUGAR CONTROL IN DIABETICS. Acta Med Scand. 1965 Jan;177:95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1965.tb01810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel J. M., Cramb R., Duncan L. J. How useful are patient-operated blood glucose meters? Practitioner. 1980 Jun;224(1344):651–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönksen P. H., Judd S. L., Lowy C. Home monitoring of blood-glucose. Method for improving diabetic control. Lancet. 1978 Apr 8;1(8067):729–732. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90854-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin K., Goldie D. J., Hartog M., Robinson A. P. Measurement of capillary blood glucose in filter-paper spots: an aid to the assessment of diabetic control. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 12;2(6135):468–469. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6135.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford S., Clarke P., Paisey R., Hartog M., Allison S. P. Home blood-glucose measurements without reflectance meter. Lancet. 1980 Mar 22;1(8169):653–654. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford S., Gale E. A., Allison S. P., Tattersall R. B. Self-monitoring of blood-glucose. Improvement of diabetic control. Lancet. 1978 Apr 8;1(8067):732–735. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90855-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werther G. A., Jenkins P. A., Turner R. C., Baum J. D. Twenty-four-hour metabolic profiles in diabetic children receiving insulin injections once or twice daily. Br Med J. 1980 Aug 9;281(6237):414–418. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6237.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West P., Marsland I., Bradshaw P. Automated capillary blood spot glucose estimation. Med Lab Sci. 1979;36(4):379–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. L., Savage D. C. Glycosylated haemoglobin levels in children with diabetes mellitus. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Apr;54(4):295–298. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.4.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


