Abstract
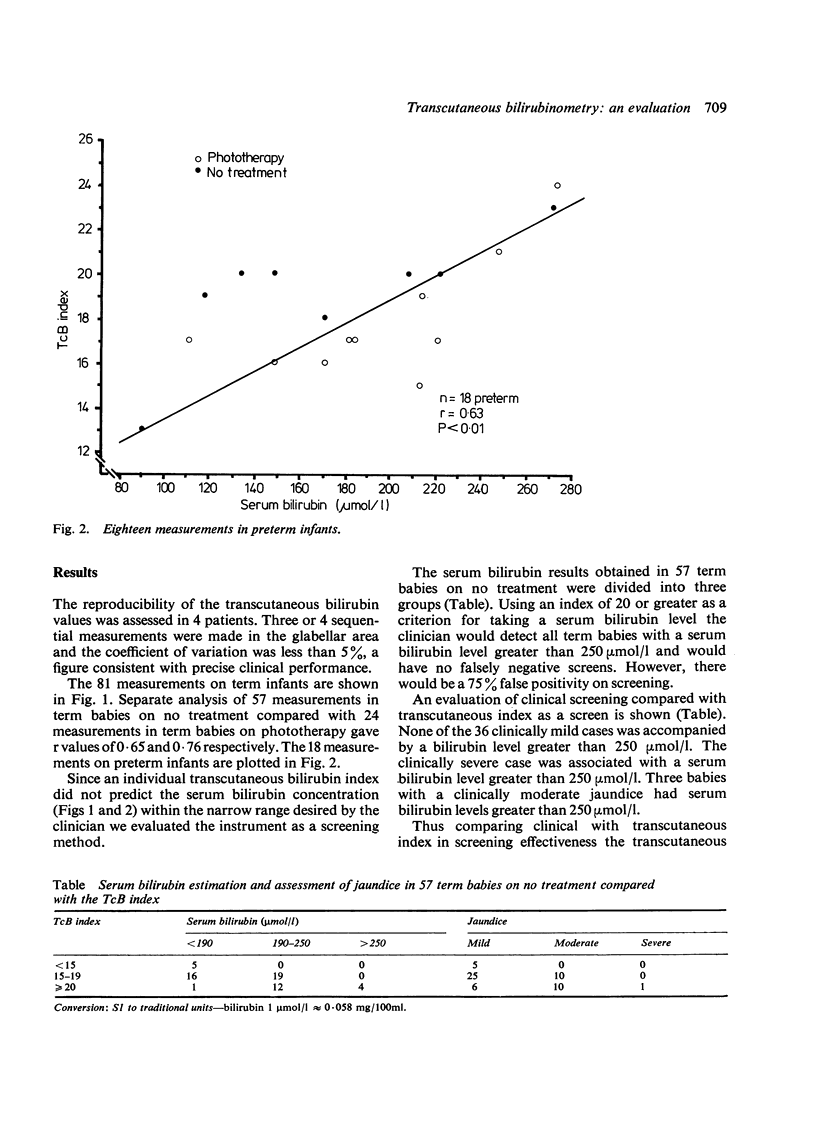
The transcutaneous bilirubinometer was evaluated in 60 term and 10 preterm infants. A significant correlation was found between the transcutaneous index and the total serum bilirubin concentration for both term and preterm infants. The reliability of the transcutaneous bilirubinometer as a screening method was confirmed, and index criteria for serum bilirubin analysis have been suggested for term babies. The instrument was precise and accurate and the method both noninvasive and atraumatic. Since individual serum bilirubin levels and the transcutaneous index may correlate poorly the transcutaneous method cannot replace traditional serum bilirubin estimation.
Full text
PDF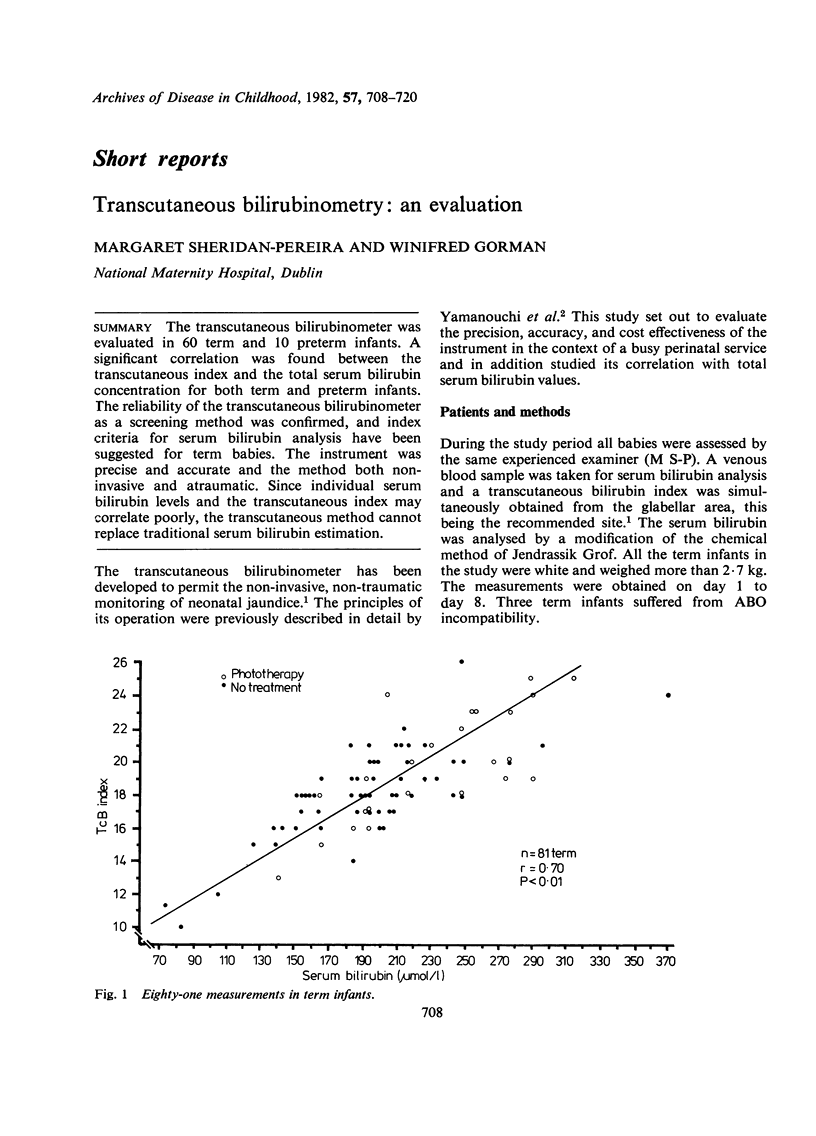

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hegyi T., Hiatt I. M., Indyk L. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry. I. Correlations in term infants. J Pediatr. 1981 Mar;98(3):454–457. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80721-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanouchi I., Yamauchi Y., Igarashi I. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry: preliminary studies of noninvasive transcutaneous bilirubin meter in the Okayama National Hospital. Pediatrics. 1980 Feb;65(2):195–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


