Abstract
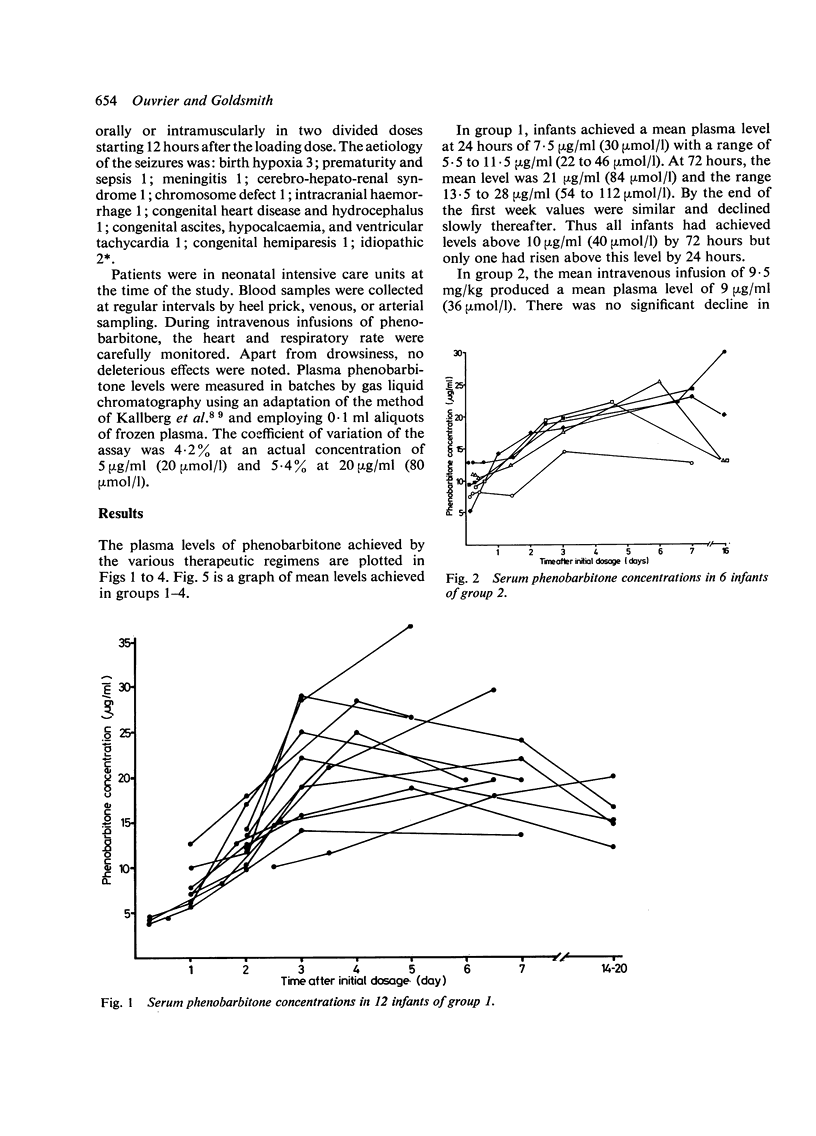
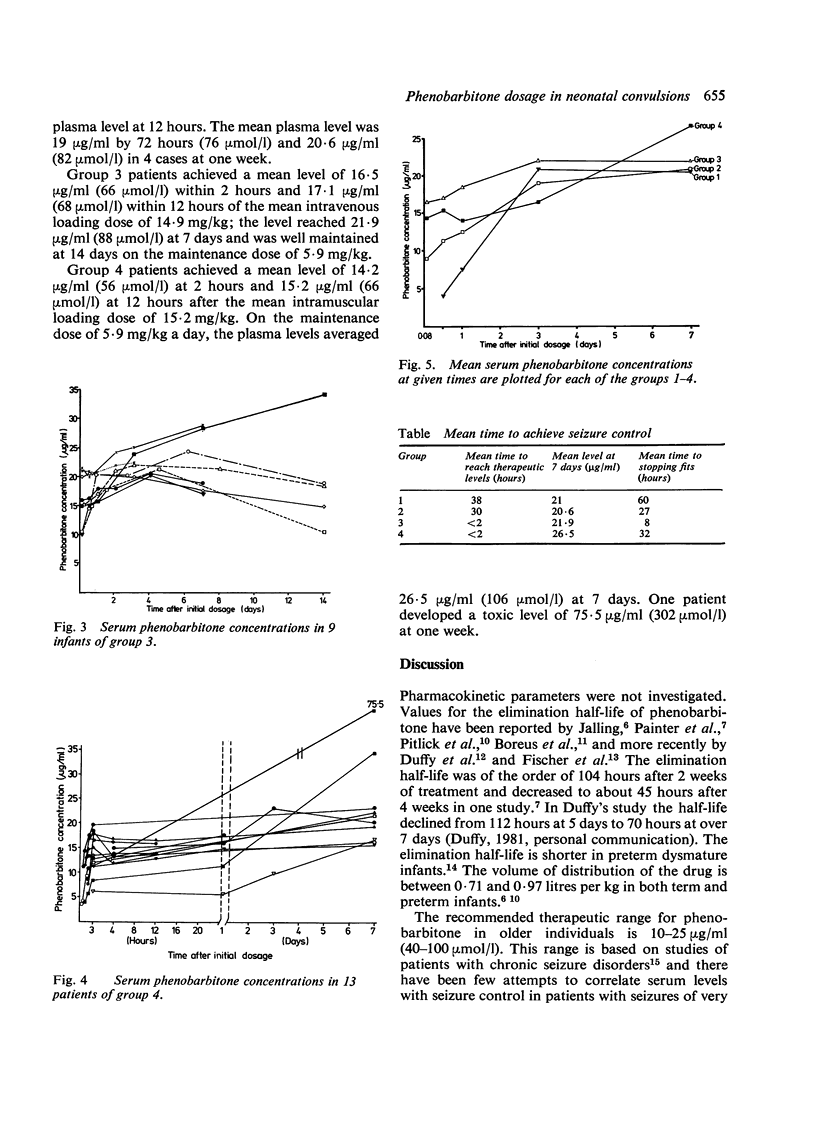
In order to find the optimal dosage schedule of phenobarbitone for neonatal convulsions, four groups of patients were studied. Twelve infants (group 1) received a mean phenobarbitone dose of 9.5 mg/kg a day given intramuscularly for 3 days followed by 5.8 mg/kg a day given intramuscularly and then orally. Six infants (group 2) received a mean intravenous loading dose of 9.5 mg/kg followed by 6.8 mg/kg a day given intramuscularly or orally. Nine infants (group 3) received a mean loading dose of 14.9 mg/kg intravenously followed by a maintenance dose of 5.9 mg/kg a day. Thirteen patients (group 4) received a mean intramuscular loading dose of 15.2 mg/kg followed by 5.9 mg/kg a day. Blood samples were taken regularly and phenobarbitone levels were determined by gas liquid chromatography. A mean intravenous or intramuscular loading dose of 15 mg/kg of phenobarbitone safely achieved therapeutic levels within 2 hours of injection and high therapeutic levels were maintained with a dose of 6 mg/kg a day.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aicardi J., Chevrie J. J. Convulsive status epilepticus in infants and children. A study of 239 cases. Epilepsia. 1970 Jun;11(2):187–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1970.tb03880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boréus L. O., Jalling B., Kållberg N. Phenobarbital metabolism in adults and in newborn infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1978 Mar;67(2):193–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1978.tb16302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnebo M., Agurell S., Jalling B., Boréus L. O. Age differences in drug binding by plasma proteins: studies on human foetuses, neonates and adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;3(4):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00565004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. H., Lockman L. A., Zaske D., Kriel R. Phenobarbital maintenance dose requirements in treating neonatal seizures. Neurology. 1981 Aug;31(8):1042–1044. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.8.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalling B. Plasma concentrations of phenobarbital in the treatment of seizures in newborns. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 May;64(3):514–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb03873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockman L. A., Kriel R., Zaske D., Thompson T., Virnig N. Phenobarbital dosage for control of neonatal seizures. Neurology. 1979 Nov;29(11):1445–1449. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.11.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S., Horton R. W., Brierley J. B. Epileptic brain damage in adolescent baboons following seizures induced by allylgycine. Brain. 1974 Jun;97(2):407–418. doi: 10.1093/brain/97.1.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouvrier R. A., Goldsmith R. Phenobarbitone dosage in the neonate--preliminary communication. Clin Exp Neurol. 1977;14:194–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter M. J., Pippenger C., MacDonald H., Pitlick W. Phenobarbital and diphenylhydantoin levels in neonates with seizures. J Pediatr. 1978 Feb;92(2):315–319. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitlick W., Painter M., Pippenger C. Phenobarbital pharmacokinetics in neonates. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Mar;23(3):346–350. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978233346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. L., Lombroso C. T. A study of clinical, pathological, and electroencephalographic features in 137 full-term babies with a long-term follow-up. Pediatrics. 1970 Mar;45(3):404–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer R. J., Vert P., Mur J. M., Pladys J. C., Humbert F., Royer-Morrot M. J. Données pharmacocinétiques sur le phénobarbital. Etude de l'influence de l'age gestationnel et de la dysmaturité. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1976 Nov;33(G):905–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasterlain C. G. Neonatal seizures and brain growth. Neuropadiatrie. 1978 Aug;9(3):213–228. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


