Abstract
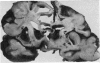
We report a case of infantile multicystic encephalomalacia after maternal bee sting anaphylaxis in the 30th week of pregnancy. The clinical features and findings at necropsy are described, and it is suggested that these are the result of severe fetal hypoxia secondary to maternal hypotension.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aicardi J., Goutières F., De Verbois A. H. Multicystic encephalomalacia of infants and its relation to abnormal gestation and hydranencephaly. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Apr;15(4):357–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manterola A., Towbin A., Yakovlev P. I. Cerebral infarction in the human fetus near term. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1966 Jul;25(3):479–488. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196607000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. E. Four patterns of perinatal brain damage and their conditions of occurrence in primates. Adv Neurol. 1975;10:223–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. E. Two patterns of perinatal brain damage and their conditions of occurrence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Jan 15;112(2):246–276. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARPE O., HALL E. G. Renal impairment, hypertension and encephalomalacia in an infant surviving severe intra-uterine anoxia. Proc R Soc Med. 1953 Dec;46(12):1063–1065. doi: 10.1177/003591575304601215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. F., Rodeck C. Multiple cystic and focal encephalomalacia in infancy and childhood with brain stem damage. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Jul;25(3):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]