Abstract
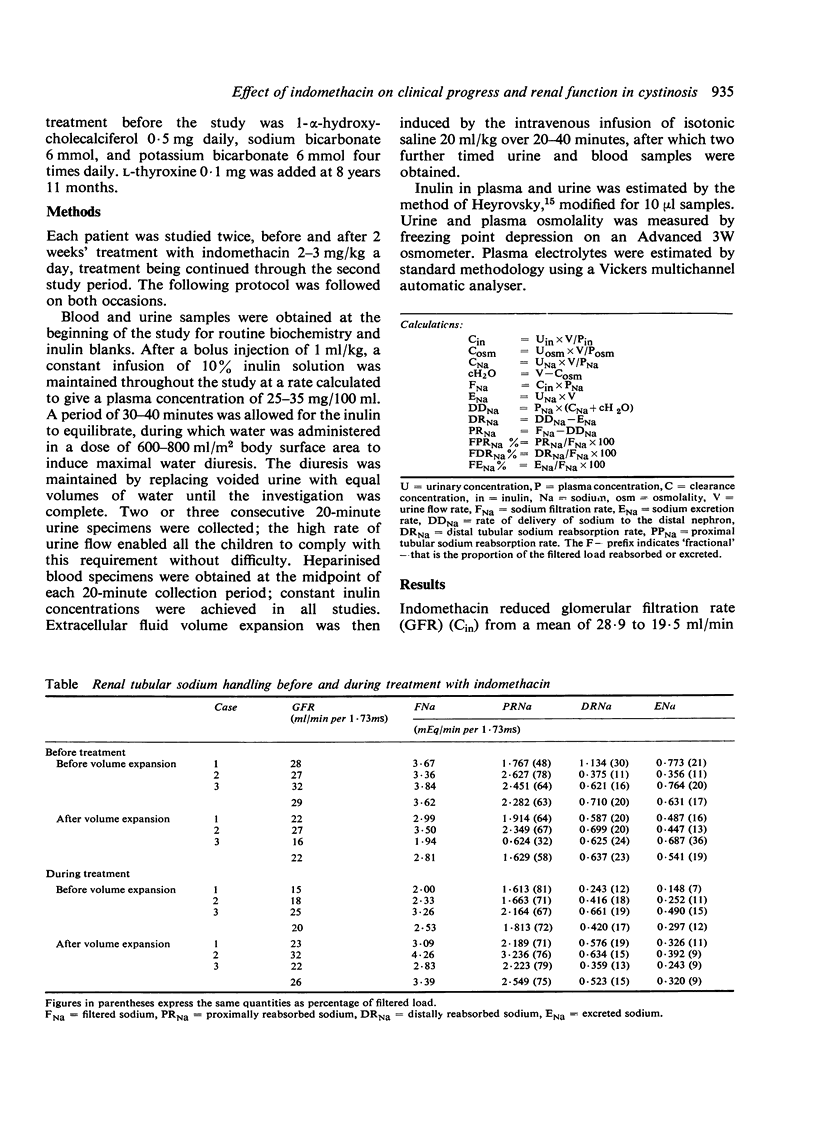
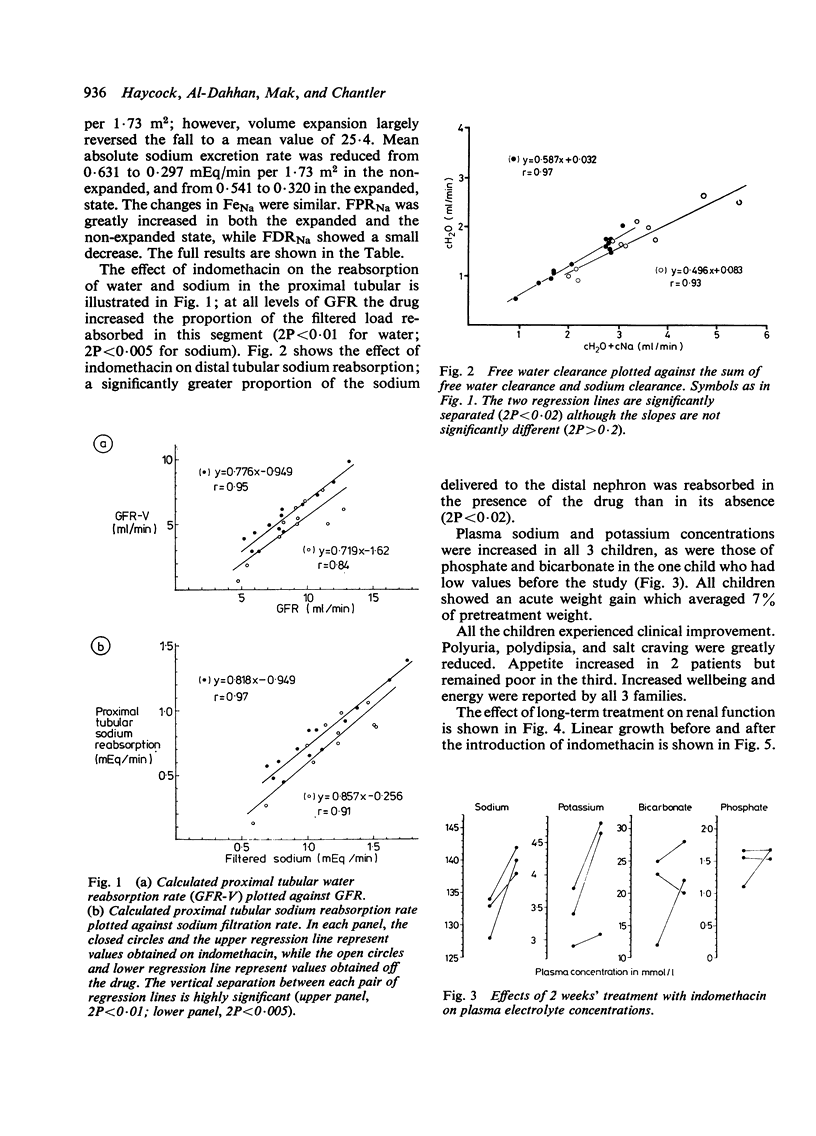
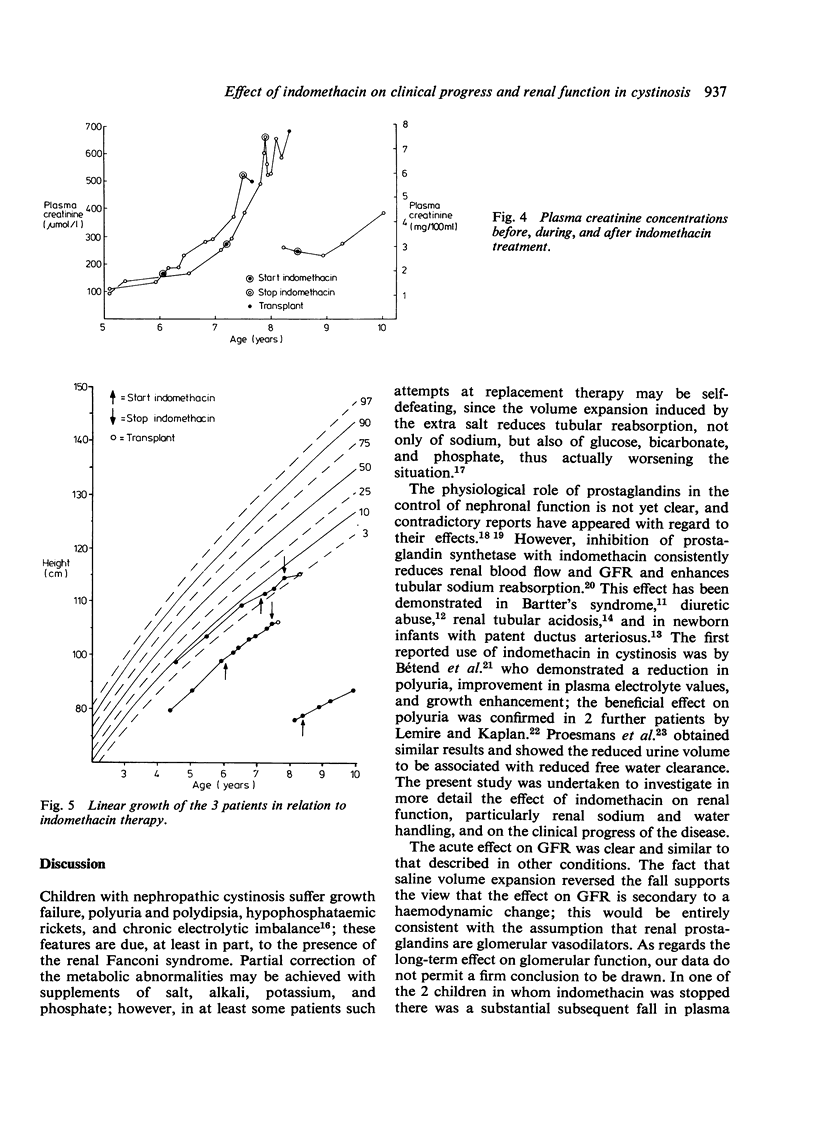
Three children with nephropathic cystinosis were treated with indomethacin 3 mg/kg a day for periods ranging from 9 to 18 months. The drug produced worthwhile clinical improvement in all, with marked beneficial effects on polyuria, polydipsia, and general wellbeing. Clearance studies performed under conditions of maximal water diuresis showed that proximal tubular sodium reabsorption was increased in all children, with consequent reduction in sodium delivery to the distal nephron leading to reduced free water clearance and distal tubular cation exchange. Plasma sodium and potassium concentrations became normal in all patients, with improvement in phosphate and bicarbonate concentrations in one. Renal function continued to deteriorate, but without obvious acceleration of the process by the drug. We were unable to demonstrate a beneficial effect on growth; nevertheless, indomethacin is a useful adjunct to the symptomatic treatment of children with severe nephropathic cystinosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arant B. S., Greifer I., Edelmann C. M., Jr, Spitzer A. Effect of chronic salt and water loading on the tubular defects of a child with Fanconi syndrome (cystinosis). Pediatrics. 1976 Sep;58(3):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. D., Tietze F., Pellefigue F., Spielberg S. P., Schulman J. D. Depletion of cystine in cystinotic fibroblasts by drugs enclosed in liposomes. Pediatr Res. 1978 Jan;12(1):46–51. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197801000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bétend B., David L., Vincent M., Hermier M., François R. Successful indomethacin treatment of two paediatric patients with severe tubulopathies. A boy with an unusual hypercalciuria and a girl with cystinosis. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1979 Sep;34(4):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruana R. J., Buckalew V. M., Jr Improvement of hypercalciuria, potassium wasting and hyperreninemia in incomplete distal renal tubular acidosis by indomethacin. Nephron. 1979;24(5):232–235. doi: 10.1159/000181722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes R. F., Olley P. M., Balfe J. W., Radde I. C., Soldin S. J. Indomethacin and renal function in premature infants with persistent patent ductus arteriosus. J Pediatr. 1979 Oct;95(4):583–587. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80775-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donker A. J., Arisz L., Brentjens J. R., van der Hem G. K., Hollemans H. J. The effect of indomethacin on kidney function and plasma renin activity in man. Nephron. 1976;17(4):288–296. doi: 10.1159/000180733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etches P., Pickering D., Smith R. Cystinotic rickets treated with vitamin D metabolites. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Aug;52(8):661–664. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.8.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E. P., DeWolfe M. S., Crocker J. F. Treatment of cystinosis with cysteamine. J Pediatr. 1979 May;94(5):838–840. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYROVSKY A. A new method for the determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1956 Sep-Oct;1(5):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(56)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambraeus L., Broberger O. Penicillamine treatment of cystinosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967 May;56(3):243–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb15374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. W., Moncada S. The renal haemodynamic and excretory actions of prostacyclin and 6-oxo-PGF1 alpha in anaesthetized dogs. Prostaglandins. 1979 Jan;17(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Itskovitz H. D. Prostaglandins and renal function. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patak R. V., Mookerjee B. K., Bentzel C. J., Hysert P. E., Babej M., Lee J. B. Antagonism of the effects of furosemide by indomethacin in normal and hypertensive man. Prostaglandins. 1975 Oct;10(4):649–659. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy L. P., Pollard A. C. Cysteamine therapy for cystinosis. Lancet. 1978 Sep 30;2(8092 Pt 1):729–730. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92717-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Lutz P., Bickel H. Wertbeurteilung der diätetischen Behandlung der Cystinose. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1973 May;121(5):171–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Schlesselman J. J., Mendoza S. A., Orloff S., Thoene J. G., Kroll W. A., Godfrey A. D., Schulman J. D. Ineffectiveness of ascorbic acid therapy in nephropathic cystinosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 5;300(14):756–759. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904053001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Schulman J. D. Cystinosis: a review. Metabolism. 1977 Jul;26(7):817–839. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoene J. G., Lemons R. Cystine depletion of cystinotic tissues by phosphocysteamine (WR638). J Pediatr. 1980 Jun;96(6):1043–1044. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80637-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verberckmoes R., van Damme B B., Clement J., Amery A., Michielsen P. Bartter's syndrome with hyperplasia of renomedullary cells: successful treatment with indomethacin. Kidney Int. 1976 Mar;9(3):302–307. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkoff M., Foreman J. W., Segal S. Effects of cysteamine therapy in nephropathic cystinosis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 15;304(3):141–145. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101153040303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



