Abstract
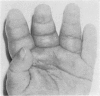
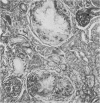
A month old infant had gout and renal failure caused by hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRTase) deficiency. Investigations showed a high uric acid value, crystal nephropathy on ultrasound, and uric acid deposition on renal biopsy. The HGPRTase value was low in red cells and fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dancis J., Yip L. C., Cox R. P., Piomelli S., Balis M. E. Disparate enzyme activity in erythocytes and leukocytes. A variant of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl-transferase deficiency with an unstable enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):2068–2074. doi: 10.1172/JCI107391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson B. T., Thompson L. The spectrum of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency. Q J Med. 1973 Apr;42(166):423–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESCH M., NYHAN W. L. A FAMILIAL DISORDER OF URIC ACID METABOLISM AND CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION. Am J Med. 1964 Apr;36:561–570. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegmiller J. E., Rosenbloom F. M., Kelley W. N. Enzyme defect associated with a sex-linked human neurological disorder and excessive purine synthesis. Science. 1967 Mar 31;155(3770):1682–1684. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3770.1682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruyn C. H. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency. Hum Genet. 1976 Feb 29;31(2):127–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00296142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]