Abstract
A preterm infant with hypophosphataemic rickets became hypocalcaemic when given milk specially formulated for preterm infants that contained increased phosphorus and calcium. The rickets resolved spontaneously. Routine calcium and phosphorus supplementation for preterm neonates should be investigated further.
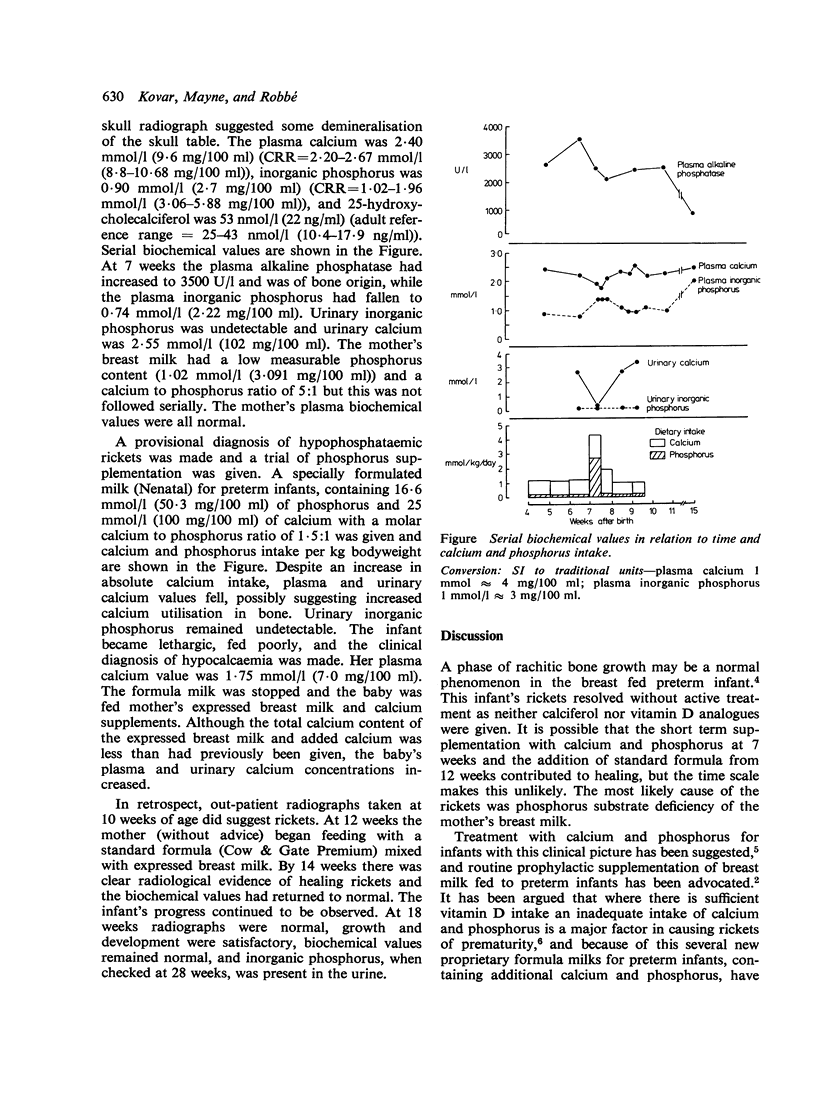
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chesney R. W., Hamstra A. J., DeLuca H. F. Rickets of prematurity. Supranormal levels of serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Am J Dis Child. 1981 Jan;135(1):34–37. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1981.02130250022008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EEK S., GABRIELSEN L. H., HALVORSEN S. Prematurity and rickets. Pediatrics. 1957 Jul;20(1 Pt 1):63–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes G. B. Human milk and the small baby. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Jul;136(7):577–578. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970430009001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer F. R., Steichen J. J., Tsang R. C. Calcium and phosphate supplements in breast milk-related rickets. Results in a very-low-birth-weight infant. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Jul;136(7):581–583. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970430013003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovar I., Mayne P., Barltrop D. Plasma alkaline phosphatase activity: a screening test for rickets in preterm neonates. Lancet. 1982 Feb 6;1(8267):308–310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91569-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino Y., Ishii T., Shimotsuji T., Ishida M., Yabuuchi H. Plasma active vitamin D concentration in low birthweight infants with rickets and its response to vitamin D treatment. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Aug;56(8):628–632. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.8.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


