Abstract
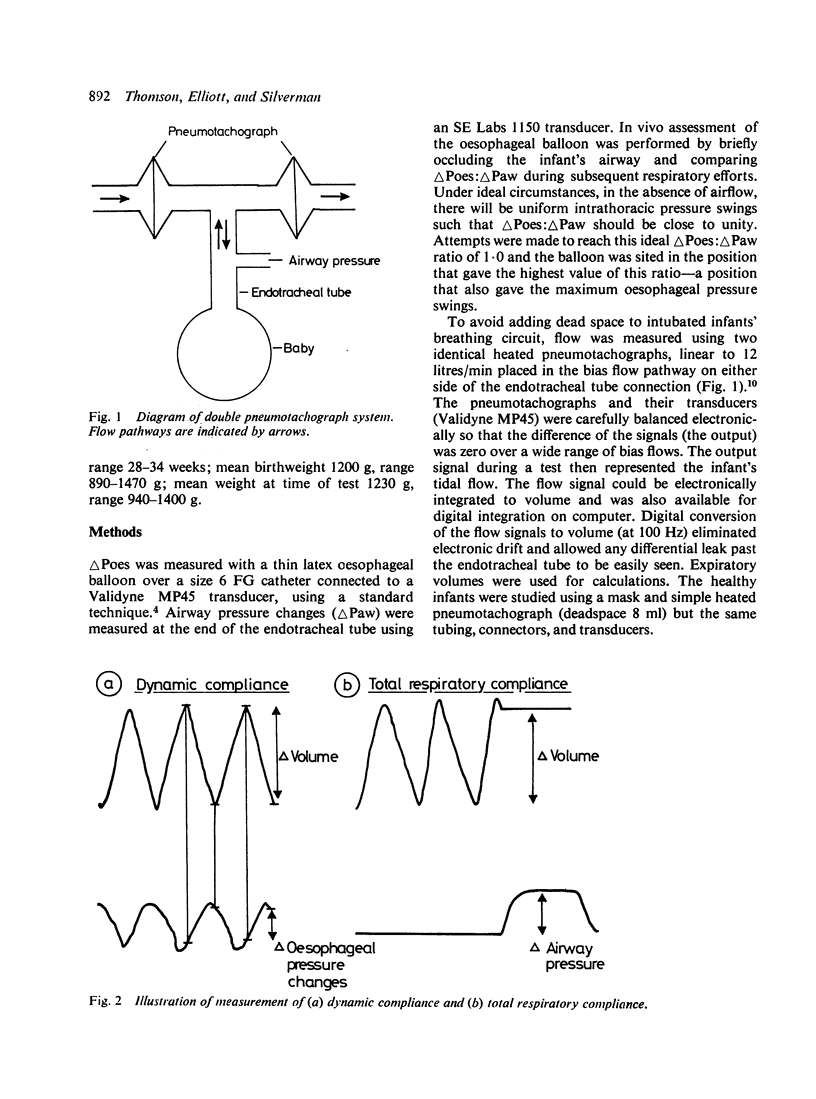
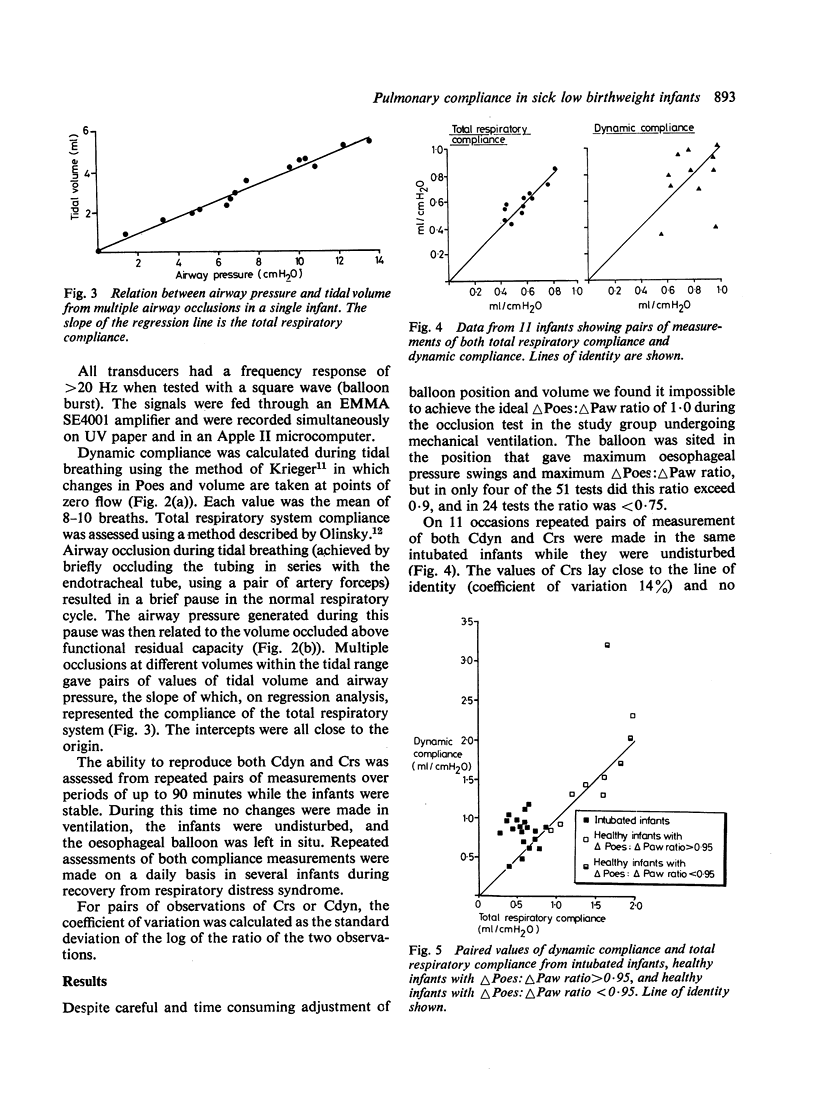
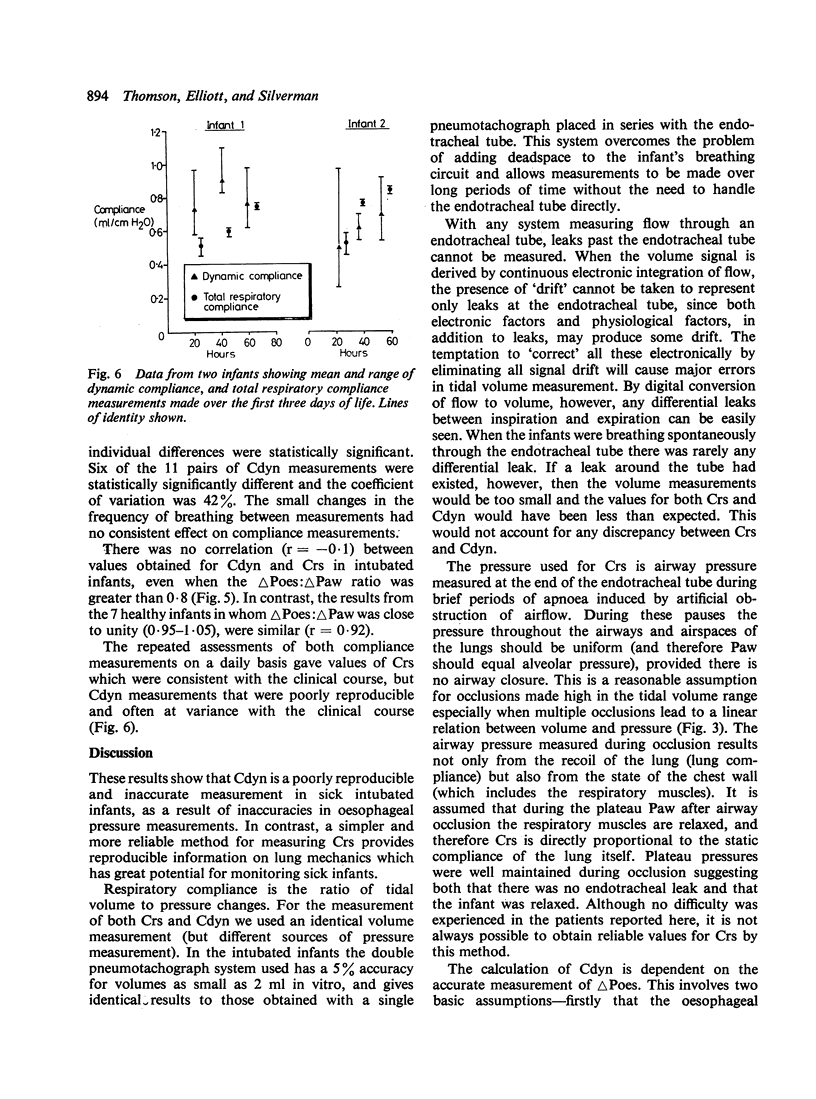
Measurements of dynamic lung compliance (Cdyn) were made on 42 occasions in a group of 15 intubated very low birthweight infants with respiratory distress syndrome, using an oesophageal balloon and pneumotachograph system. Values of Cdyn were compared with those of total respiratory system compliance (Crs) using an occlusion technique. Ten very low birthweight infants with no respiratory disease were similarly studied while breathing through a facemask. The occlusion tests for oesophageal balloon assessment were unsatisfactory in 14 of 15 intubated infants, but in only 3 of the 10 normal infants. Values of Cdyn were poorly reproducible and correlated poorly with Crs. We conclude that in sick intubated preterm infants oesophageal pressure (and hence Cdyn) cannot be reliably measured, but that Crs may be a useful parameter of lung stiffness.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVERY M. E., COOK C. D. Volume-pressure relationships of lungs and thorax in fetal, newborn, and adult goats. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Nov;16:1034–1038. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.6.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baydur A., Behrakis P. K., Zin W. A., Jaeger M., Milic-Emili J. A simple method for assessing the validity of the esophageal balloon technique. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):788–791. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beardsmore C. S., Helms P., Stocks J., Hatch D. J., Silverman M. Improved esophageal balloon technique for use in infants. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Oct;49(4):735–742. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.4.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonta B. W., Uauy R., Warshaw J. B., Motoyama E. K. Determination of optimal continuous positive airway pressure for the treatment of IRDS by measurement of esophageal pressure. J Pediatr. 1977 Sep;91(3):449–454. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81323-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Angelo E., Sant'Ambrogio G., Agostoni E. Effect of diaphragm activity or paralysis on distribution of pleural pressure. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Sep;37(3):311–315. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinwiddie R., Russell G. Relationship of intraesophageal pressure to intrapleural pressure in the newborn. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Oct;33(4):415–417. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt T., Bancalari E. Chestwall compliance in full-term and premature infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1980 May;69(3):359–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1980.tb07093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenough A., Morley C. J. Oesophageal pressure measurements in ventilated preterm babies. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Nov;57(11):851–855. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.11.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIEGER I. Studies on mechanics of respiration in infancy. Am J Dis Child. 1963 May;105:439–448. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1963.02080040441003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korvenranta H. J., Kero P. O., Välimäki I. A. Intraesophageal pressure monitoring and the severity of respiratory distress syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 Jul;138(4):297–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00442500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeSouëf P. N., Lopes J. M., England S. J., Bryan M. H., Bryan A. C. Influence of chest wall distortion on esophageal pressure. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):353–358. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindroth M., Johnson B., Ahlström H., Svenningsen N. W. Pulmonary mechanics in early infancy. Subclinical grunting in low-birth-weight infants. Pediatr Res. 1981 Jul;15(7):979–984. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198107000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naulty C. M., Horn S., Conry J., Avery G. B. Improved lung compliance after ligation of patent ductus arteriosus in hyaline membrane disease. J Pediatr. 1978 Oct;93(4):682–684. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80917-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olinsky A., Bryan A. C., Bryan M. H. A simple method of measuring total respiratory system compliance in newborn infants. S Afr Med J. 1976 Jan 31;50(5):128–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruttimann U. E., Galioto F. M., Jr, Franke J. R., Rivera O. Measurement of tracheal airflow in newborns by a differential flow system. Crit Care Med. 1981 Nov;9(11):801–804. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198111000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simbruner G., Coradello H., Lubec G., Pollak A., Salzer H. Respiratory compliance of newborns after birth and its prognostic value for the course and outcome of respiratory disease. Respiration. 1982;43(6):414–423. doi: 10.1159/000194512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stănescu D. C., Rodenstein D., Cauberghs M., Van de Woestijne K. P. Failure of body plethysmography in bronchial asthma. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Apr;52(4):939–948. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanswell A. K., Clubb R. A., Smith B. T., Boston R. W. Individualised continuous distending pressure applied within 6 hours of delivery in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Jan;55(1):33–39. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagaman M. J., Shutack J. G., Moomjian A. S., Schwartz J. G., Shaffer T. H., Fox W. W. Improved oxygenation and lung compliance with prone positioning of neonates. J Pediatr. 1979 May;94(5):787–791. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh T. F., Thalji A., Luken L., Lilien L., Carr I., Pildes R. S. Improved lung compliance following indomethacin therapy in premature infants with persistent ductus arteriosus. Chest. 1981 Dec;80(6):698–700. doi: 10.1378/chest.80.6.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


