Abstract
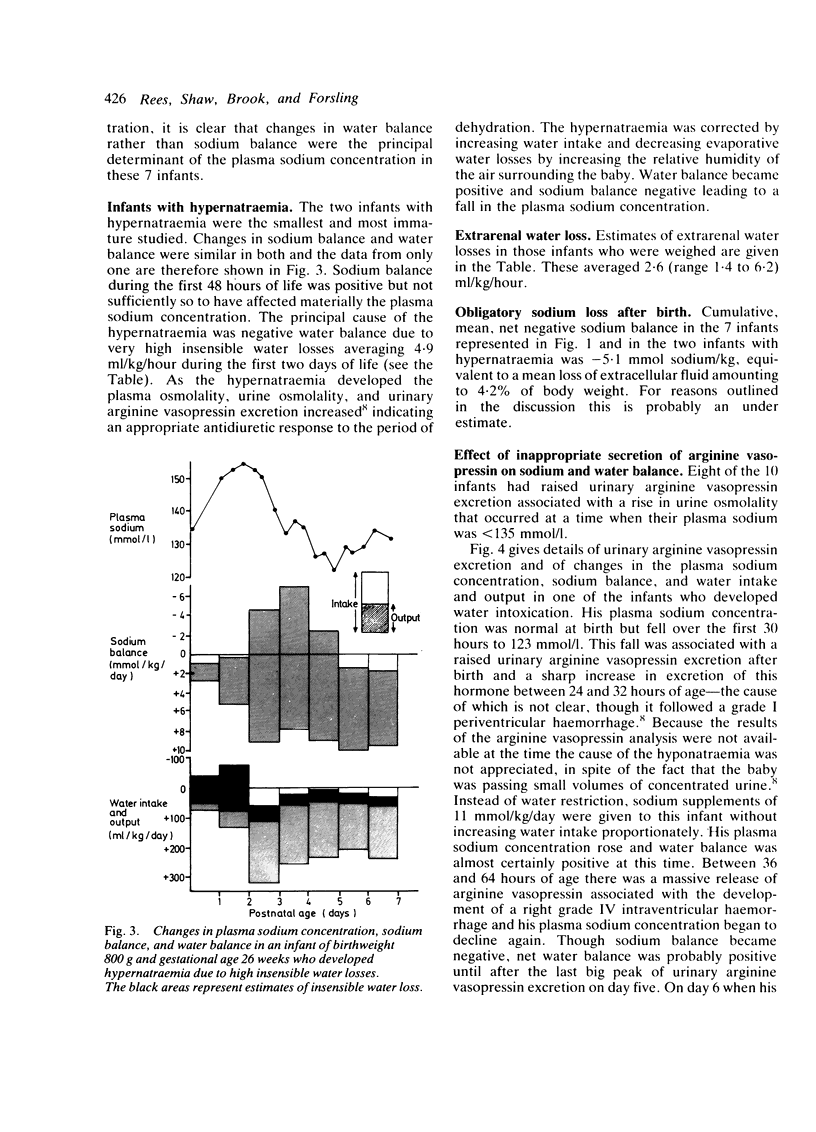
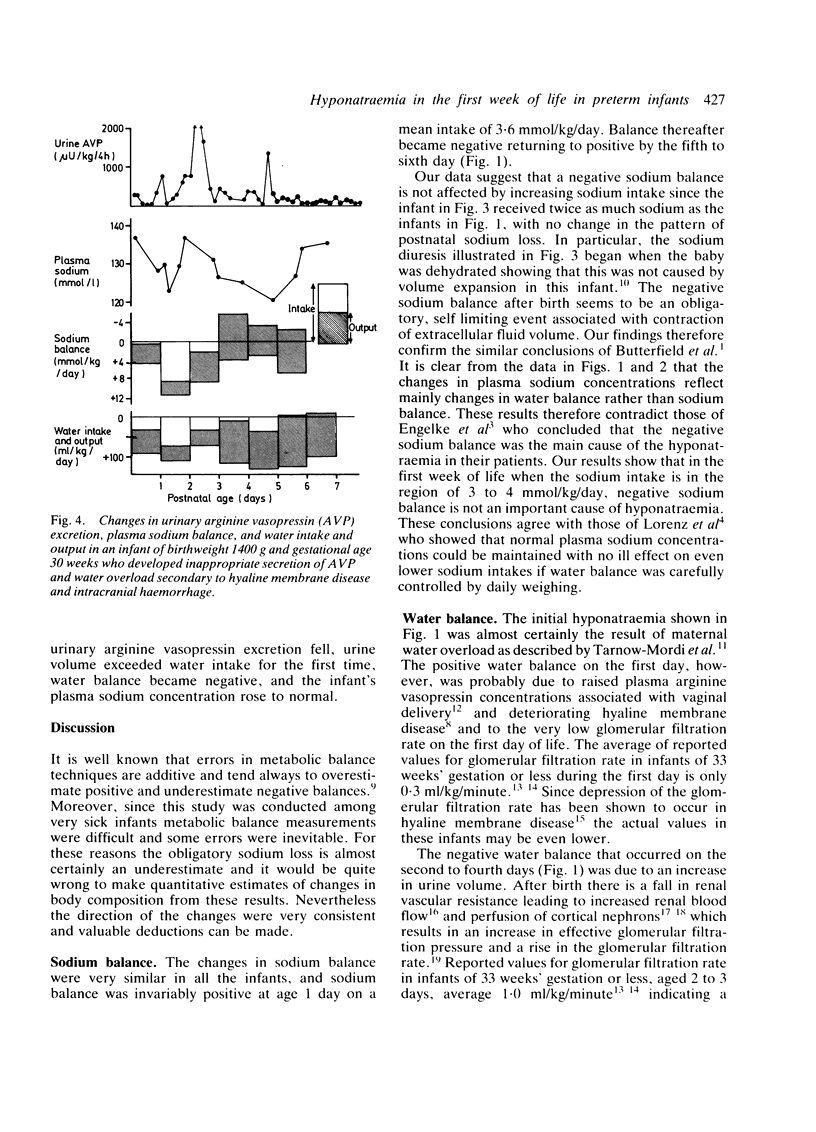
Serial measurements of plasma sodium, sodium balance, water intake, and urine volume were made for a mean period of 5.9 days in 10 preterm infants of mean gestation 30.5 weeks and mean birthweight 1506 g. In five infants weighed regularly, estimates of insensible water loss averaged 2.6 (range 1.4 to 6.2) ml/kg/hour. High insensible water losses were the cause of hypernatraemia that occurred in two of the 10 infants. Net sodium balance was negative during the study and represented contraction of the extracellular fluid volume associated with weight loss. The negative sodium balance did not seem diminished by increasing sodium intake and there was no evidence that sodium intake need exceed 3 to 4 mmol/kg/day. Hyponatraemia was not due to changes in sodium balance but to water retention associated with inappropriate increases in urinary arginine vasopressin excretion and urine osmolality in 8 of 10 infants. Frequent, accurate measurements of body weight and of plasma sodium are the two most reliable indicators of changes in water balance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Dahhan J., Haycock G. B., Chantler C., Stimmler L. Sodium homeostasis in term and preterm neonates. I. Renal aspects. Arch Dis Child. 1983 May;58(5):335–342. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.5.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Broberger O., Elinder G., Herin P., Zetterström R. Postnatal development of renal function in pre-term and full-term infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Mar;70(2):183–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb05539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aschinberg L. C., Goldsmith D. I., Olbing H., Spitzer A., Edelmann C. M., Jr, Blaufox M. D. Neonatal changes in renal blood flow distribution in puppies. Am J Physiol. 1975 May;228(5):1453–1461. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.5.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTERFIELD J., LUBCHENCO L. O., BERGSTEDT J., O'BRIEN D. Patterns in electrolyte and nitrogen balance in the newborn premature infant. Pediatrics. 1960 Nov;26:777–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch H. Childhood in the early colonial period. Pediatrics. 1974 Jul;54(1):71–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day G. M., Radde I. C., Balfe J. W., Chance G. W. Electrolyte abnormalities in very low birthweight infants. Pediatr Res. 1976 May;10(5):522–526. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197605000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawer C. L., Torrado A., Guignard J. P. Maturation of renal function in full-term and premature neonates. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1979 Feb;34(1):11–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruskin A. B., Edelmann C. M., Jr, Yuan S. Maturational changes in renal blood flow in piglets. Pediatr Res. 1970 Jan;4(1):7–13. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197001000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarlund K., Sedin G., Strömberg B. Transepidermal water loss in newborn infants. VII. Relation to post-natal age in very pre-term and full-term appropriate for gestational age infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1982 May;71(3):369–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1982.tb09436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake R. D., Trygstad C. W., Oh W. Inulin clearance in the newborn infant: relationship to gestational and postnatal age. Pediatr Res. 1976 Aug;10(8):759–762. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197608000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake R. D., Zakauddin S., Trygstad C. W., Fu P., Oh W. The effects of large volume intravenous fluid infusion on neonatal renal function. J Pediatr. 1976 Dec;89(6):968–972. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80612-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz J. M., Kleinman L. I., Kotagal U. R., Reller M. D. Water balance in very low-birth-weight infants: relationship to water and sodium intake and effect on outcome. J Pediatr. 1982 Sep;101(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olbing H., Blaufox M. D., Aschinberg L. C., Silkalns G. I., Bernstein J., Spitzer A., Edelmann C. M., Jr Postnatal changes in renal glomerular blood flow distribution in puppies. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2885–2895. doi: 10.1172/JCI107485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L., Brook C. G., Shaw J. C., Forsling M. L. Hyponatraemia in the first week of life in preterm infants. Part I. Arginine vasopressin secretion. Arch Dis Child. 1984 May;59(5):414–422. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.5.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B., Cowett R. M., Oh W. Renal functions of low birth weight infants during the first two months of life. Pediatr Res. 1977 Nov;11(11):1162–1164. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197711000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedewie H. K., Odell W. D., Fisher D. A., Krutzik S. R., Dodge M., Cousins L., Fiser W. P. Parathormone and perinatal calcium homeostasis. Pediatr Res. 1979 Jan;13(1):1–6. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197901000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer A., Edelmann C. M., Jr Maturational changes in pressure gradients for glomerular filtration. Am J Physiol. 1971 Nov;221(5):1431–1435. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.5.1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulyok E., Varga F., Györy E., Jobst K., Csaba I. F. Postnatal development of renal sodium handling in premature infants. J Pediatr. 1979 Nov;95(5 Pt 1):787–792. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80737-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnow-Mordi W. O., Shaw J. C., Liu D., Gardner D. A., Flynn F. V. Iatrogenic hyponatraemia of the newborn due to maternal fluid overload: a prospective study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Sep 5;283(6292):639–642. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6292.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


