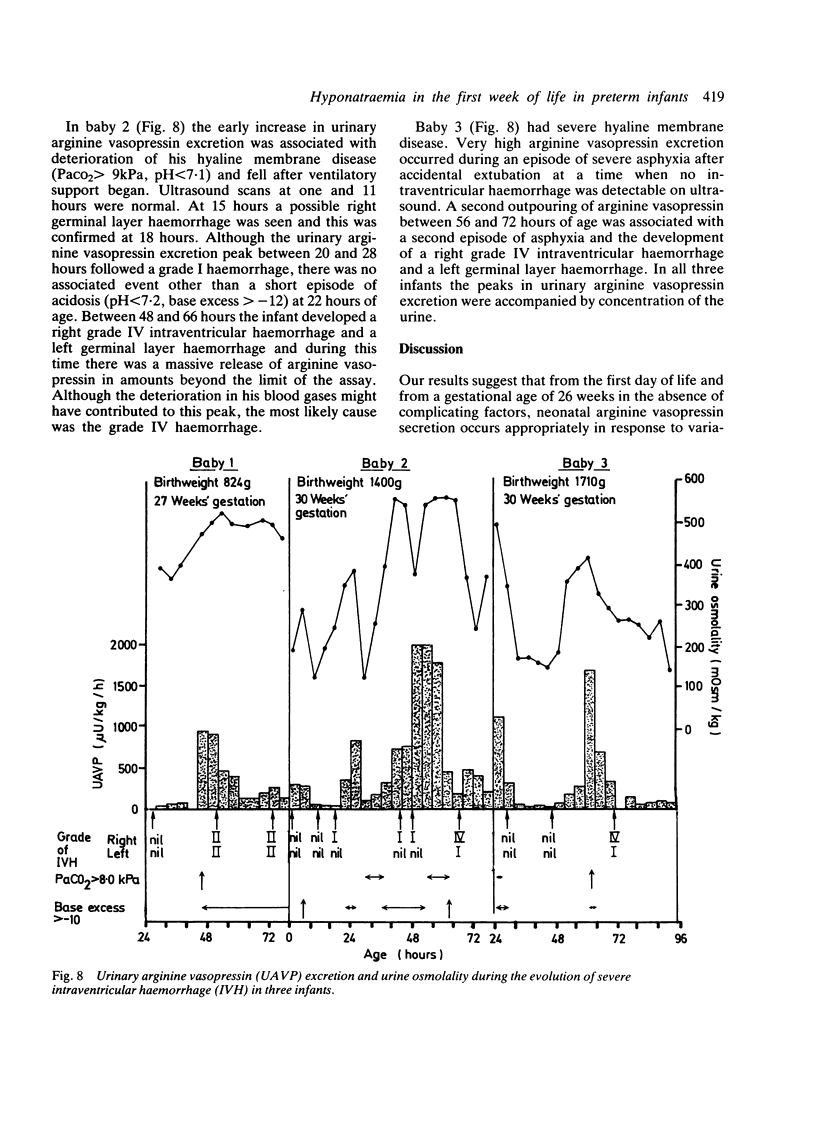
Abstract
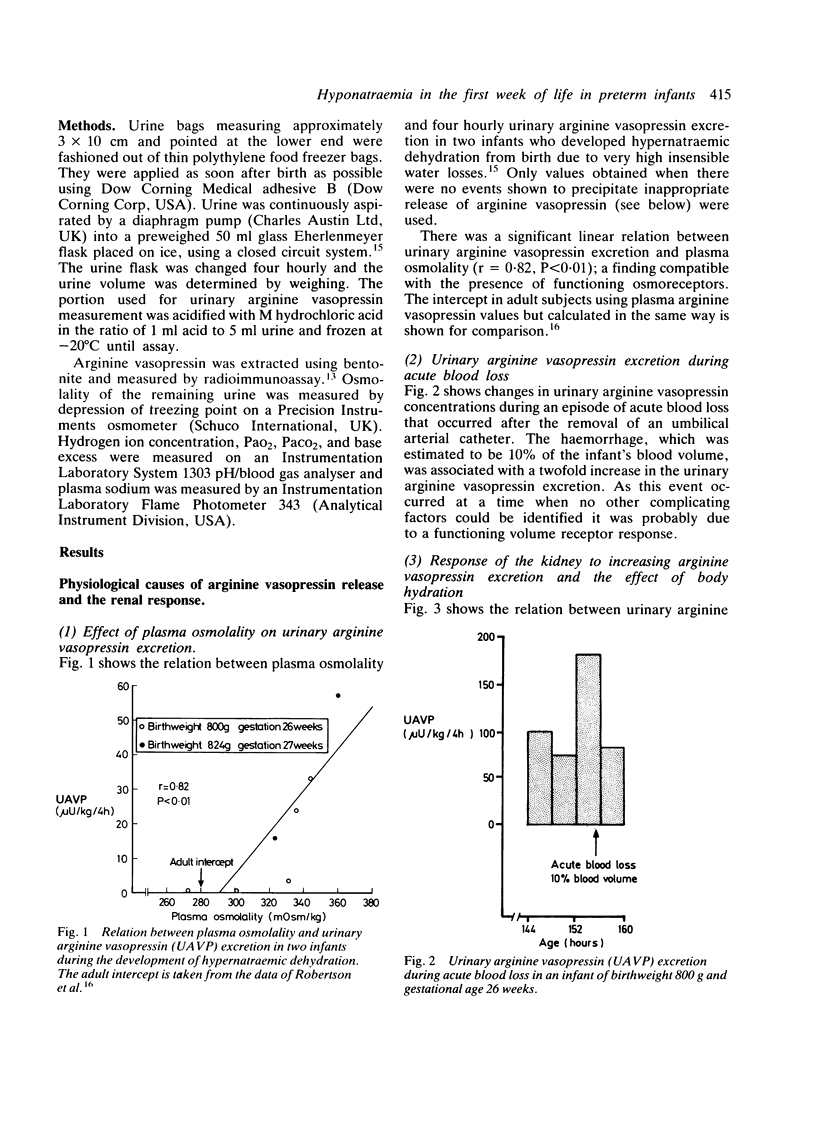
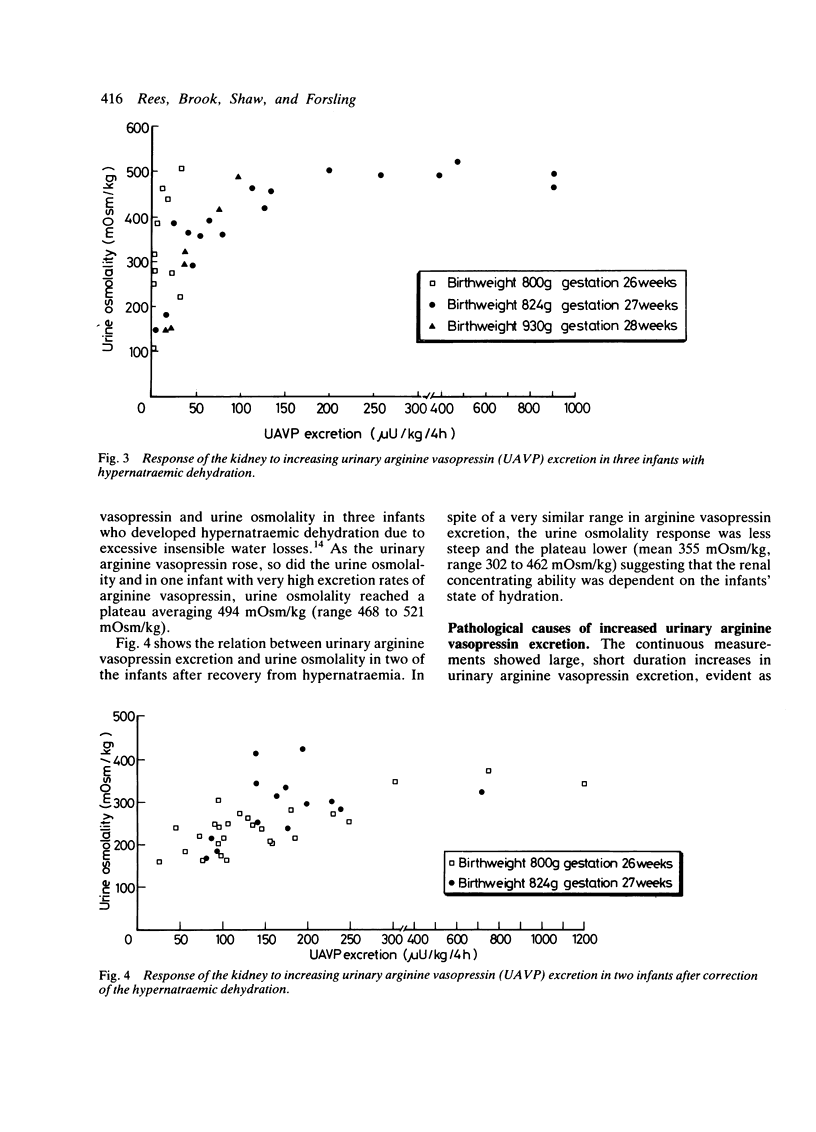
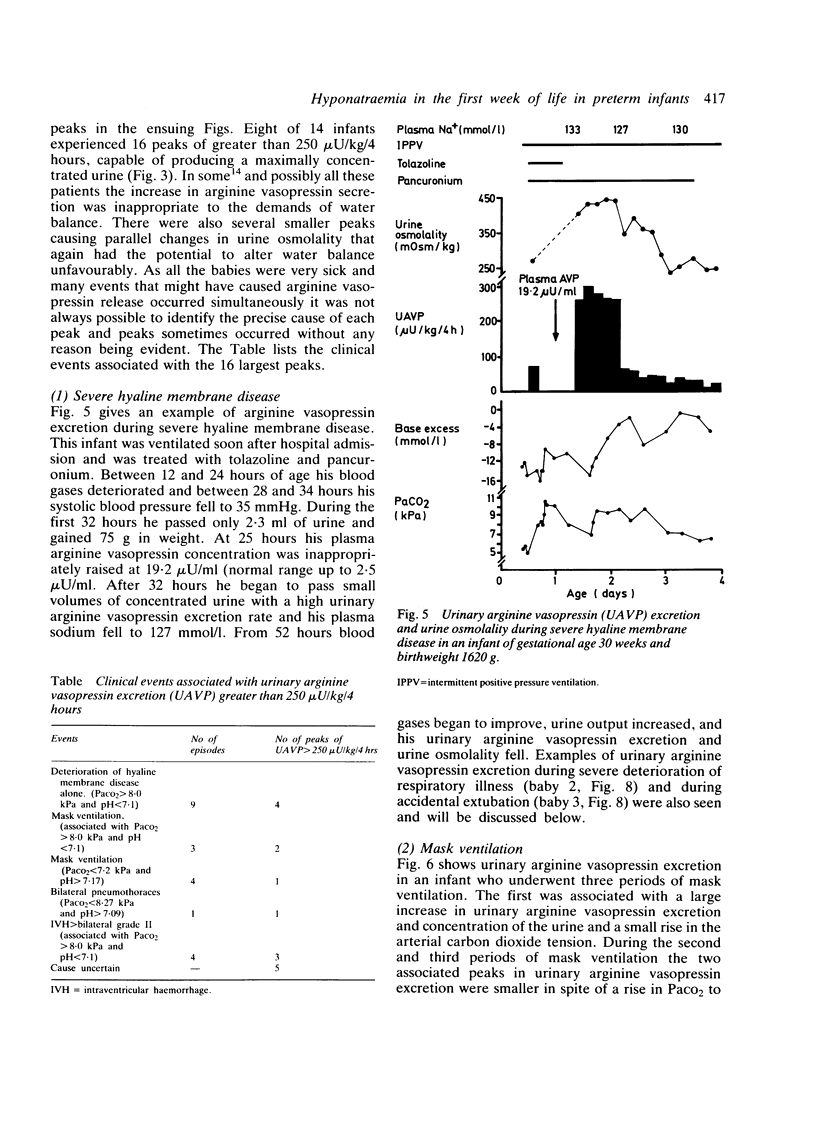
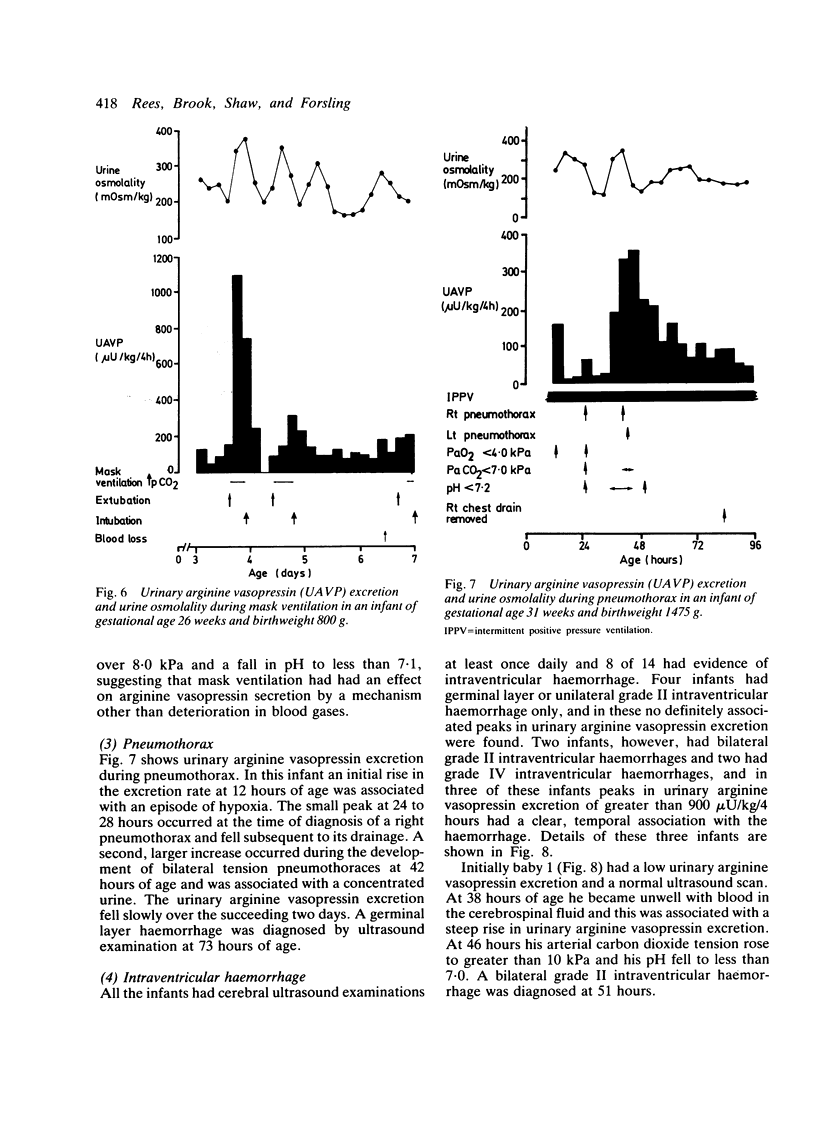
Continuous sequential urinary arginine vasopressin measurements in 14 preterm, ventilated infants suggest that both osmoreceptor and volume receptor systems are able to stimulate the prolonged secretion of arginine vasopressin from 26 weeks' gestation. The kidney is able to respond to arginine vasopressin stimulation from the first day of life and from 26 weeks' gestation. A maximum urine osmolality not exceeding 550 mOsm/kg was reached which varied with hydration of the infant. Excretion of arginine vasopressin and urine osmolality increased during deterioration of respiratory illness, mask ventilation, bilateral pneumothoraces, and severe intraventricular haemorrhage. The data show that inappropriate arginine vasopressin secretion is common during illness in the first week of life in preterm infants and that strict attention must be paid to water balance during this time.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES R. G. Urinary water excretion and neurohypophysial function in full term and premature infants shortly after birth. Pediatrics. 1953 Sep;12(31):272–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Herin P., Eklöv A. C., Johnsson V. Importance of AVP for blood pressure control during development: a study in the Brattleboro rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;394:350–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb37446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H., Segal M. B. The effects of some inhibitors and accelerators of sodium transport on the turnover of 22Na in the cerebrospinal fluid and the brain. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):131–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVane G. W., Porter J. C. An apparent stress-induced release or arginine vasopressin by human neonates. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Dec;51(6):1412–1416. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-6-1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond W. H., Rudolph A. M., Keil L. C., Gluckman P. D., MacDonald A. A., Heymann M. A. Arginine vasopressin and prolactin after hemorrhage in the fetal lamb. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):E214–E219. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann C. M., Jr Physiologic adaptations required of a newborn's kidney. Contrib Nephrol. 1979;15:1–9. doi: 10.1159/000402588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber M. O., Roberts L. R., Weinberger M. H., Robertson G. L., Fineberg N. S., Manfredi F. Abnormalities of sodium and H2O handling in chronic obstructive lung disease. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Jul;142(7):1326–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaufin L., Skowsky W. R., Goodman S. J. Release of antidiuretic hormone during mass-induced elevation of intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg. 1977 May;46(5):627–637. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.46.5.0627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY J. P., GAUER O. H., REEVES J. L. Evidence of the atrial location of receptors influencing urine flow. Circ Res. 1956 Jan;4(1):85–90. doi: 10.1161/01.res.4.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppenstein J. M., Miltenberger F. W., Moran W. H., Jr The increase in blood levels of vasopressin in infants during birth and surgical procedures. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1968 Nov;127(5):966–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto H. S., Rudolph A. M., Keil L. C., Heymann M. A. Hemodynamic responses of the sheep fetus to vasopressin infusion. Circ Res. 1979 Mar;44(3):430–436. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joppich R., Scherer B., Weber P. C. Renal prostaglandins: relationship to the development of blood pressure and concentrating capacity in pre-term and full term healthy infants. Eur J Pediatr. 1979;132(4):253–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00496848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Feigin R. D. Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone complicating neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 1978 Mar;92(3):431–433. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. Y., Anderson G. J. A method for long-term quantitative and fractional urine collection. J Pediatr. 1967 Feb;70(2):276–279. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moylan F. M., Herrin J. T., Krishnamoorthy K., Todres I. D., Shannon D. C. Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion in premature infants with cerebral injury. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Apr;132(4):399–402. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120290071014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxson C. L., Jr, Stoerner J. W., Denson S. E., Adcock E. W., 3rd, Morriss F. H., Jr Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion in neonates with pneumothorax or atelectasis. J Pediatr. 1977 Sep;91(3):459–463. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philbin D. M., Baratz R. A., Patterson R. W. The effect of carbon dioxide on plasma antidiuretic hormone levels during intermittent positive-pressure breathing. Anesthesiology. 1970 Sep;33(3):345–349. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197009000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohjavuori M., Fyhrquist F. Hemodynamic significance of vasopressin in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1980 Sep;97(3):462–465. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomarède R., Moriette G., Czernichow P., Relier J. P. Etude de la vasopressine plasmatique chez les enfants prématurés soumis à la ventilation artificelle. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1978 Dec;35(10 Suppl):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rap Z. M., Chwalbińska-Moneta J. Vasopressin concentration in the blood during acute short-term intracranial hypertension in cats. Adv Neurol. 1978;20:381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L., Brook C. G., Forsling M. L. Continuous urine collection in the study of vasopressin in the newborn. Horm Res. 1983;17(3):134–140. doi: 10.1159/000179688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L., Shaw J. C., Brook C. G., Forsling M. L. Hyponatraemia in the first week of life in preterm infants. Part II. Sodium and water balance. Arch Dis Child. 1984 May;59(5):423–429. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.5.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. L., Mahr E. A., Athar S., Sinha T. Development and clinical application of a new method for the radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2340–2352. doi: 10.1172/JCI107423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. W., Berl T., Anderson R. J. Osmotic and nonosmotic control of vasopressin release. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):F321–F332. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.4.F321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert F., George J. M., Rao M. B. Vasopressin and oxytocin content of human fetal brain at different stages of gestation. Brain Res. 1981 May 25;213(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. I., Wardlaw S. L., Daniel S. S., Husain M. K., Sanocka U. M., James L. S., Vande Wiele R. L. Vasopressin secretion induced by hypoxia in sheep: developmental changes and relationship to beta-endorphin release. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 May 15;143(2):204–215. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(82)90656-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P., LaRochelle F. T., Jr, Little G. A. Vasopressin and pneumothorax in the neonate. Pediatrics. 1981 Oct;68(4):499–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenningsen N. W., Aronson A. S. Postnatal development of renal concentration capacity as estimated by DDAVP-test in normal and asphyxiated neonates. Biol Neonate. 1974;25(3-4):230–241. doi: 10.1159/000240695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn R. J., Lipscomb A. P., Stewart A. L., Reynolds E. O., Hope P. L. Timing and antecedents of periventricular haemorrhage and of cerebral atrophy in very preterm infants. Early Hum Dev. 1982 Dec 6;7(3):221–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(82)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. A., Weitzman R. E., Zakauddin S., Leake R. D. Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone in a premature infant. J Pediatr. 1977 Jan;90(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman R. E., Fisher D. A., Robillard J., Erenberg A., Kennedy R., Smith F. Arginine vasopressin response to an osmotic stimulus in the fetal sheep. Pediatr Res. 1978 Jan;12(1):35–38. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197801000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


