Abstract
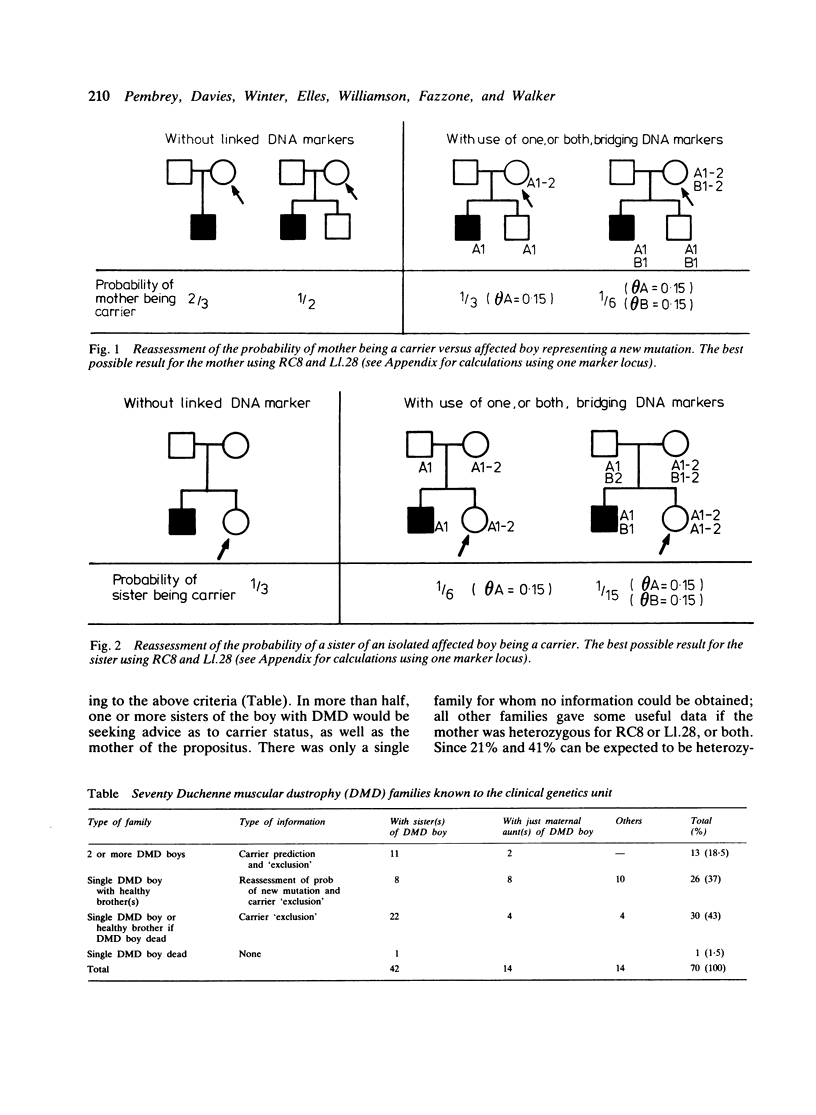
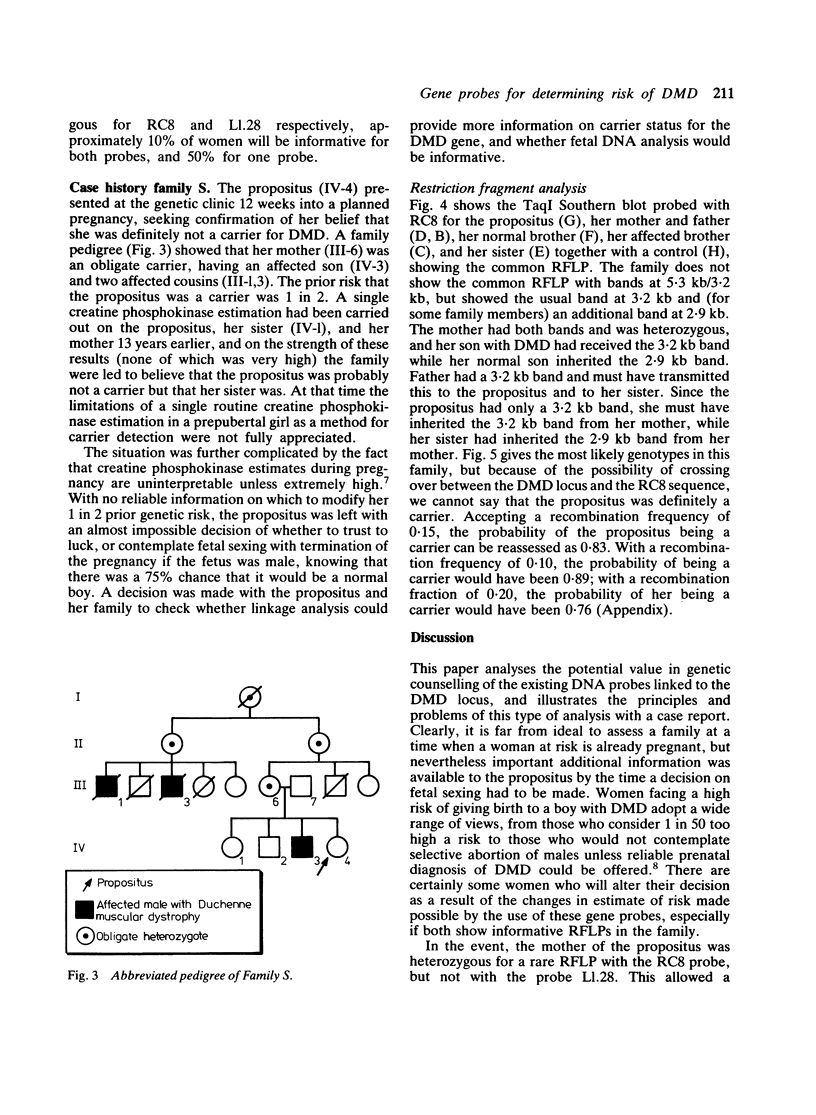
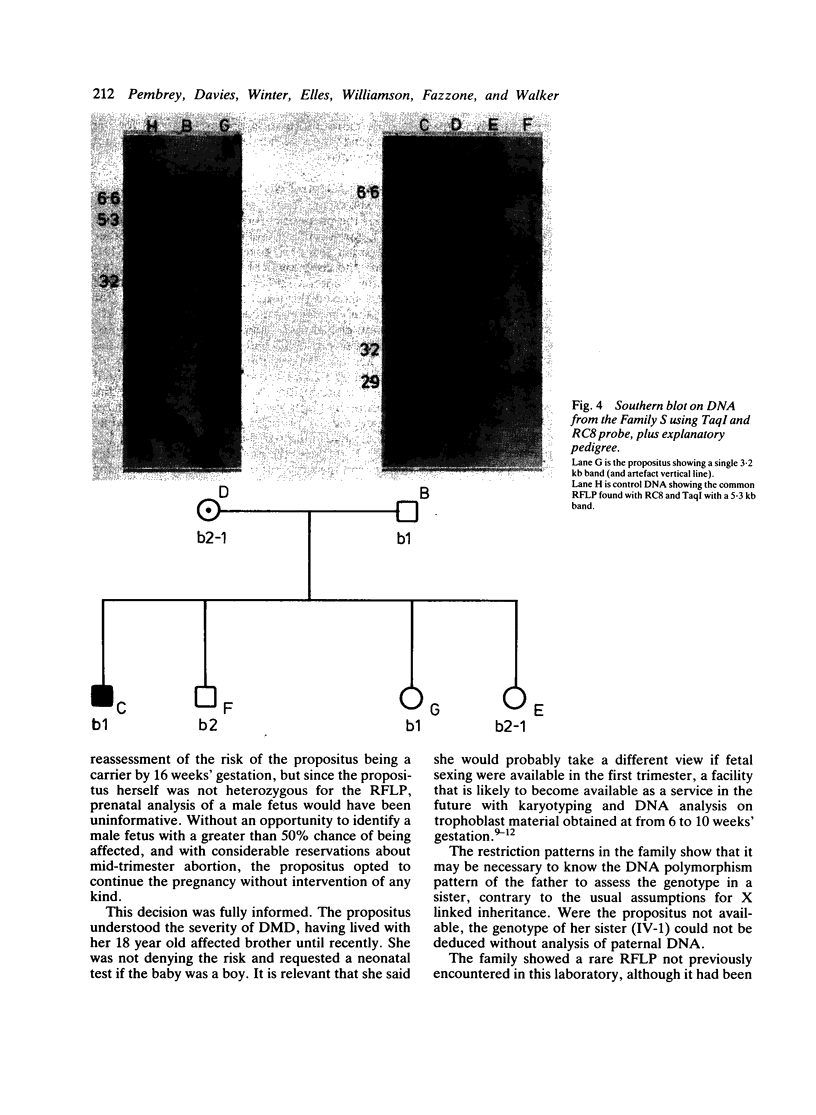
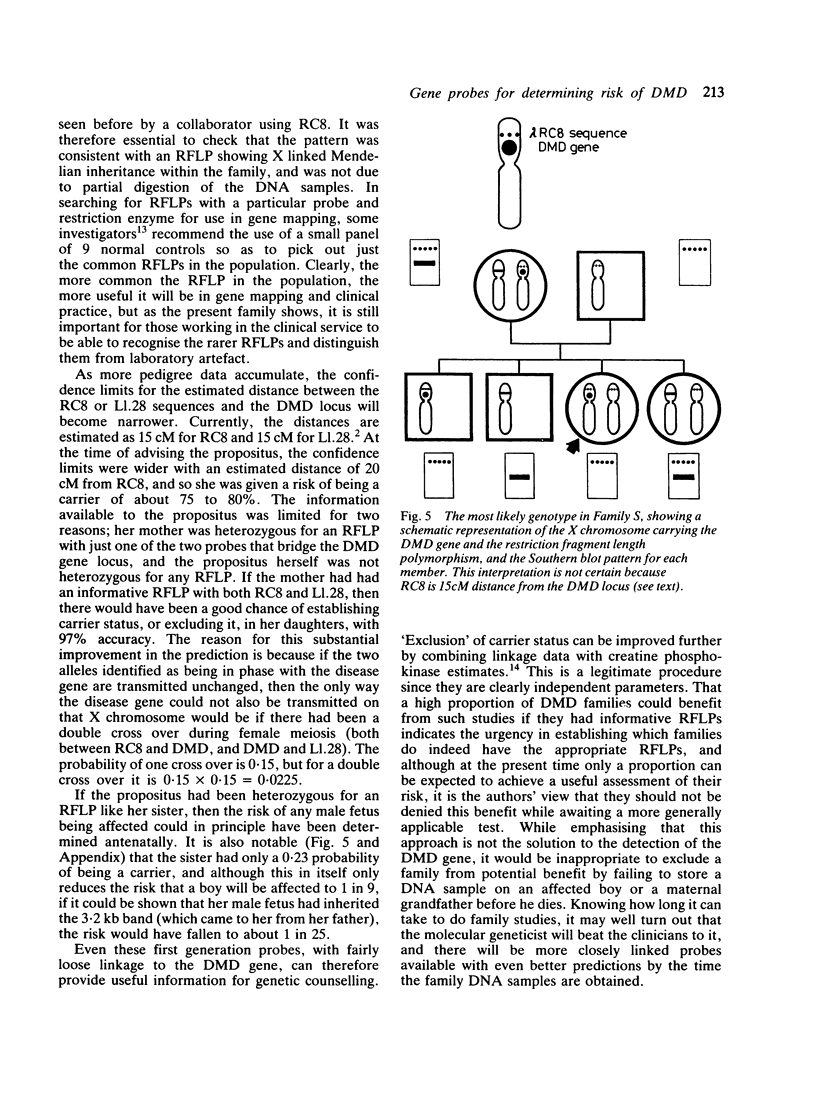
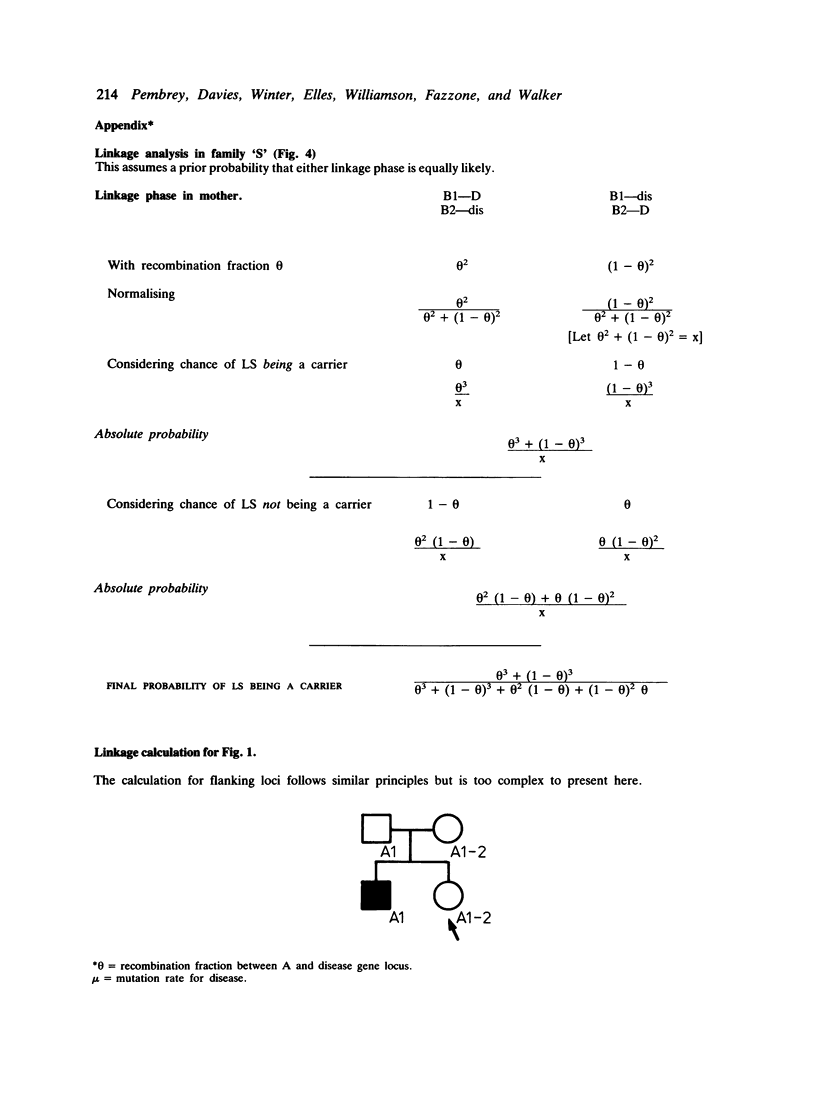
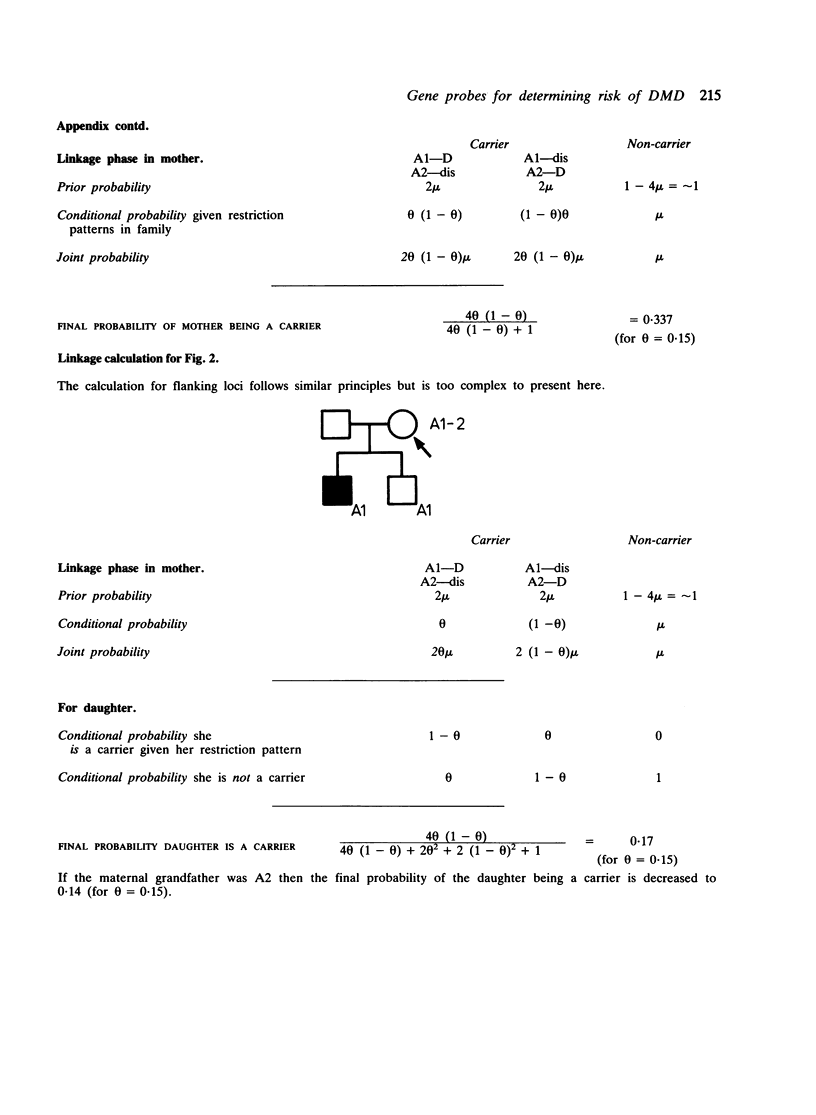
Seventy families with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) known to the Institute of Child Health fall into three categories with respect to potential linkage analysis with the X chromosome DNA markers RC8 and L1.28 that bridge the DMD gene. Families in which there is at least one obligatory female heterozygote (n = 13). Here 'prediction' and 'exclusion' of DMD gene transmission may be possible, the accuracy being dependent on the closeness of the linkage of the DNA marker(s) to the DMD gene; an illustrative case is reported. Families in which there is a single affected boy, who also has one or more healthy brothers (n = 26). Given an informative restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), the probability that the boy represents a new mutation can be reassessed; it is also possible to 'exclude' the DMD gene in a sister. Families with a single affected boy with no brother (n = 30). Here 'exclusion' of the DMD gene in a sister may be possible. Only in one family was there no possibility of useful linkage analysis. The linkage analysis required is described, and the need to check DMD families for informative RFLPs is stressed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bundey S., Crawley J. M., Edwards J. H., Westhead R. A. Serum creatine kinase levels in pubertal, mature, pregnant, and postmenopausal women. J Med Genet. 1979 Apr;16(2):117–121. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Pearson P. L., Harper P. S., Murray J. M., O'Brien T., Sarfarazi M., Williamson R. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2303–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elles R. G., Williamson R., Niazi M., Coleman D. V., Horwell D. Absence of maternal contamination of chorionic villi used for fetal-gene analysis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 16;308(24):1433–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306163082401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Mitchell A. R., Gosden C. M., Rodeck C. H., Morsman J. M. Direct vision chorion biopsy and chromosome-specific DNA probes for determination of fetal sex in first-trimester prenatal diagnosis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1416–1419. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91325-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S., O'Brien T., Murray J. M., Davies K. E., Pearson P., Williamson R. The use of linked DNA polymorphisms for genotype prediction in families with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1983 Aug;20(4):252–254. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.4.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Davies K. E., Harper P. S., Meredith L., Mueller C. R., Williamson R. Linkage relationship of a cloned DNA sequence on the short arm of the X chromosome to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):69–71. doi: 10.1038/300069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niazi M., Coleman D. V., Loeffler F. E. Trophoblast sampling in early pregnancy. Culture of rapidly dividing cells from immature placental villi. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 Nov;88(11):1081–1085. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1981.tb01756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick M. H., White R. Strategies for detecting and characterizing restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP's). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;32(1-4):58–67. doi: 10.1159/000131687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Eskdale J., Coleman D. V., Niazi M., Loeffler F. E., Modell B. M. Direct gene analysis of chorionic villi: A possible technique for first-trimester antenatal diagnosis of haemoglobinopathies. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1125–1127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90583-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



