Abstract
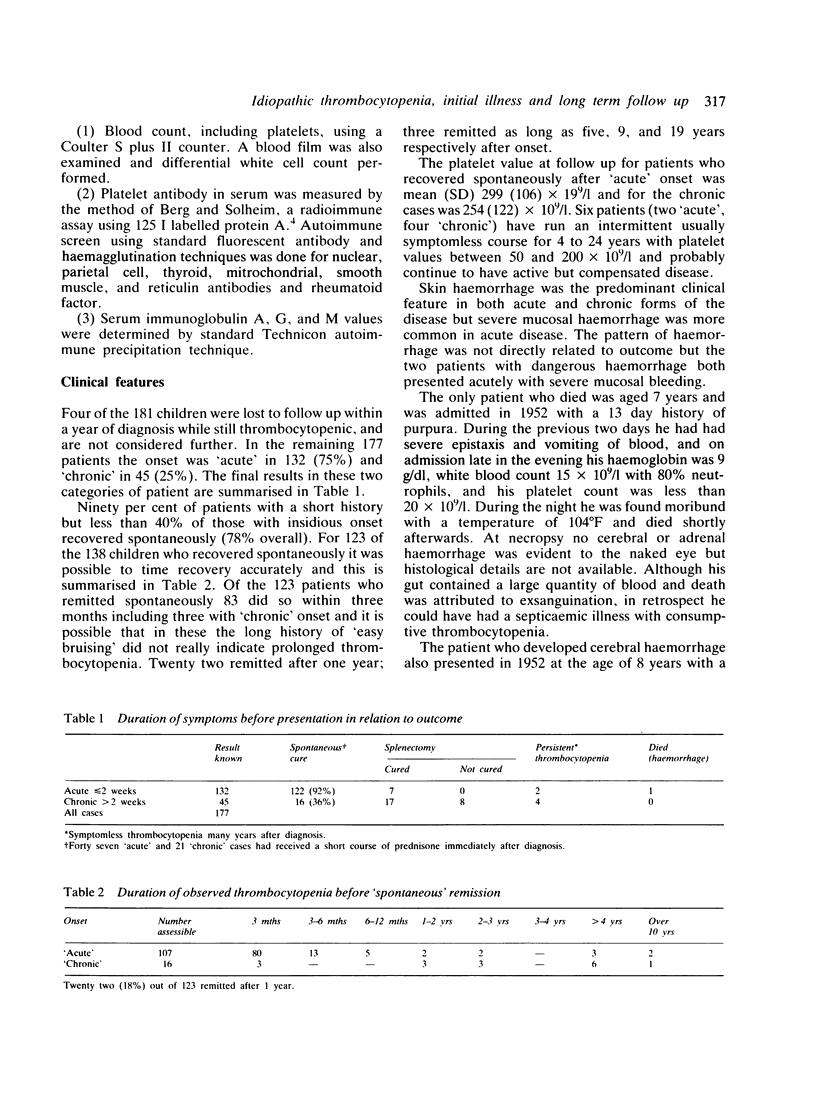
One hundred and eighty one children with thrombocytopenia for which no cause could be found have been studied. One patient died with severe bleeding possibly from disseminated intravascular coagulation and one developed cerebral haemorrhage, both within two weeks of onset. Ninety one per cent of the 135 with acute disease but only 36% of those with chronic disease remitted spontaneously. Twenty per cent of spontaneous remission occurred more than one year after onset. Six patients have run an intermittent course for 10 to 20 years. Four patients have had symptomless thrombocytopenia for between 10 and 30 years. Of 32 children treated by splenectomy 24 maintained normal platelet values thereafter. One boy died from pneumococcal septicaemia two years after splenectomy but he had not received prophylactic penicillin. One hundred and fifty eight patients were followed up 3 to 37 years (mean 16.4 years) after onset. None who recovered spontaneously or after splenectomy had had further bleeding problems. No patient nor immediate relative had developed other autoimmune disease. We consider that a short course of corticosteroids immediately after diagnosis is justified in all cases even though we cannot produce proof that it influences the course of the disease. We do not accept any place for long term immunosuppressant treatment.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn Y. S., Byrnes J. J., Harrington W. J., Cayer M. L., Smith D. S., Brunskill D. E., Pall L. M. The treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenia with vinblastine-loaded platelets. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 18;298(20):1101–1107. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805182982001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn Y. S., Harrington W. J., Simon S. R., Mylvaganam R., Pall L. M., So A. G. Danazol for the treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 9;308(23):1396–1399. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306093082306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branehög I., Weinfeld A. Platelet survival and platelet production in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) before and during treatment with corticosteroids. Scand J Haematol. 1974;12(1):69–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN P., GARDNER F. H. The thrombocytopenic effect of sustained high-dosage prednisone therapy in thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1961 Sep 28;265:611–617. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196109282651301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R. L., Muller H. K., Ward H. A. Immunodeficiency and grouping with thyrogastric autoimmune disease in patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Aust N Z J Med. 1974 Jun;4(3):243–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1974.tb03182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Rosse W., Ebbert L. Quantitative determination of antibody in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Correlation of serum and platelet-bound antibody with clinical response. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 30;292(5):230–236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501302920503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRINGTON W. J., MINNICH V., HOLLINGSWORTH J. W., MOORE C. V. Demonstration of a thrombocytopenic factor in the blood of patients with thrombocytopenic purpura. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jul;38(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyns A. D., Lötter M. G., Badenhorst P. N., de Kock F., Pieters H., Herbst C., van Reenen O. R., Kotze H., Minnaar P. C. Kinetics and sites of destruction of 111Indium-oxine-labeled platelets in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a quantitative study. Am J Hematol. 1982 Apr;12(2):167–177. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830120209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymes K., Shulman S., Karpatkin S. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for bound anti-platelet antibody: studies on 45 patients with autoimmune platelet disorders. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Oct;94(4):639–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbach P., Barandun S., d'Apuzzo V., Baumgartner C., Hirt A., Morell A., Rossi E., Schöni M., Vest M., Wagner H. P. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood. Lancet. 1981 Jun 6;1(8232):1228–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOMROWER G. M., WATSON G. H. Prognosis in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura of childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1954 Dec;29(148):502–506. doi: 10.1136/adc.29.148.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin M., Karpatkin S. Immune thrombocytopenia in children. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1981 Summer;3(2):213–219. doi: 10.1097/00043426-198100320-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Fotino M., Gibofsky A., Winchester R. J. Association of HLA-DRw2 with autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1085–1088. doi: 10.1172/JCI109378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Powers P. J., Carter C. J. A prospective study of the usefulness of the measurement of platelet-associated IgG for the diagnosis of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1982 Oct;60(4):1050–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernoff M., Malan E. Platelet antibody levels do not correlate with response to therapy in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1983 Apr;53(4):559–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb07307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
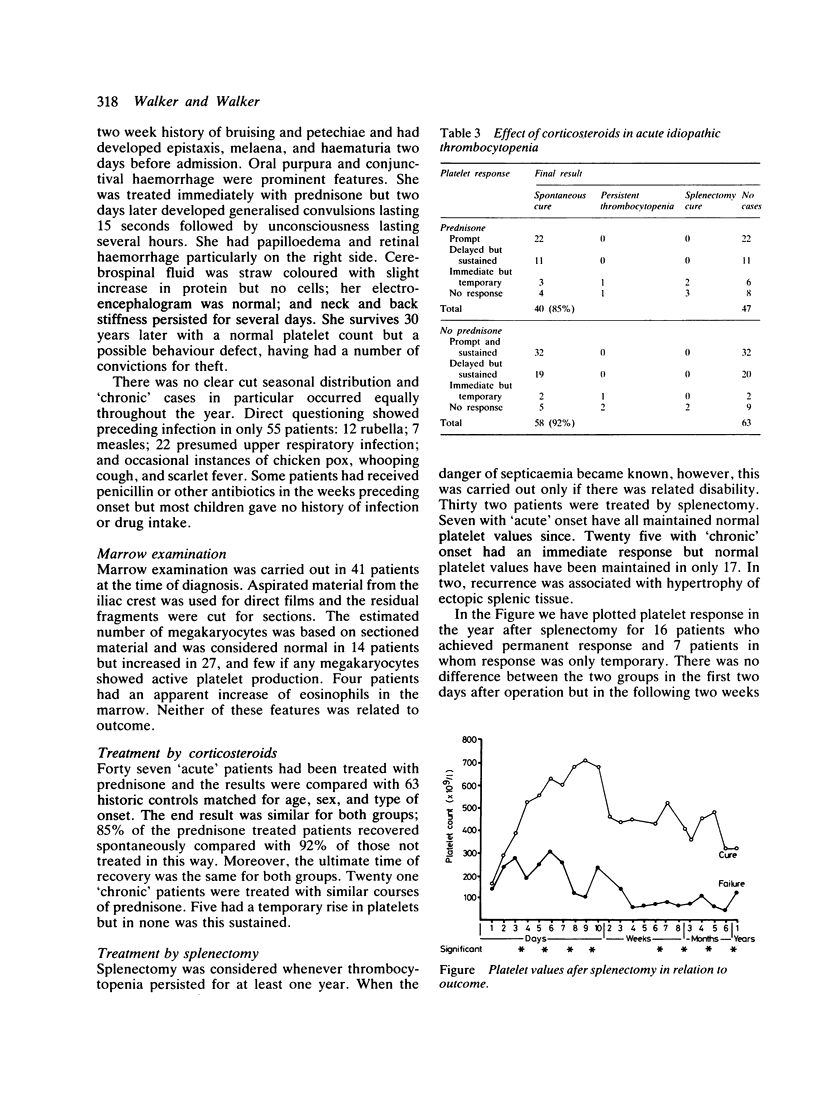
- Lilleyman J. S. Management of childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1983 May;54(1):11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusher J. M., Iyer R. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in children. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1977 Jan;3(3):175–199. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1086136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1981 May 7;304(19):1135–1147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198105073041904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R. Immune thrombocytopenia. Clin Haematol. 1983 Feb;12(1):69–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R., Tani P., Mason D. The demonstration of antibody binding to platelet-associated antigens in patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):993–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori P. G., Mancuso G., del Principe D., Duse M., Miniero R., Tovo R., Bardare M., Carnelli V., de Mattia D. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenia treated with immunoglobulin. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Nov;58(11):851–855. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.11.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak R., Wilimas J. Plasmapheresis in catastrophic complications of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Pediatr. 1978 Mar;92(3):434–436. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80439-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozsoylu S., Allahverdi H., Lâlei Y., Pirnar A. Platelet survival in childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in remission. J Pediatr. 1976 Sep;89(3):388–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80533-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman N. R., Marder V. J., Weinrach R. S. Similarities between known antiplatelet antibodies and the factor responsible for thrombocytopenia in idiopathic purpura. Physiologic, serologic and isotopic studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun 30;124(2):499–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb18984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomar R. H., Stuart M. J. Predicting acute vs chronic childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Dis Child. 1981 May;135(5):446–449. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1981.02130290044016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent R. J., Clancy R. L., Danis V., Basten A. Immune complexes in thrombocytopenic patients: cause or effect? Br J Haematol. 1980 Apr;44(4):645–654. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb08719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER J. H., WALKER W. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1961 Dec;36:649–657. doi: 10.1136/adc.36.190.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. Splenectomy in childhood: a review in England and Wales, 1960-4. Br J Surg. 1976 Jan;63(1):36–43. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerella J. T., Martin L. W., Lampkin B. C. Emergency splenectomy for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1978 Jun;13(3):243–246. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(78)80394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuelzer W. W., Lusher J. M. Childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Mar;131(3):360–362. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120160114019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


