Abstract
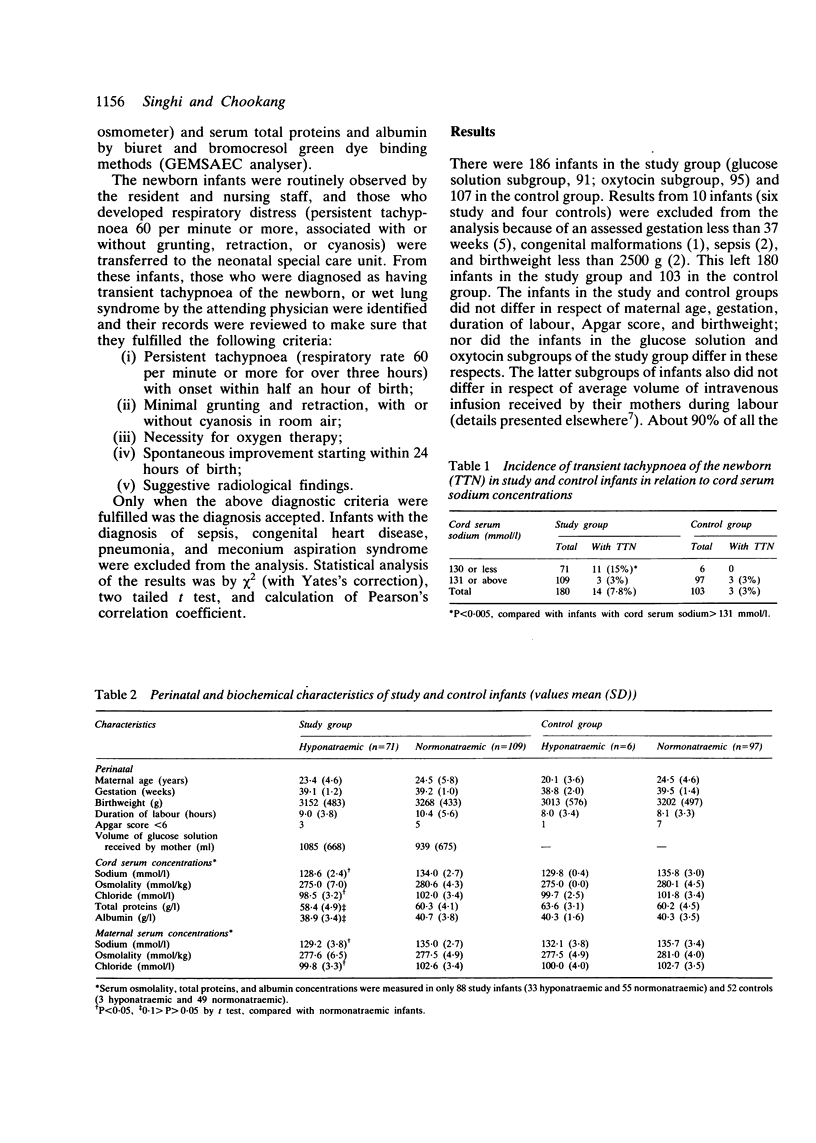
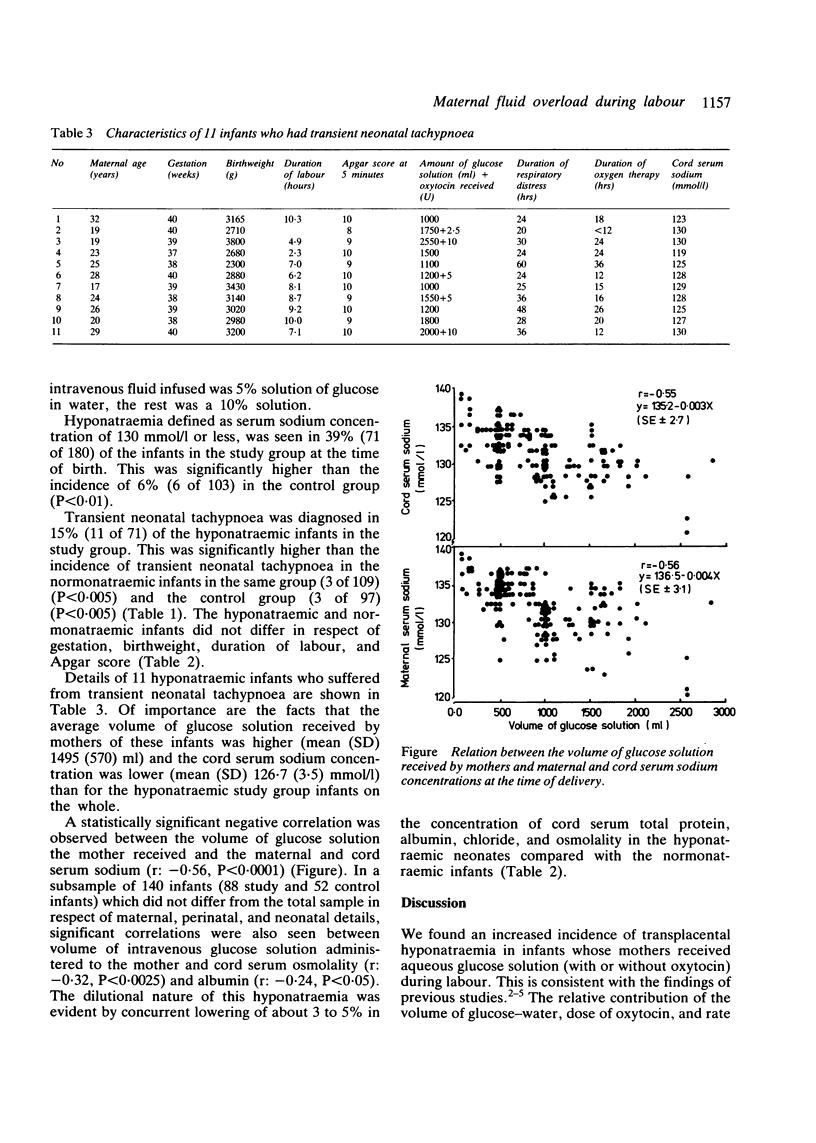
Cord serum sodium concentrations in two groups of vaginally delivered, singleton term infants were correlated with the incidence of transient neonatal tachypnoea. Hyponatraemia (cord serum sodium less than 130 mmol/l) was seen in 71 of 180 (39%) infants born to mothers who received an intravenous infusion of aqueous glucose solution during labour (study group) compared with 6 of 103 (6%) infants born to mothers who did not receive any intravenous fluid treatment (controls). The incidence of transient neonatal tachypnoea was 4.5 times higher for hyponatraemic infants in the study group (11 of 71) than for normonatraemic infants in the same group (3 of 109) and the control group (3 of 97). The difference was not attributable to other perinatal or neonatal characteristics. Our findings suggest an increased risk of transient neonatal tachypnoea in term infants who suffer from transplacental hyponatraemia after their mothers received intrapartum infusion of aqueous glucose solutions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avery M. E., Gatewood O. B., Brumley G. Transient tachypnea of newborn. Possible delayed resorption of fluid at birth. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Apr;111(4):380–385. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090070078010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlenburg G. W., Burnell R. H., Braybrook R. The relation between cord serum sodium levels in newborn infants and maternal intravenous therapy during labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1980 Jun;87(6):519–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1980.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys P. W., Normand I. C., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Pulmonary lymph flow and the uptake of liquid from the lungs of the lamb at the start of breathing. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):1–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kero P., Korvenranta H., Alamaakala P., Selänne P., Kiilholma P., Välimäki I. Colloid osmotic pressure of cord blood in relation to neonatal outcome and mode of delivery. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1983;305:88–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhi S., Choo Kang E., Hall J. S. Hazards of maternal hydration with 5% dextrose. Lancet. 1982 Aug 7;2(8293):335–336. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhi S., Singh M. Transplacental asymptomatic hyponatremia following oxytocin infusion during labour. Indian J Med Res. 1979 Jul;70:55–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. A., Mann N. P., Smith M. L., Woolfson A. M., Benson S. The effect of intravenous therapy during labour on maternal and cord serum sodium levels. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 May;88(5):480–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1981.tb01020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnow-Mordi W. O., Shaw J. C., Liu D., Gardner D. A., Flynn F. V. Iatrogenic hyponatraemia of the newborn due to maternal fluid overload: a prospective study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Sep 5;283(6292):639–642. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6292.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesenberg R. L., Graven S. N., McCabe E. B. Radiological findings in wet-lung disease. Radiology. 1971 Jan;98(1):69–74. doi: 10.1148/98.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


