Abstract
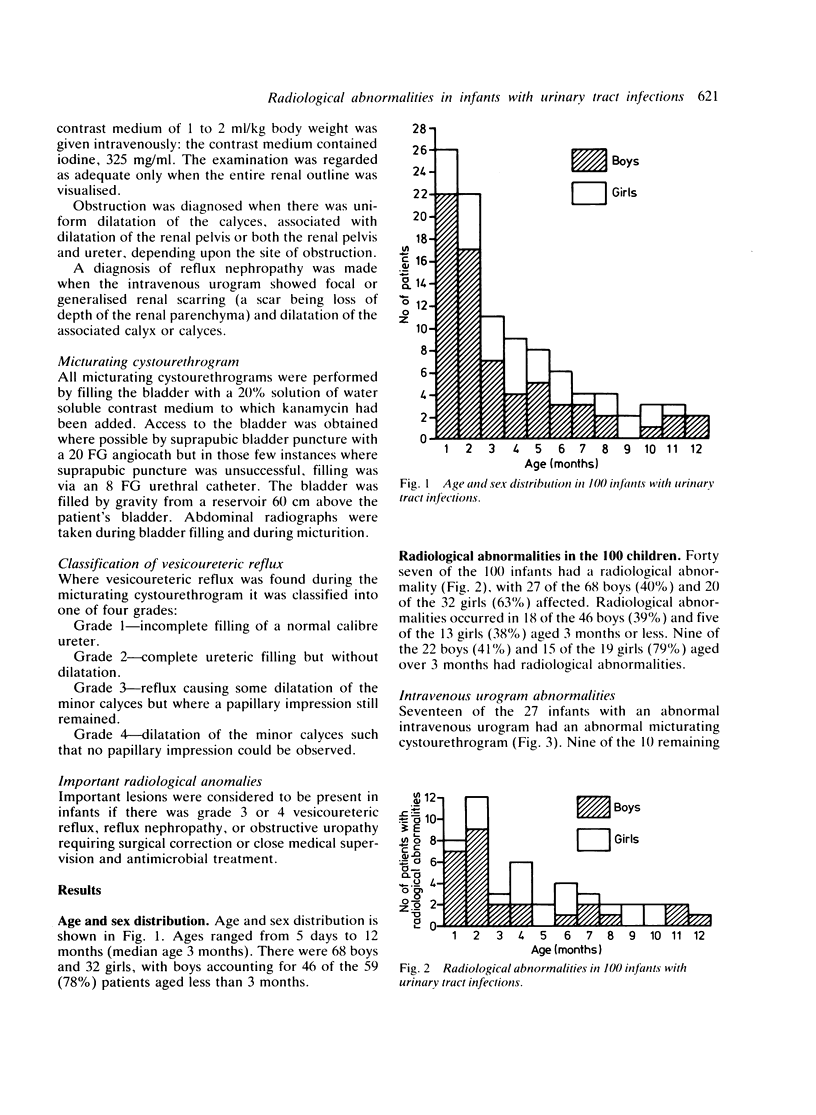
An intravenous urogram and micturating cystourethrogram were carried out in 100 infants presenting with documented urinary tract infections. Ninety three cases were identified by suprapubic aspiration and 7 by culture of two voided urine samples containing greater than 100 X 10(6) organisms per litre. The urinary tract abnormalities were analysed in respect of their clinical importance, patient's age, sex, and prematurity (in the 10 preterm infants). Radiological abnormalities were found in 47% of the infants (40% of boys; 63% of girls). Twenty nine per cent of the infants had a urinary tract abnormality regarded as clinically important--namely grade 3 or 4 vesicoureteric reflux, reflux nephropathy, or obstructive lesions requiring surgery. Six of the 10 preterm infants had radiological abnormalities. Spontaneous resolution or improvement occurred within 6 months of birth in three of the four preterm infants with severe vesicoureteric reflux.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Rolleston G. L., Shannon F. T., Utley W. L. Relationship of infantile vesicoureteric reflux to renal damage. Br Med J. 1970 Feb 21;1(5694):460–463. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5694.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


