Abstract
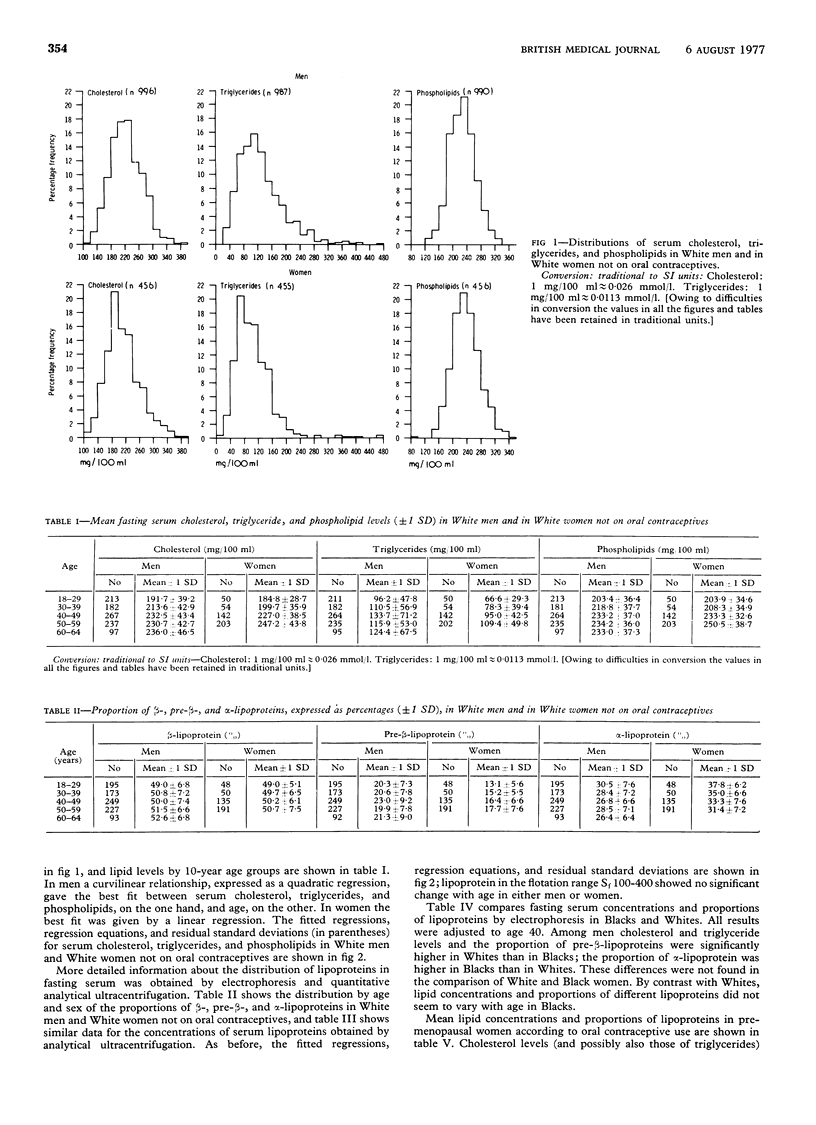
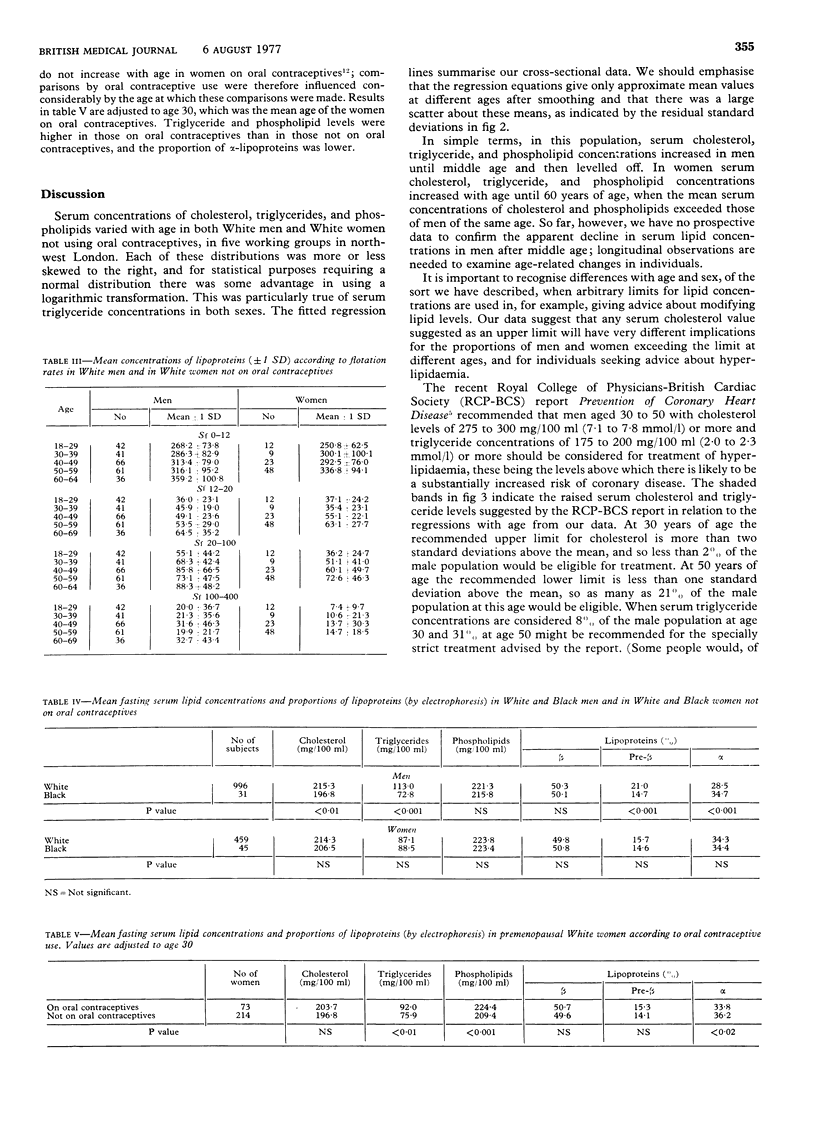
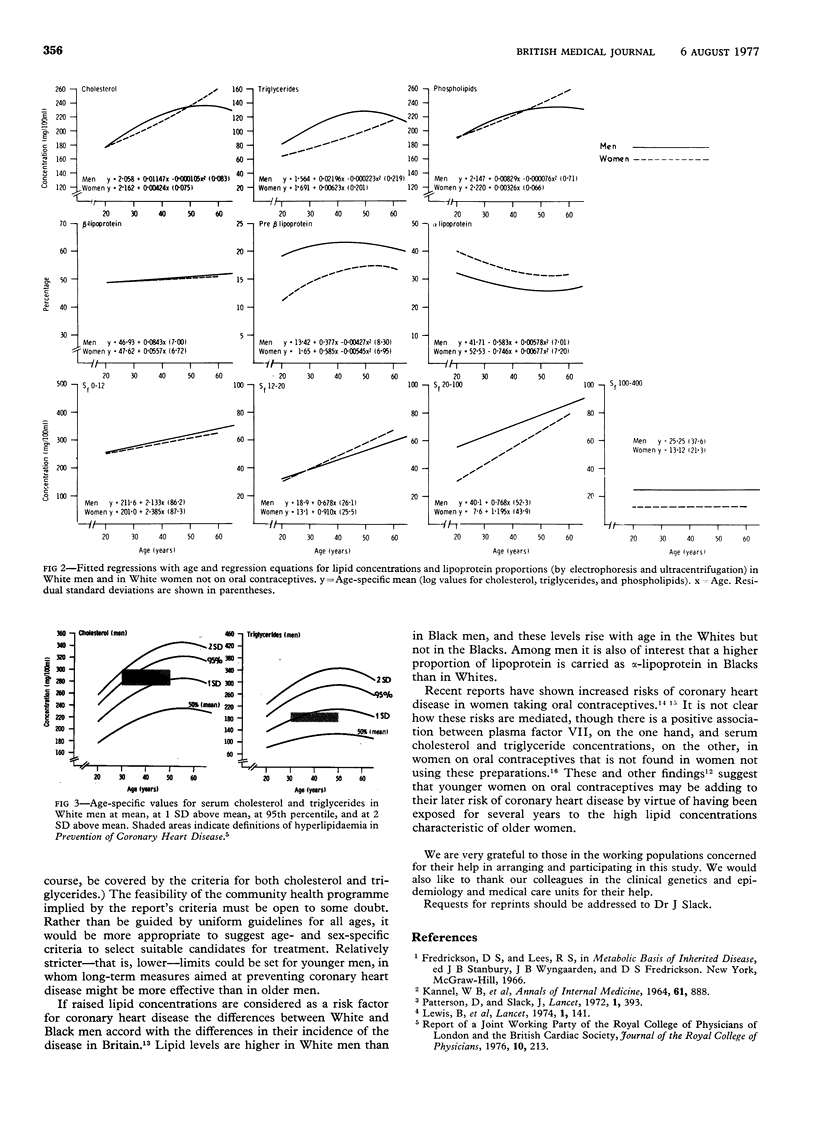
Serum lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in men and women vary with age, and so-called "normal" limits should take account of this. Serum cholesterol, triglyceride, and phospholipid concentrations were measured in 1027 men and 577 women in five working populations in north-west London, and lipoprotein electrophoresis and quantitative analyses of lipoprotein concentrations were also performed. In men the best fit between serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and phospholipids, on the one hand, and age, on the other, was given by a curvilinear relationship expressed as a quadratic regression. In women the best fit was given by a linear regression. White men had higher serum cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations than Black men, and these differences were reflected in the distributions of the lipoproteins. There were no differences between values in White and Black women. Young women on oral contraceptives had lipid concentrations similar to those of older women not on these preparations. These data suggest that the adoption of concentrations of serum cholesterol (275-300 mg/100 ml (7-1-7-8 mmol/l) and triglycerides (175-200 mg/100 ml (2-0--2-3 mmol/l) recommended by a recent report on the prevention of coronary disease as limits above which special attention should be given to the management of hyperlipidaemia could result in as few as 2% of younger men or as many as 31% of older men being selected for treatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANNEL W. B., DAWBER T. R., FRIEDMAN G. D., GLENNON W. E., MCNAMARA P. M. RISK FACTORS IN CORONARY HEART DISEASE. AN EVALUATION OF SEVERAL SERUM LIPIDS AS PREDICTORS OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE; THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Nov;61:888–899. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-5-888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Chait A., Wootton I. D., Oakley C. M., Krikler D. M., Sigurdsson G., February A., Maurer B., Birkhead J. Frequency of risk factors for ischaemic heart-disease in a healthy British population. With particular reference to serum-lipoprotein levels. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):141–146. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. I., Doll R., Thorogood M., Vessey M. P., Waters W. E. Risk factors for myocardial infarction in young women. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1976 Jun;30(2):94–100. doi: 10.1136/jech.30.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. I., Inman W. H., Thorogood M. Oral contraceptive use in older women and fatal myocardial infarction. Br Med J. 1976 Aug 21;2(6033):445–447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6033.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Slack J. Lipid abnormalities in male and female survivors of myocardial infarction and their first-degree relatives. Lancet. 1972 Feb 19;1(7747):393–399. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90853-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedoe H. T., Clayton D., Morris J. N., Brigden W., McDonald L. Coronary heart-attacks in East London. Lancet. 1975 Nov 1;2(7940):833–838. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HANDEL E., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Micromethod for the direct determination of serum triglycerides. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jul;50(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


