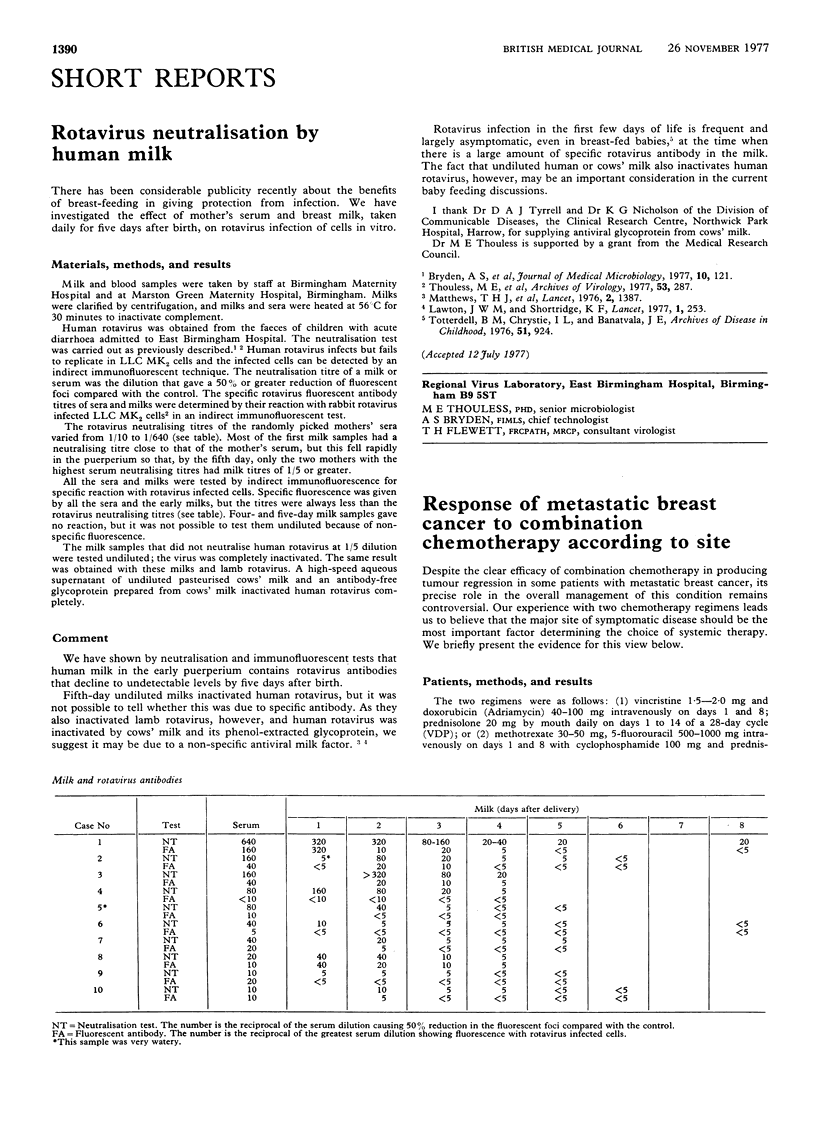
Full text
PDFPage 1390
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lawton J. W., Shortridge K. F. Protective factors in human breast milk and colostrum. Lancet. 1977 Jan 29;1(8005):253–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews T. H., Nair C. D., Lawrence M. K., Tyrrell D. A. Antiviral activity in milk of possible clinical importance. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1387–1389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91922-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralization. Arch Virol. 1977;53(4):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01315627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totterdell B. M., Chrystie I. L., Banatvala J. E. Rotavirus infections in a maternity unit. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Dec;51(12):924–928. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.12.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


