Abstract
The increasing number of children admitted to this hospital with poisoning by tricyclic antidepressants is causing concern. Of 60 children admitted between January 1966 and July 1973, half were admitted in the last 18 months. In 60% of these patients the tricyclic compounds had been prescribed for nocturnal enuresis. One child aged 2 years and 4 months died of imipramine poisoning. It is imperative that all children with poisoning by tricyclic compounds, irrespective of the dosage, are admitted to hospital for continuous cardiac monitoring. Cardiac arrhythmias induced in children by amitriptyline and imipramine are prominent and dangerous.
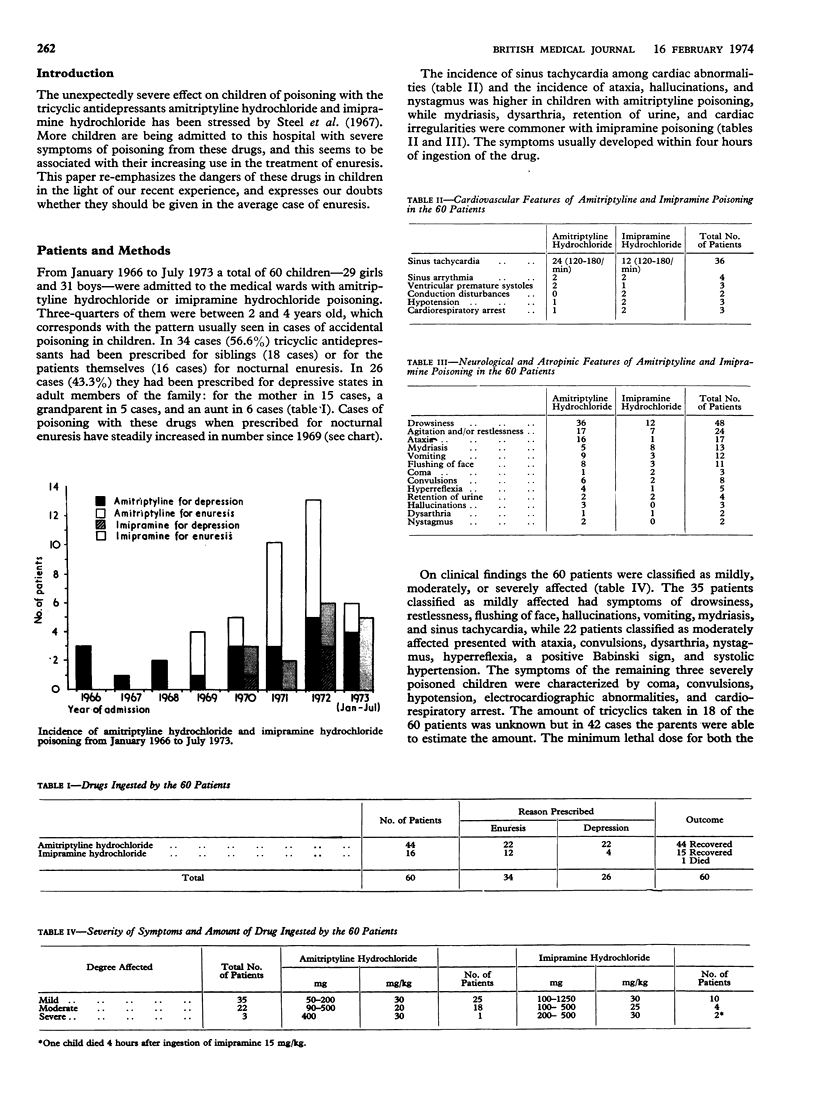
In the earlier years of this survey the antidepressants taken by children had usually been prescribed for adults, but recently they have been increasingly prescribed as a treatment for enuresis in children themselves. Medicine for a trivial complaint is unlikely to be regarded by parents as potentially dangerous and practitioners should therefore warn them accordingly; if, indeed, the transient effect of these potentially dangerous drugs upon the average case of bed-wetting in childhood can be justified.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown T. C., Dwyer M. E., Stocks J. G. Antidepressant overdosage in children--a new menace. Med J Aust. 1971 Oct 23;2(17):848–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN S. J., GUILFOYLE F. M. IMIPRAMINE (TOFRANIL) IN THE CONTROL OF ENURESIS. Am J Dis Child. 1965 May;109:412–415. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1965.02090020414006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser M. S. Nocturnal enuresis. Practitioner. 1972 Feb;208(244):203–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardash S., Hillman E. S., Werry J. Efficacy of imipramine in childhood enuresis: a double-blind control study with placebo. Can Med Assoc J. 1968 Aug 10;99(6):263–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolvin I., Taunch J., Currah J., Garside R. F., Nolan J., Shaw W. B. Enuresis: a descriptive analysis and a controlled trial. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1972 Dec;14(6):715–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb03314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. I. Imipramine pamoate in the treatment of childhood enuresis. A double-blind study. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Jul;122(1):42–47. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02110010078013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. Amitriptyline and imipramine poisoning. Lancet. 1965 Oct 23;2(7417):850–851. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNSHINE P., YAFFE S. J. AMITRIPTYLINE POISONING. CLINICAL AND PATHOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN A FATAL CASE. Am J Dis Child. 1963 Nov;106:501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel C. M., O'Duffy J., Brown S. S. Clinical effects and treatment of imipramine and amitriptyline poisoning in children. Br Med J. 1967 Sep 9;3(5566):663–667. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5566.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. A., Galloway W. H. Treatment of severe imipramine poisoning. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Jun;46(247):353–355. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.247.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


