Abstract
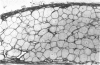
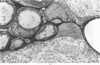
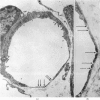
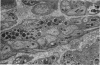
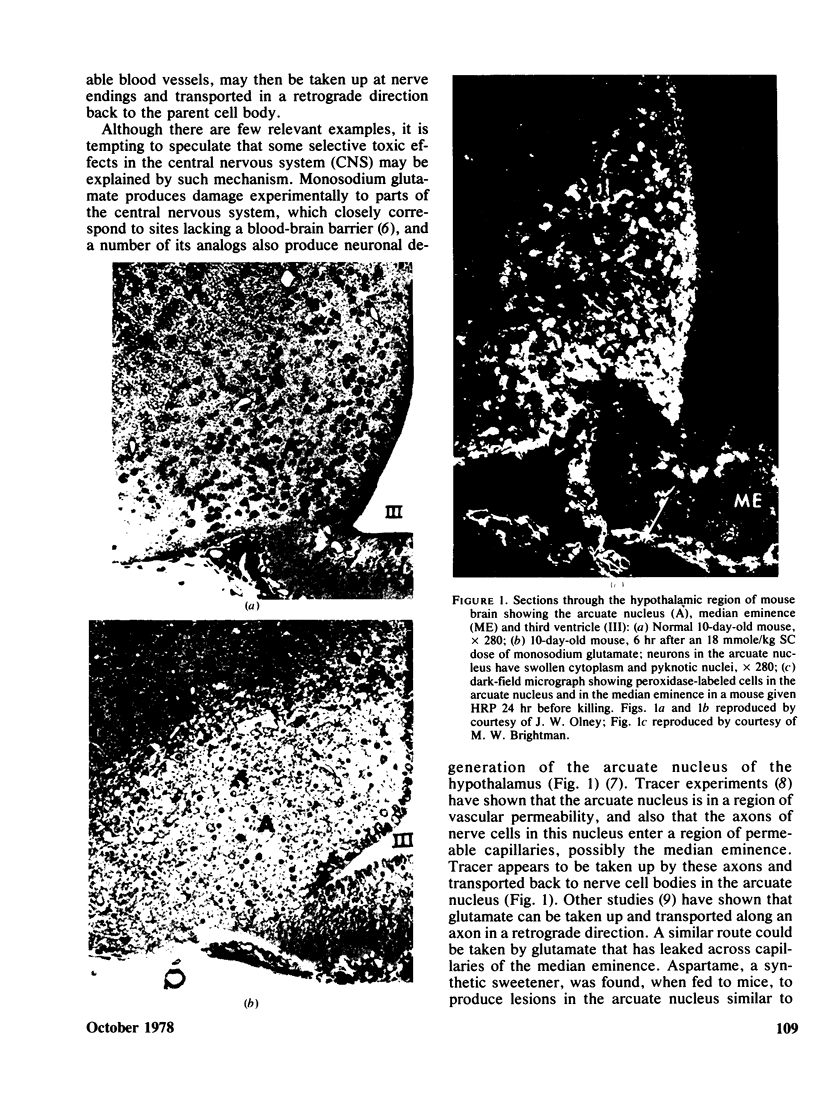
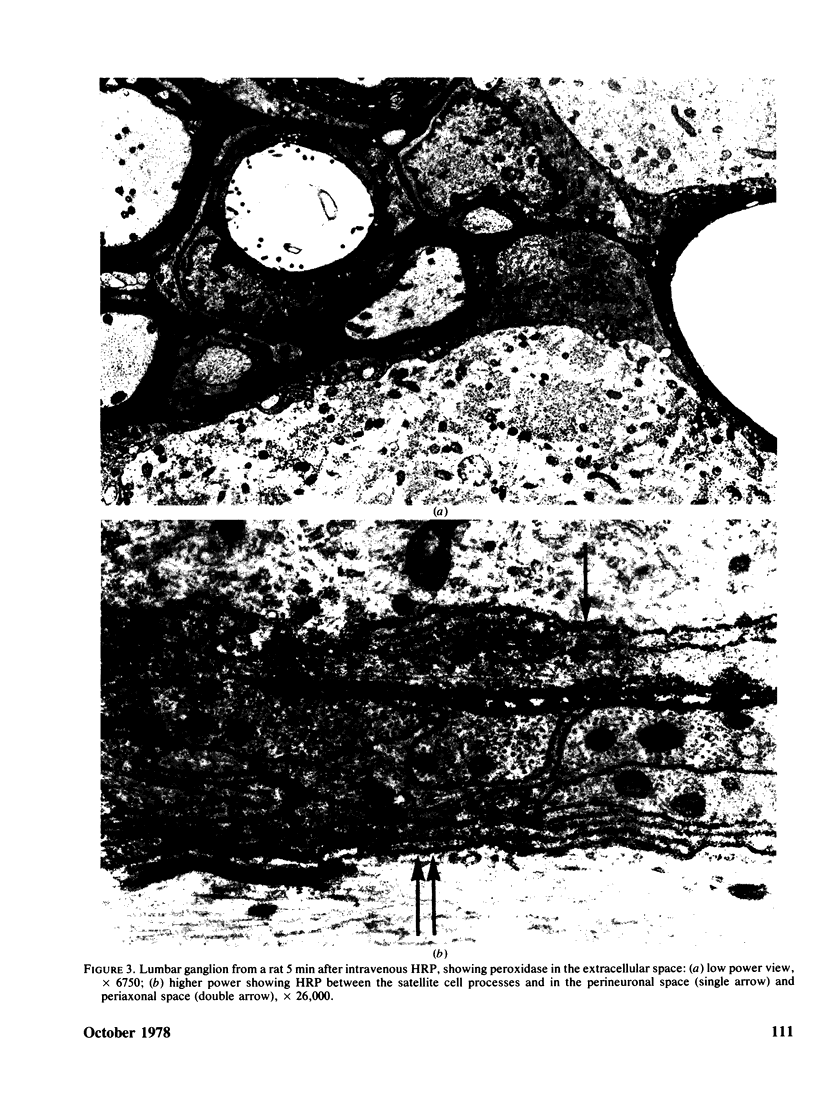
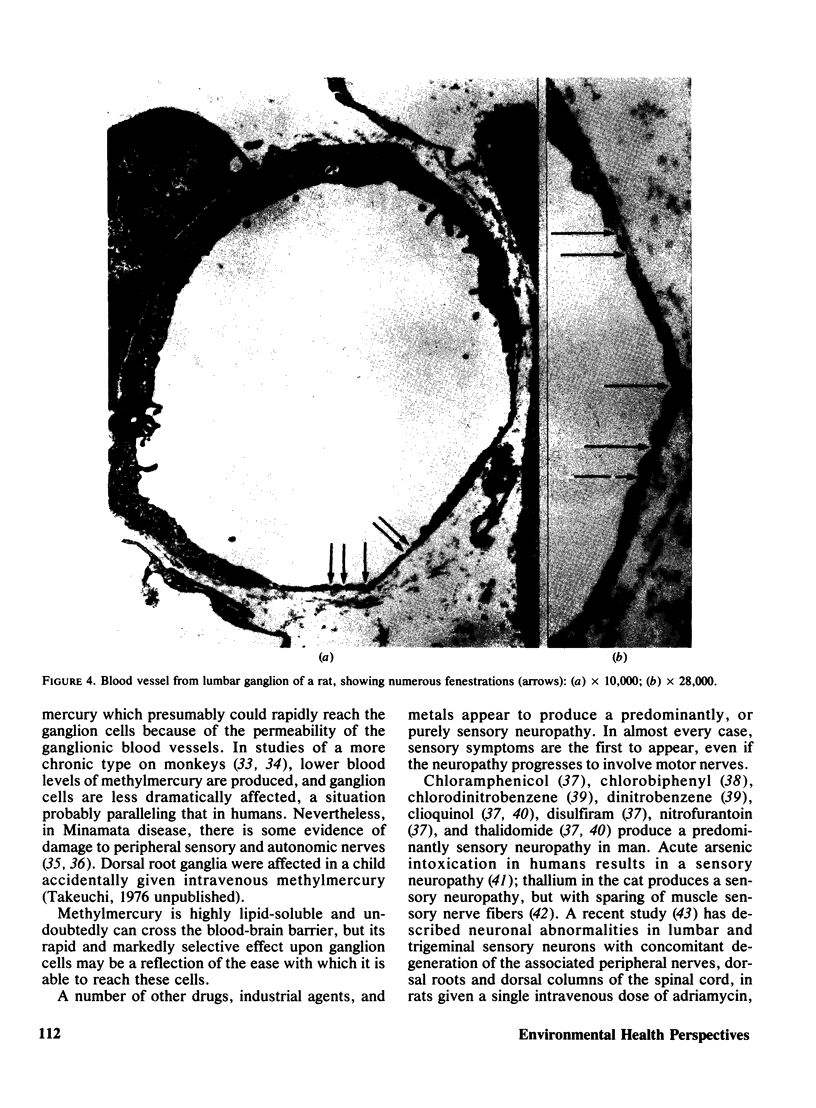
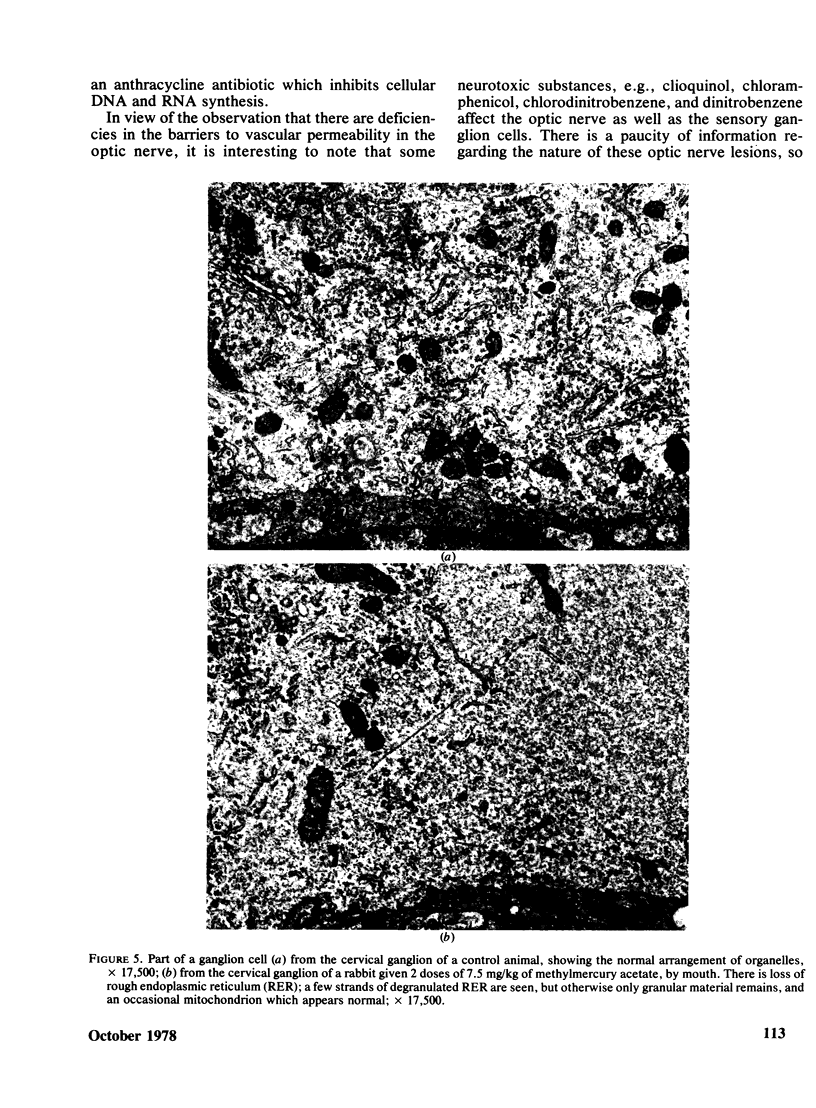
Neurotoxic substances affect the nervous system in a selective manner. One possible basis for this selectivity is blood vessel permeability. In general, the central nervous system and the peripheral nerve trunks have impermeable blood vessels, but in certain parts the capillaries are "leaky," allowing the passage of a plasma filtrate. Intravenously injected protein tracers rapidly reach nerve cells in these regions, with the implication that these nerve cells are also readily accessible to circulating neurotoxic substances. Some examples of neurotoxicity in the central nervous system show a selectivity that could be due to capillary permeability. In experimental methylmercury poisoning, cranial nerve V and sensory dorsal root ganglia, which lie in regions of vascular permeability, are particularly susceptible. A number of drug and chemically induced neuropathies are predominantly sensory, and may be due, directly or indirectly, to the accessibility of neurotoxic substances to sensory neurons. Examination of areas of potential vulnerability to circulating toxic substances may be of value in the experimental testing of substances for neurotoxicity, where pharmacological tests may be negative and clinical symptoms difficult to assess.
Full text
PDF


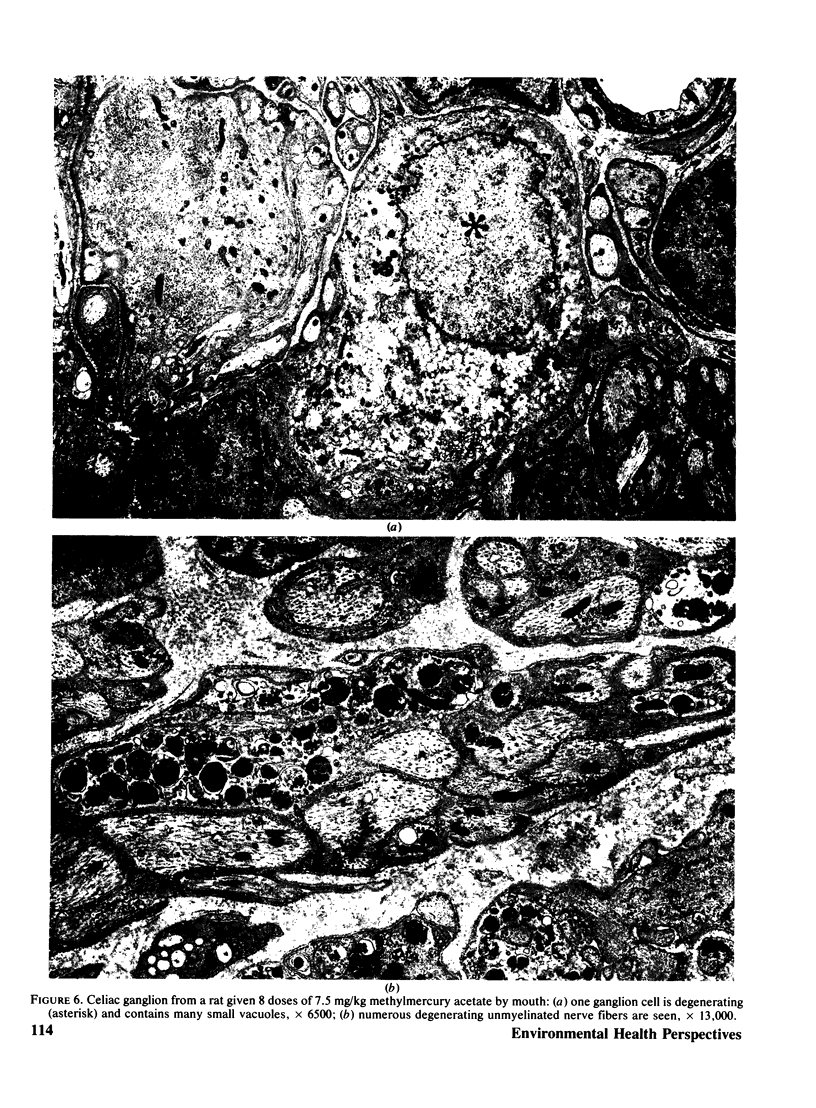


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alder S., Zbinden G. Use of pharmacological screening tests in subacute neurotoxicity studies of isoniazid, pyridoxine HCl and hexachlorophene. Agents Actions. 1973 Nov;3(4):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF01968549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell R. D., Brightman M. W. Entry of peroxidase into neurons of the central and peripheral nervous systems from extracerebral and cerebral blood. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Apr 1;166(3):257–283. doi: 10.1002/cne.901660302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael N., Cavanagh J. B., Rodda R. A. Some effects of methyl mercury salts on the rabbit nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 1975 Aug 11;32(2):115–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00689565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh J. B., Chen F. C. The effects of methyl-mercury-dicyandiamide on the peripheral nerves and spinal cord of rats. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;19(3):208–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00684597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh J. B. Peripheral neuropathy caused by chemical agents. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1973 Nov;2(3):365–417. doi: 10.3109/10408447309082021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. W., Hartmann H. A. Ultrastructural studies of the nervous system after mercury intoxication. I. Pathological changes in the nerve cell bodies. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;20(2):122–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00691129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton K. M. Experimental alkylmercurial poisoning in swine. Lesions in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jan;38(1):75–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garman R. H., Weiss B., Evans H. L. Alkylmercurial encephalopathy in the monkey (Saimiri sciureus and Macaca arctoides): a histopathologic and autoradiographic study. Acta Neuropathol. 1975;32(1):61–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00686067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson M. C., Laties A. M. Ocular localization of sodium fluorescein. Effects of administration in rabbit and monkey. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971 May;85(5):600–passim. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1971.00990050602014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman S. P., Klein R., Talley F. A., Krigman M. R. An ultrastructural study of methylmercury-induced primary sensory neuropathy in the rat. Lab Invest. 1973 Jan;28(1):104–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Tobe M., Kobayashi K., Suzuki S., Kawasaki Y. Long-term toxicity study of methylmercuric chloride in monkeys (first report). Toxicology. 1973 Dec;1(4):361–375. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(73)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. M., Carmichael N., Cavanagh J. B. Ultrastructural changes in the nervous system of rabbits poisoned with methyl mercury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;39(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. M., Macfarlane R. M., Cavanagh J. B. Vascular leakage in the dorsal root ganglia of the rat, studied with horseradish peroxidase. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Sep;29(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. M. Penetration of systemically injected horseradish peroxidase into ganglia and nerves of the autonomic nervous system. J Neurocytol. 1977 Oct;6(5):607–618. doi: 10.1007/BF01205222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkut G. A., Shapira A., Walker R. J. The transport of 14C-labelled material from CNS to and from muscle along a nerve trunk. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1967 Dec;23(3):729–748. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(67)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Quesne P. M., McLeod J. G. Peripheral neuropathy following a single exposure to arsenic. Clincal course in four patients with electrophysiological and histological studies. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Jul;32(3):437–451. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W. Brain damage and oral intake of certain amino acids. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;69:497–506. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3264-0_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Rhee V., Gubareff T. D. Neurotoxic effects of glutamate on mouse area postrema. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 14;120(1):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90506-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson Y. Studies on vascular permeability in peripheral nerves. IV. Distribution of intravenously injected protein tracers in the peripheral nervous system of various species. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;17(2):114–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00687487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson Y. Topographical differences in the vascular permeability of the peripheral nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 1968 Jan 2;10(1):26–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00690507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara I., Yamashita H. An electron microscopic study on the blood-optic nerve and fluid-optic nerve barrier. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1975 Sep 5;196(3):239–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00410035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino Y., Mozai T., Nakao K. Biochemical changes in the brain in rats poisoned with an alkymercury compound, with special reference to the inhibition of protein synthesis in brain cortex slices. J Neurochem. 1966 Nov;13(11):1223–1230. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]