Abstract
A wide variety of behavioral methods has been employed with animals to assess visual changes induced by drugs or toxicants. The methods range from simple to complex, from broad screening devices to narrowly focused techniques. Their relative advantages for the environmental toxicologist are discussed. Manipulation of stimulus values is an essential ingredient in the identification of specific sensory functions. The percentage of correct choices from a discrete-trial, multiple-choice discrimination procedure is to be preferred to measures of response rate, speed or reaction time when experiments require answers about specific visual functions.
Full text
PDF

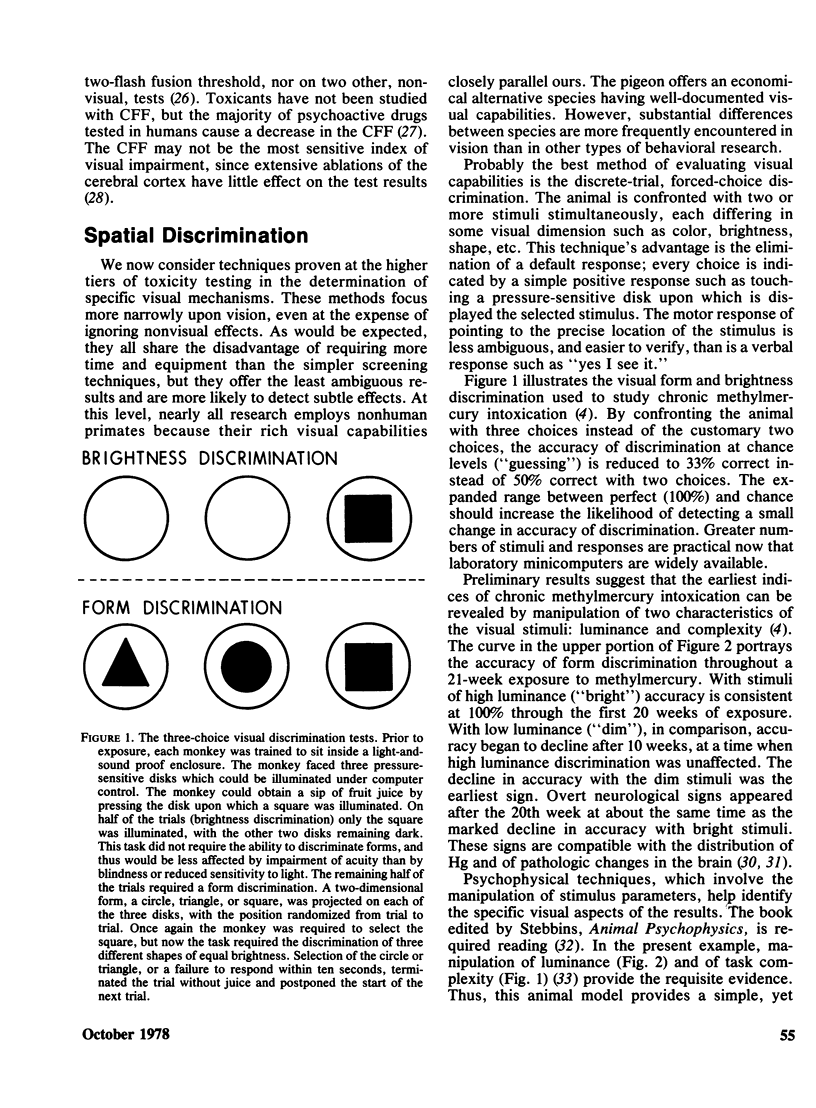
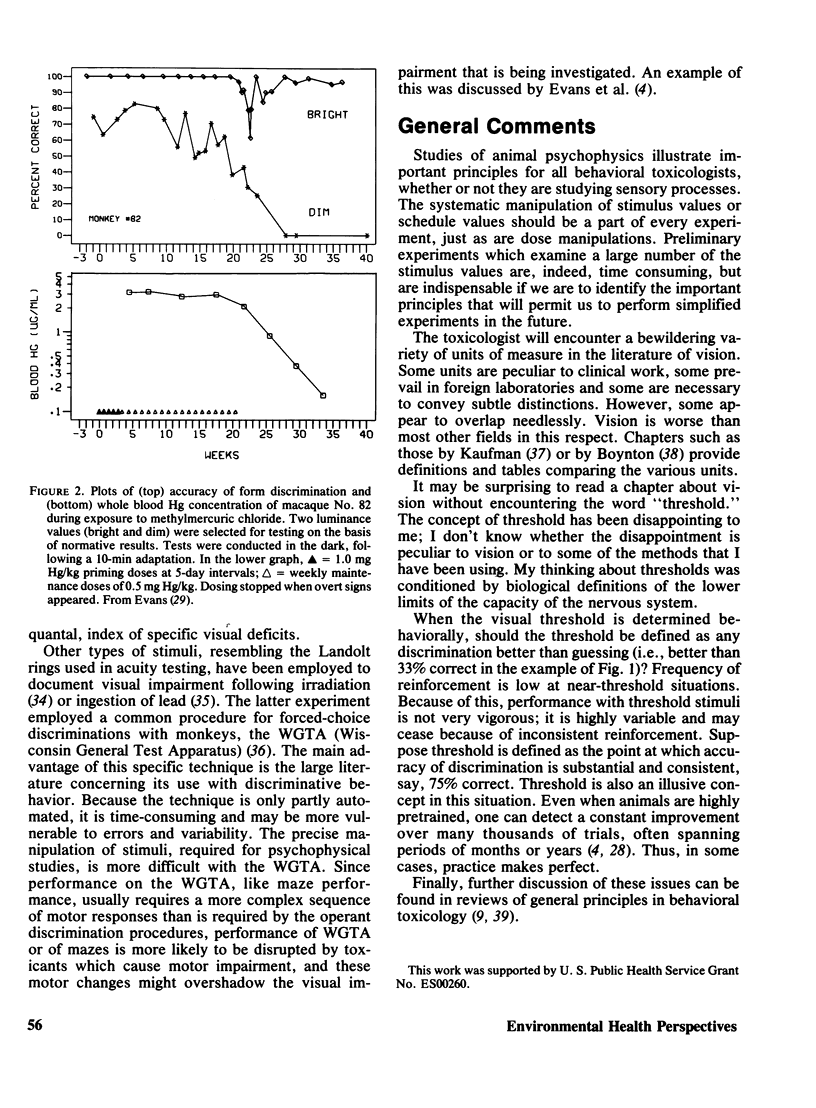

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berlin M., Grant C. A., Hellberg J., Hellström J., Schültz A. Neurotoxicity of methylmercury in squirrel monkeys. Cerebral cortical pathology, interference with scotopic vision, and changes in operant behavior. Arch Environ Health. 1975 Jul;30(7):340–348. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1975.10666717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady K., Herrera Y., Zenick H. Influence of parental lead exposure on subsequent learning ability of offspring. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1975 Jul-Aug;3(4):561–565. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(75)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R. Neonatal lead exposure in the rat: decreased learning as a function of age and blood lead concentrations. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;32(3):628–637. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushnell P. J., Bowman R. E., Allen J. R., Marlar R. J. Scotopic vision deficits in young monkeys exposed to lead. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):333–335. doi: 10.1126/science.403610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson T. L., Van Gelder G. A., Karas G. C., Buck W. B. Slowed learning in lambs prenatally exposed to lead. Arch Environ Health. 1974 Sep;29(3):154–156. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1974.10666554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINSMOOR J. A. The effect of periodic reinforcement of bar-pressing in the presence of a discriminative stimulus. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1951 Aug;44(4):354–361. doi: 10.1037/h0060006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dews P. B. Epistemology of screening for behavioral toxicity. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Oct;26:37–42. doi: 10.1289/ehp.782637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmett E. A., Stetzer L., Taphorn B. Phototoxic keratoconjunctivitis from coal-tar pitch volatiles. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):841–842. doi: 10.1126/science.918667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. L., Garman R. H., Weiss B. Methylmercury: exposure duration and regional distribution as determinants of neurotoxicity in nonhuman primates. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;41(1):15–33. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. L., Laties V. G., Weiss B. Behavioral effects of mercury and methylmercury. Fed Proc. 1975 Aug;34(9):1858–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garman R. H., Weiss B., Evans H. L. Alkylmercurial encephalopathy in the monkey (Saimiri sciureus and Macaca arctoides): a histopathologic and autoradiographic study. Acta Neuropathol. 1975;32(1):61–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00686067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham E. S., Farrer D. N., Carsten A. L., Roizin L. Decrements in the visual acuity of rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) as a delayed effect of occipital cortex irradiation. Radiat Res. 1971 Feb;45(2):373–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON H. M., WITOSLAWSKI J. J., CAMPBELL E. H. REVERSIBLE DISRUPTION OF A WAVELENGTH DISCRIMINATION IN PIGEONS FOLLOWING ADMINISTRATION OF PHENIPRAZINE. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1964 Nov;6:690–695. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(64)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson H. M. Psychophysical evaluation of toxic effects on sensory systems. Fed Proc. 1975 Aug;34(9):1852–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heise G. A. Discrete trial analysis of drug action. Fed Proc. 1975 Aug;34(9):1898–1903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. T., Morse W. H. Determinants of the specificity of behavioral effects of drugs. Ergeb Physiol. 1968;60:1–56. doi: 10.1007/BFb0107250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G. The modification of drug effects on behavior by external discriminative stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Oct;183(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G., Weiss B. Influence of drugs on behavior controlled by internal and external stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jun;152(3):388–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lushei E., Mottet N. K., Shaw C. M. Chronic methylmercury exposure in the monkey (Macaca mulatta). Behavioral test of peripheral vision, signs of neurotoxicity, and blood concentration in relation to dose and time. Arch Environ Health. 1977 May-Jun;32(3):126–131. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1977.10667268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn H., Mitran E., Crockford G. W. An investigation of lead workers for subclinical effects of lead using three performance tests. Ann Occup Hyg. 1976 Dec;19(3-4):239–249. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/19.3-4.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray O. S., Barrett R. J. Behavioral, pharmacological, and biochemical analysis of genetic differences in rats. Behav Biol. 1975 Dec;15(4):391–417. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(75)92184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger D. J., Blackman D. E. Rate-dependent effects of drugs: a review of the literature. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1976 Jan;4(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(76)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobotka T. J., Brodie R. E., Cook M. P. Psychophysiologic effects of early lead exposure. Toxicology. 1975 Nov;5(2):175–191. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(75)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swets J. A. The Relative Operating Characteristic in Psychology: A technique for isolating effects of response bias finds wide use in the study of perception and cognition. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):990–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symmes D. Flicker discrimination by brain-damaged monkeys. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1965 Dec;60(3):470–473. doi: 10.1037/h0022553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye N. C., Sahgal A., Iversen S. D. Benzodiazepines and discrimination behaviour: dissociation of response and sensory factors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1977 Apr 29;52(2):191–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00439109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


