Abstract
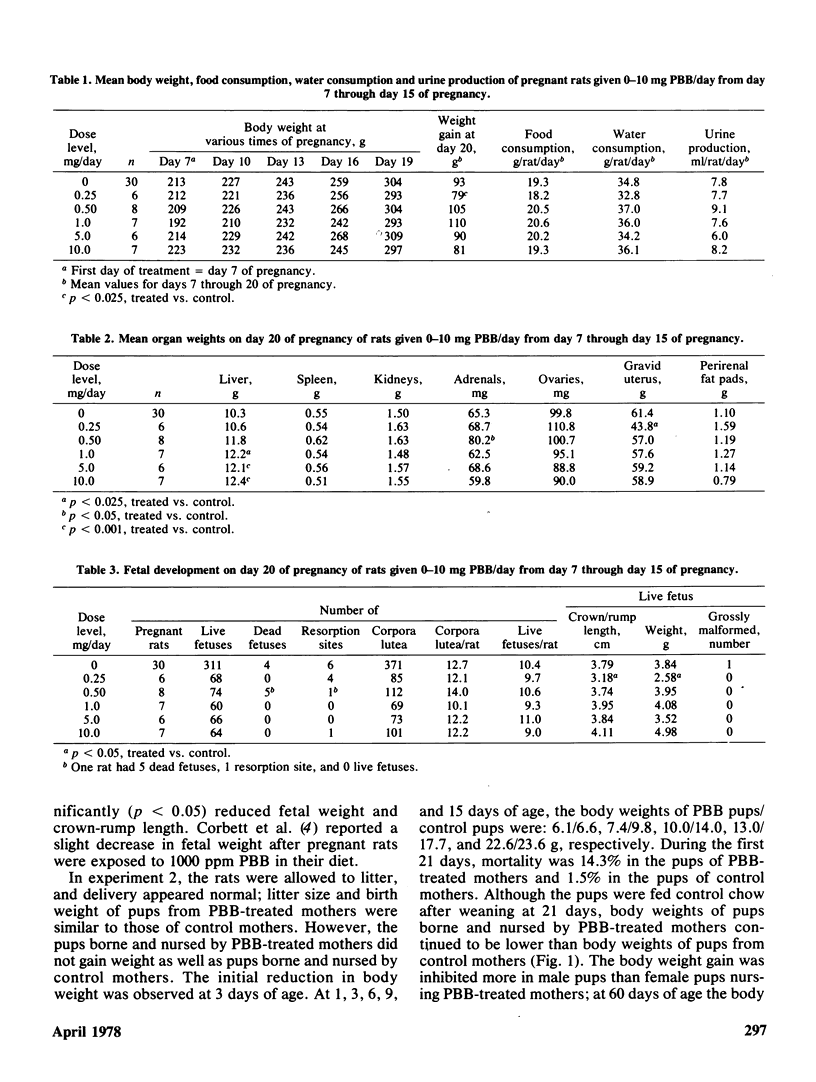
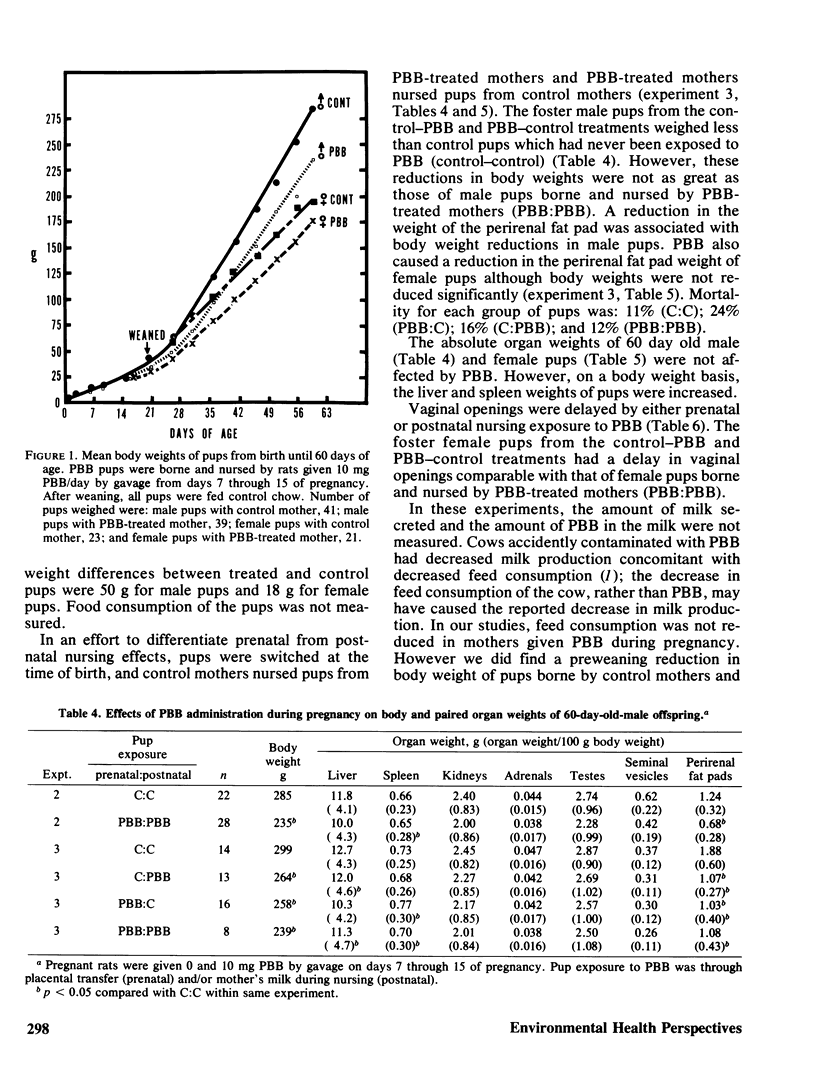
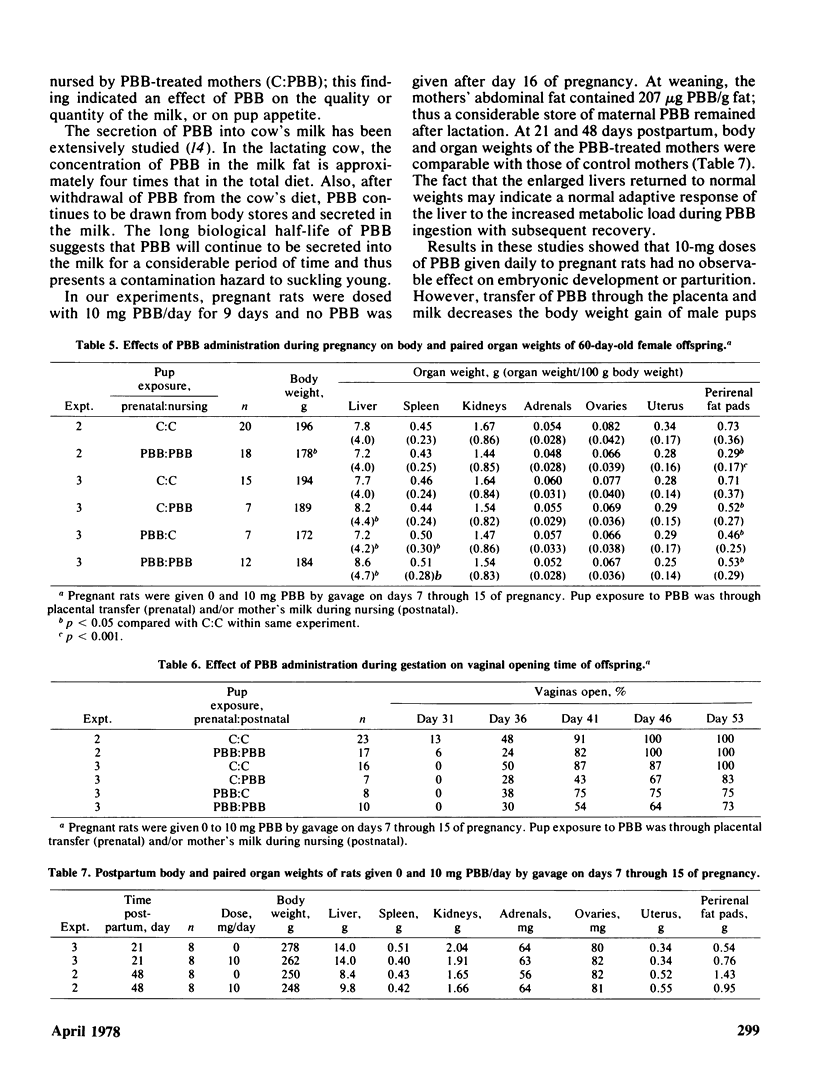
Pregnant Sprague Dawley rats were given 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 mg of a commercial polybrominated biphenyl, FireMaster BP-6 (PBB), in olive oil by gavage each day from days 7 through 15 of pregnancy. Laboratory chow and water were given ad libitum. Treatment with PBB had no significant effect on body weight gain, food and water consumption, and urine production. The mothers were killed on day 20, and the only significant effect observed was an increased liver weight of those given 1, 5, and 10 mg PBB. Spleen, kidney, ovarian, gravid uterine, and perirenal fat pad weights were similar to those of control mothers. PBB had no significant effect on number of live/dead fetuses, crown-rump length or fetal weight. No grossly malformed fetuses were observed in PBB-treated mothers. The effects of PBB transfer from mothers to nursing pups was studied by reciprocal exchange of pups between control mothers and mothers treated with 10 mg PBB. When the pups were 21 days old, they were weaned and fed control chow. The following four combinations of prenatal-postnatal exposure were studied: control-control (C:C); control-PBB (C:PBB); PBB-control (PBB:C); and PBB-PBB. Although the birth weights of pups from PBB-treated mothers were similar to those of the controls, body weights of 60-day-old males exposed prenatally and postnatally (PBB:C, C:PBB, and PBB:PBB) were less (p less than 0.05) than those of the controls (C:C). The weights of the perirenal fat pads of male and female pups exposed to PBB were less (p less than 0.05) than the control. Liver weights, on a body weight basis, were higher in male and female pups exposed to PBB. Vaginal openings were delayed; the percentages of 36-day-old pups with open vaginas were 50 (C:C), 38 (PBB:C), 28 (C:PBB), and 30 (PBB:PBB).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaudoin A. R. Teratogenicity of polybrominated biphenyls in rats. Environ Res. 1977 Aug;14(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(77)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett T. H., Beaudoin A. R., Cornell R. G., Anver M. R., Schumacher R., Endres J., Szwabowska M. Toxicity of polybrominated biphenyls Firemaster BP-6 in rodents. Environ Res. 1975 Dec;10(3):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(75)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. G., Netter K. J., Gibson J. E. Effects of chronic administration of polybrominated biphenyls on parameters associated with hepatic drug metabolism. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;13(1):75–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries G. F., Marrow G. S., Cook R. M. Distribution and kinetics of PBB residues in cattle. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:43–50. doi: 10.1289/ehp.782343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. F., Halbert F. L. A toxic syndrome associated with the feeding of polybrominated biphenyl-contaminated protein concentrate to dairy cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1974 Sep 1;165(5):437–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay K. Polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) environmental contamination in Michigan, 1973-1976. Environ Res. 1977 Feb;13(1):74–93. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(77)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead P. D., Willett L. B., Brumm C. J., Mercer H. D. Pathology of experimentally induced polybrominated biphenyl toxicosis in pregnant heifers. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1977 Feb 1;170(3):307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight S. D., Sanger V. L. Pathologic features of polybrominated biphenyl toxicosis in the rat and guinea pig. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Dec 1;169(11):1231–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


