Abstract
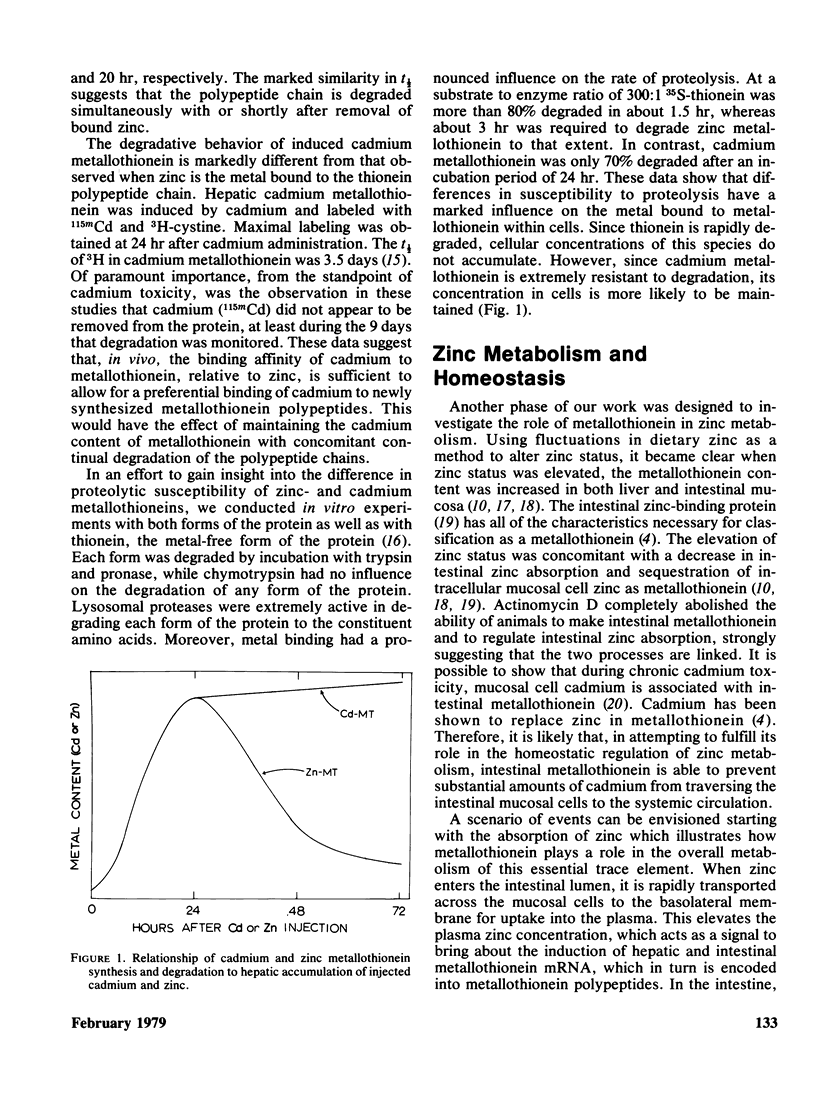
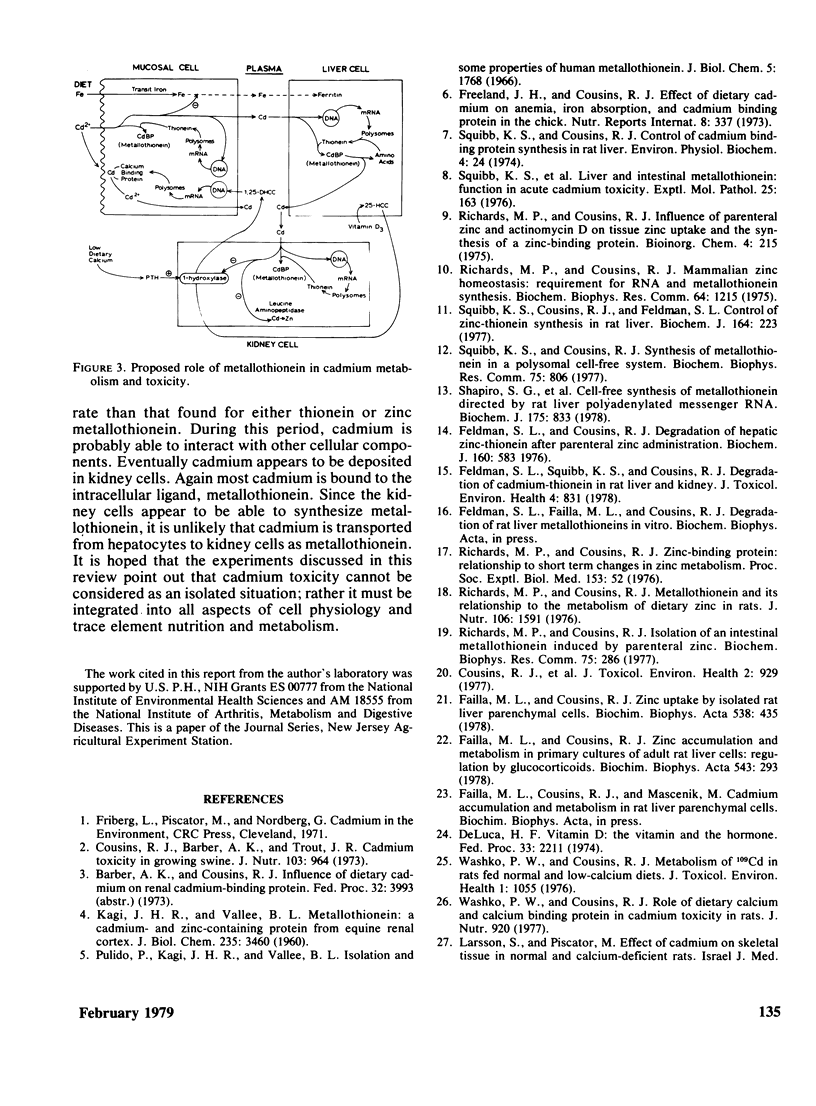
Metallothionein is an integral component of the mechanism that regulates the metabolism of cadmium and zinc. The synthesis of this protein can be "induced" by oral or parenteral administration of either metal. The metallothionein mRNA content of liver polysomes is increased shortly after an influx of small amounts of either metal into hepatocytes. After sufficient amounts of this poly (A+) RNA have been synthesized, there is a concomitant increase in metallothionein biosynthesis and metal binding. Unlike synthesis, the degradation of metallothionein is markedly influenced by the species of metal bound. By using in vivo and in vitro techniques, it has been possible to demonstrate that resistance of metallothionein to degradation follows the order: thionein less than zinc metallothionein less than cadmium metallothionein. Moreover, while the polypeptide chains of cadmium metallothionein are degraded, it appears that liberated cadmium ions are quickly incorporated into nascent chains of thionein. The latter explains why the cadmium content of liver and kidney increases with age and environmental exposure. Since both zinc and cadmium bind to metallothionein, it appears that the binding sites provided by this inducible species provide a locus for interaction between zinc, a nutrient, and cadmium, an environmental contaminant.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar A., Wasserman R. H. Control of calcium absorption and intestinal calcium-binding protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90907-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins R. J., Barber A. K., Trout J. R. Cadmium toxicity in growing swine. J Nutr. 1973 Jul;103(7):964–972. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.7.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins R. J., Squibb K. S., Feldman S. L., de Bari A., Silbon B. L. Biomedical responses of rats to chronic exposure to dietary cadmium fed in ad libitum and equalized regimes. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1977 Mar;2(4):929–943. doi: 10.1080/15287397709529492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D: the vitamin and the hormone. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2211–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Failla M. L., Cousins R. J. Zinc accumulation and metabolism in primary cultures of adult rat liver cells. Regulation by glucocorticoids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 18;543(3):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Failla M. L., Cousins R. J. Zinc uptake by isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 1;538(3):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90405-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. L., Cousins R. J. Degradation of hepatic zinc-thionein after parenteral zinc administration. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):583–588. doi: 10.1042/bj1600583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium- and zinc-containing protein from equine renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3460–3465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentzon R., Larsson S. E. Vitamin D metabolism in adult rats at low and normal calcium intake and the effect of cadmium exposure. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Nov;53(5):439–446. doi: 10.1042/cs0530439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido P., Kägi J. H., Vallee B. L. Isolation and some properties of human metallothionein. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1768–1777. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Influence of parenteral zinc and actinomycin D on tissue zinc uptake and the synthesis of a zinc - binding protein. Bioinorg Chem. 1975 Apr;4(3):215–224. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Isolation of an intestinal metallothionein induced by parenteral zinc. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 21;75(2):286–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Mammalian zinc homeostasis: requirement for RNA and metallothionein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jun 16;64(4):1215–1223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90822-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Metallothionein and its relationship to the metabolism of dietary zinc in rats. J Nutr. 1976 Nov;106(11):1591–1599. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.11.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards M. P., Cousins R. J. Zinc-binding protein: relationship to short term changes in zinc metabolism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Oct;153(1):52–56. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. G., Squibb K. S., Markowitz L. A., Cousins R. J. Cell-free synthesis of metallothionein directed by rat liver polyadenylated messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):833–840. doi: 10.1042/bj1750833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J. Control of cadmium binding protein synthesis in rat liver. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1974;4(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J., Feldman S. L. Control of zinc-thionein synthesis in rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):223–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1640223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J., Silbon B. L., Levin S. Liver and intestinal metallothionein: function in acute cadmium toxicity. Exp Mol Pathol. 1976 Oct;25(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(76)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J. Synthesis of metallothionein in a polysomal cell-free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 11;75(3):806–812. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washko P. W., Cousins R. J. Metabolism of 109Cd in rats fed normal and low-calcium diets. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1976 Jul;1(6):1055–1066. doi: 10.1080/15287397609529408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


