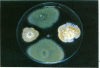
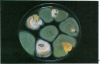
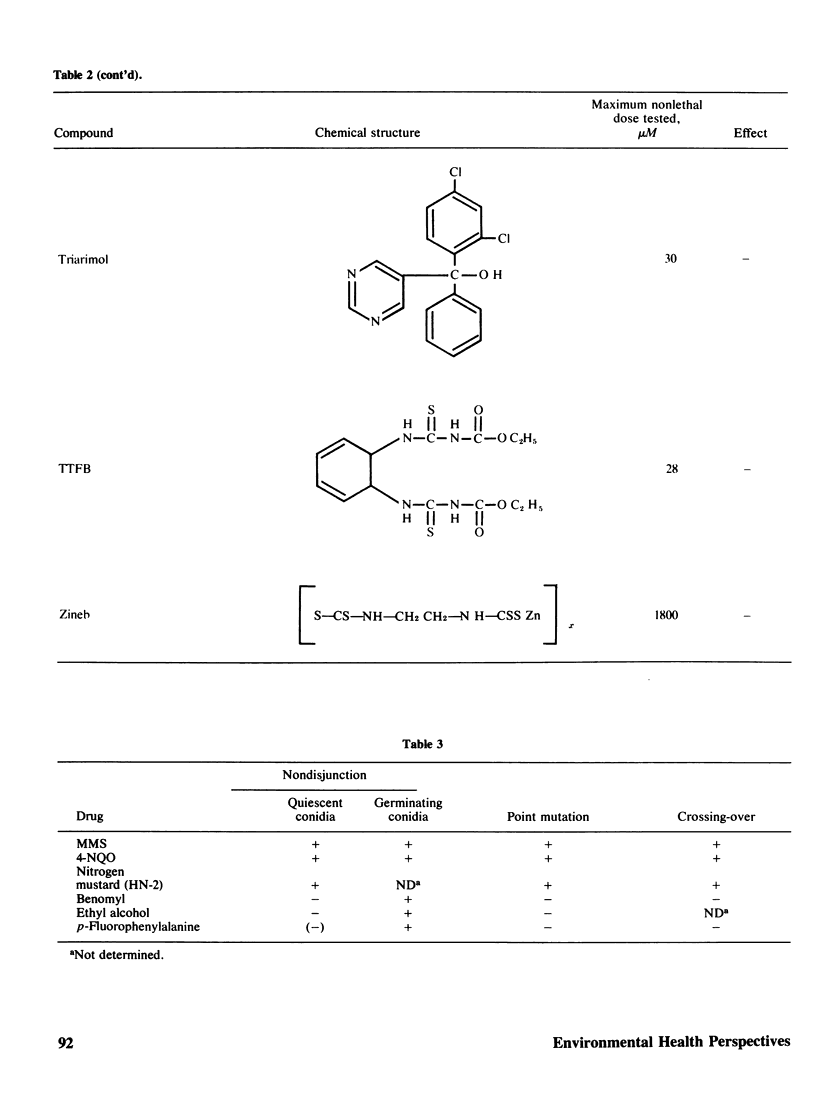
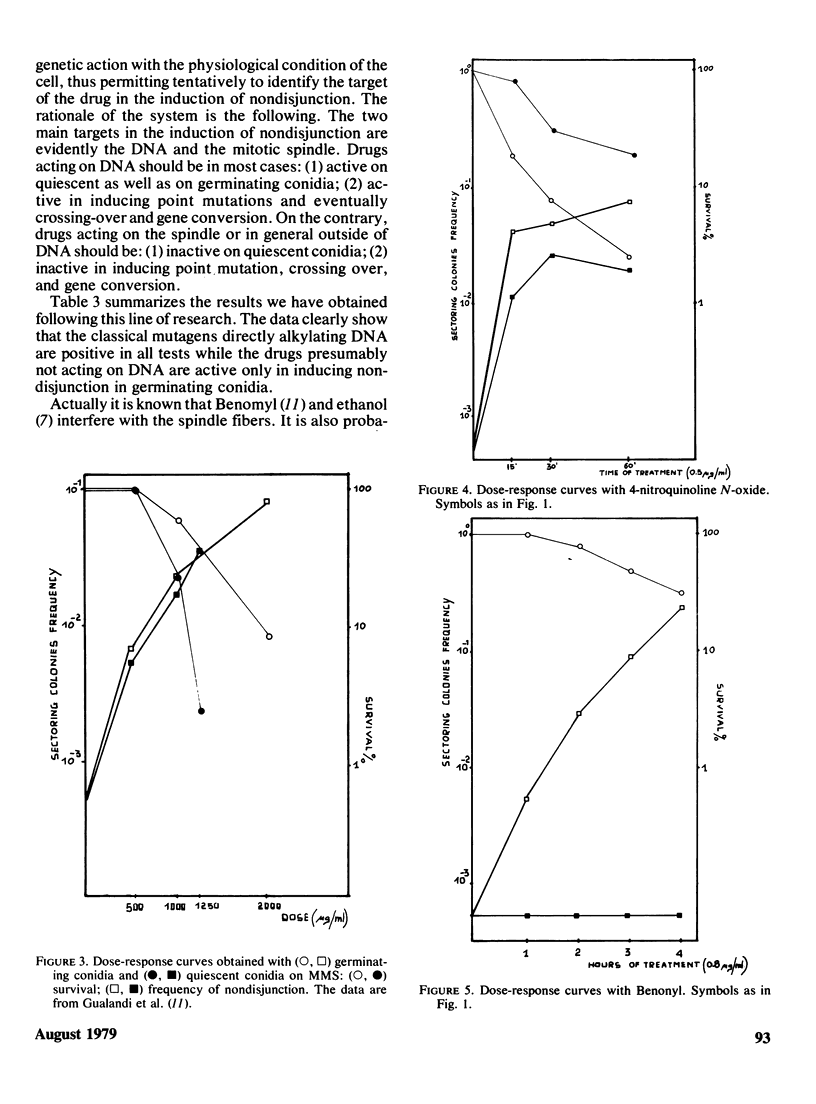
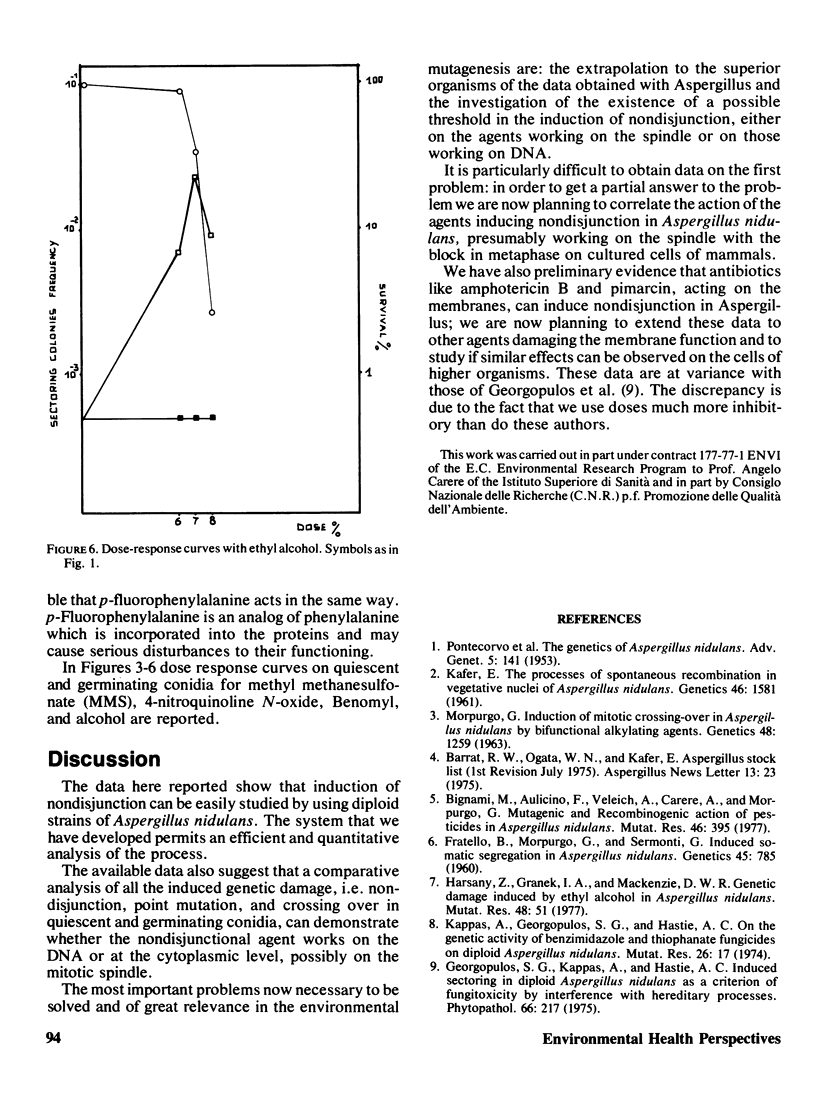
Abstract
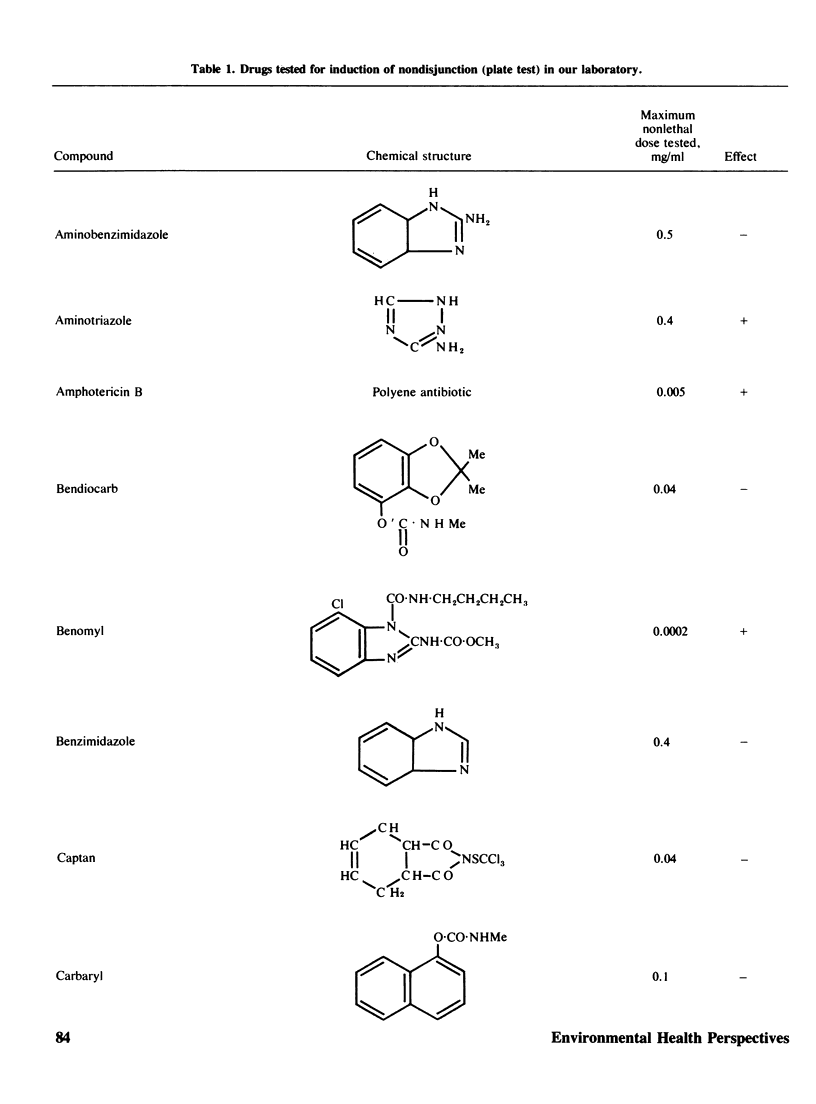
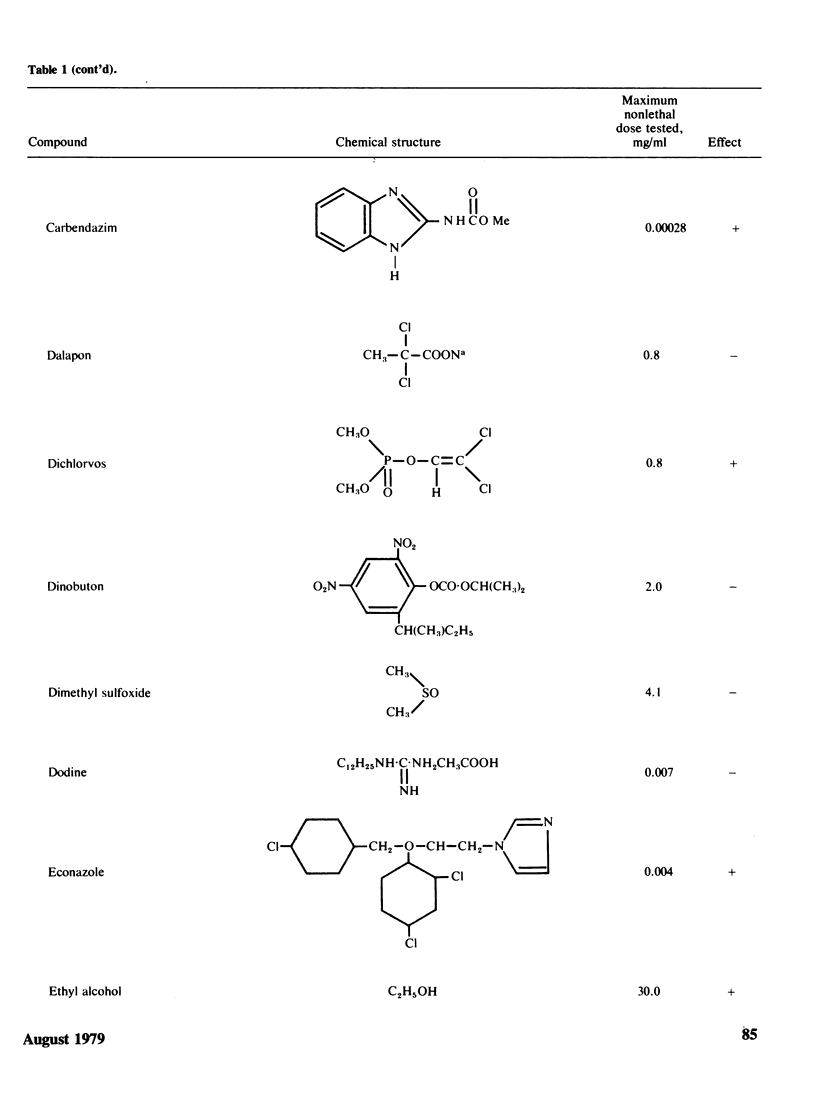
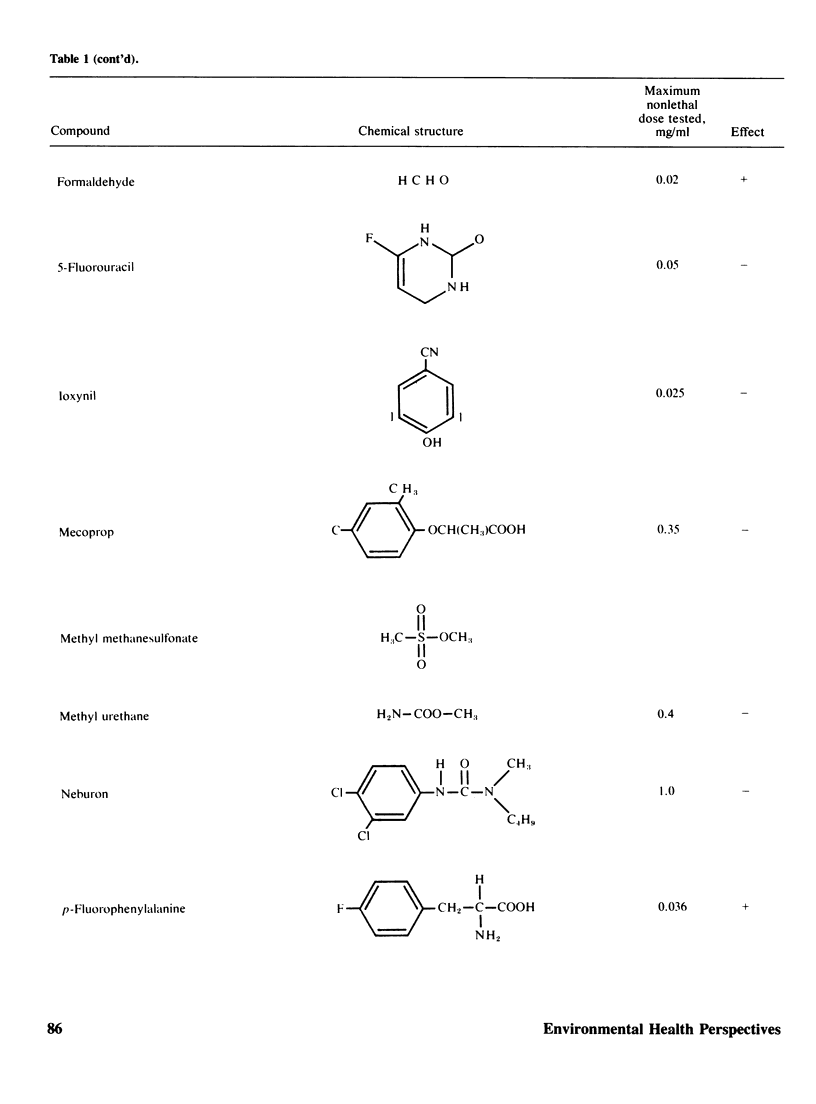
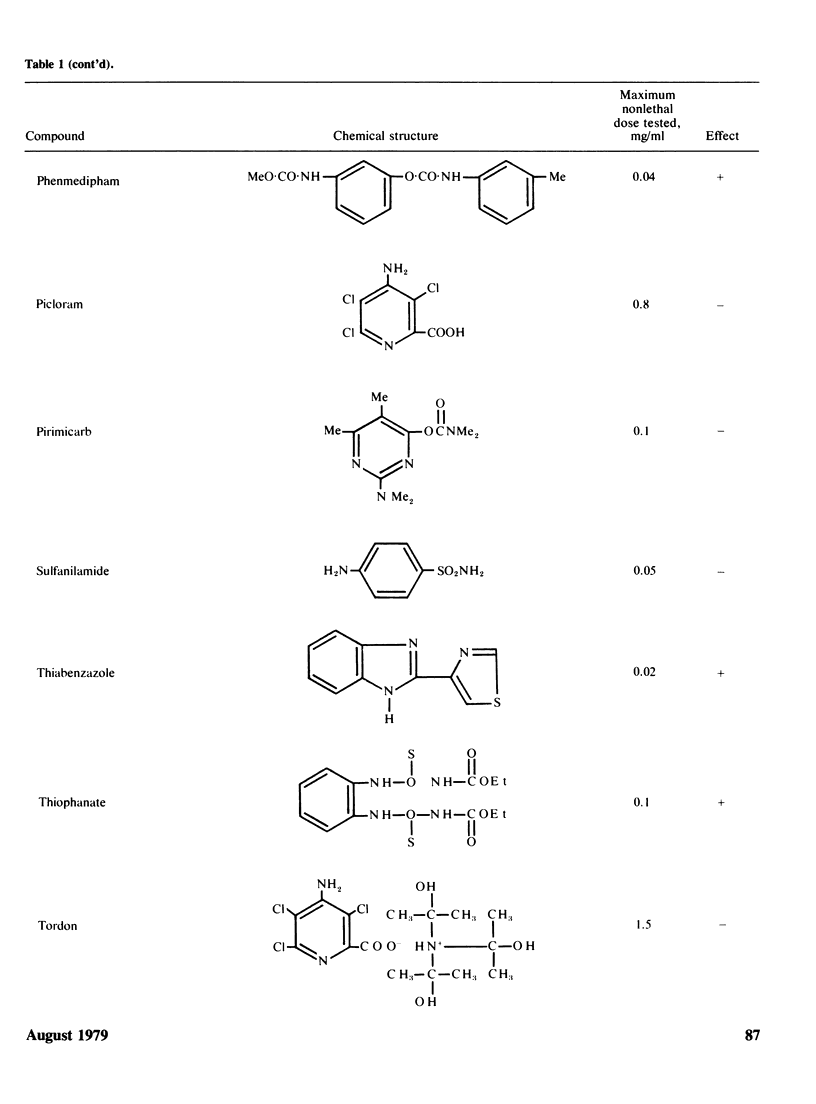
Two methods to detect the induction of nondisjunction with a diploid stable strain of A. nidulans are described. The first method gives only qualitative results, while the second method is quantitative and dose-effect curves can be done. Some physiological parameters affecting the induction of nondisjunction can also be studied, because either quiescent or germinating conidia can be treated with the drug under test. Some agents inducing nondisjunction were also tested for the induction of point mutation and somatic crossing-over with these comparative analysis. Two classes of agents inducing nondisjunction may be detected: the first causes all possible types of genetic damage either on quiescent or germinating conidia (a representative of this class is MMS) and acts presumably on the DNA level; the second acts only on germinating conidia and does not produce point mutation or crossing over. A representative of this class is Benomyl which interferes with spindle microtubules. A list of compounds tests is included.
Full text
PDF

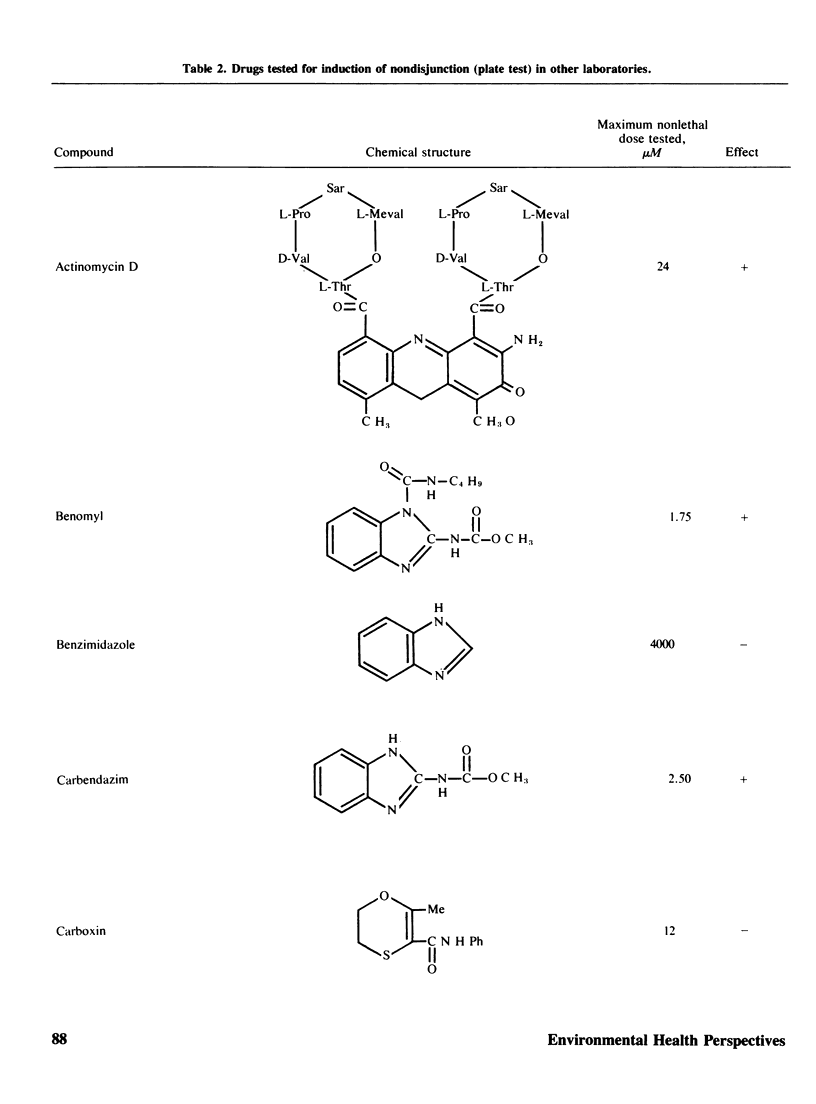
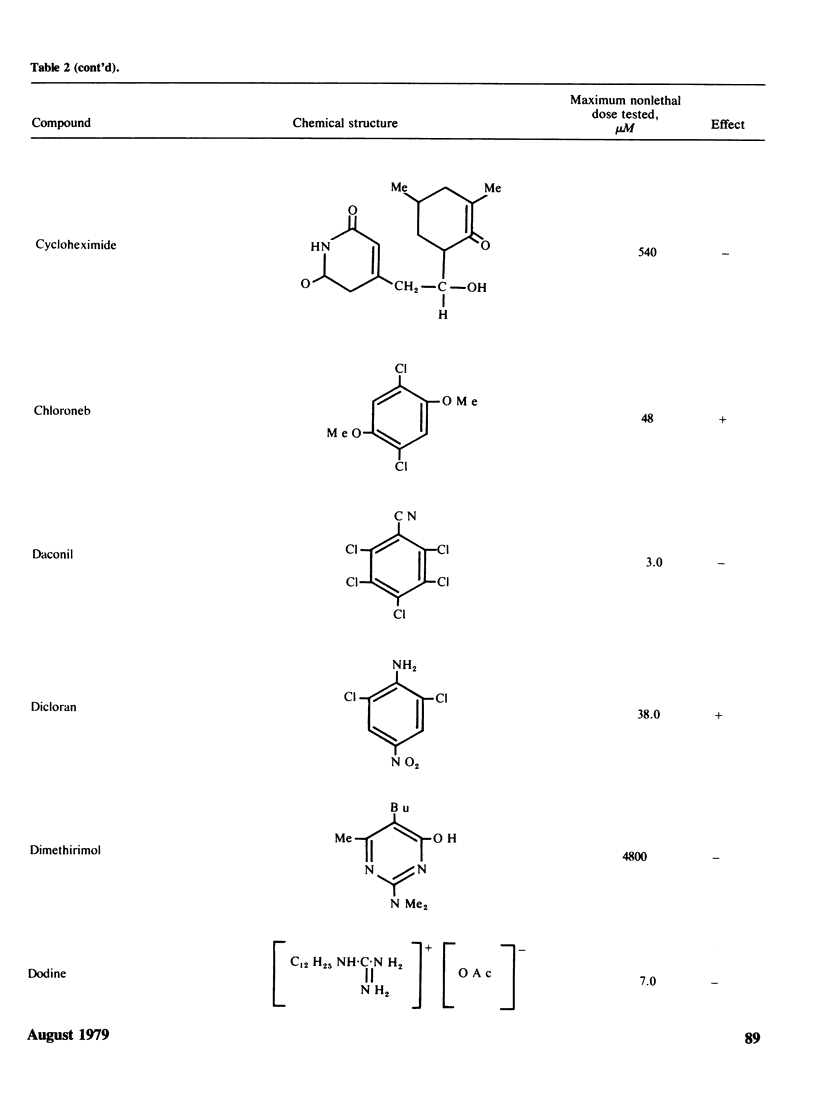
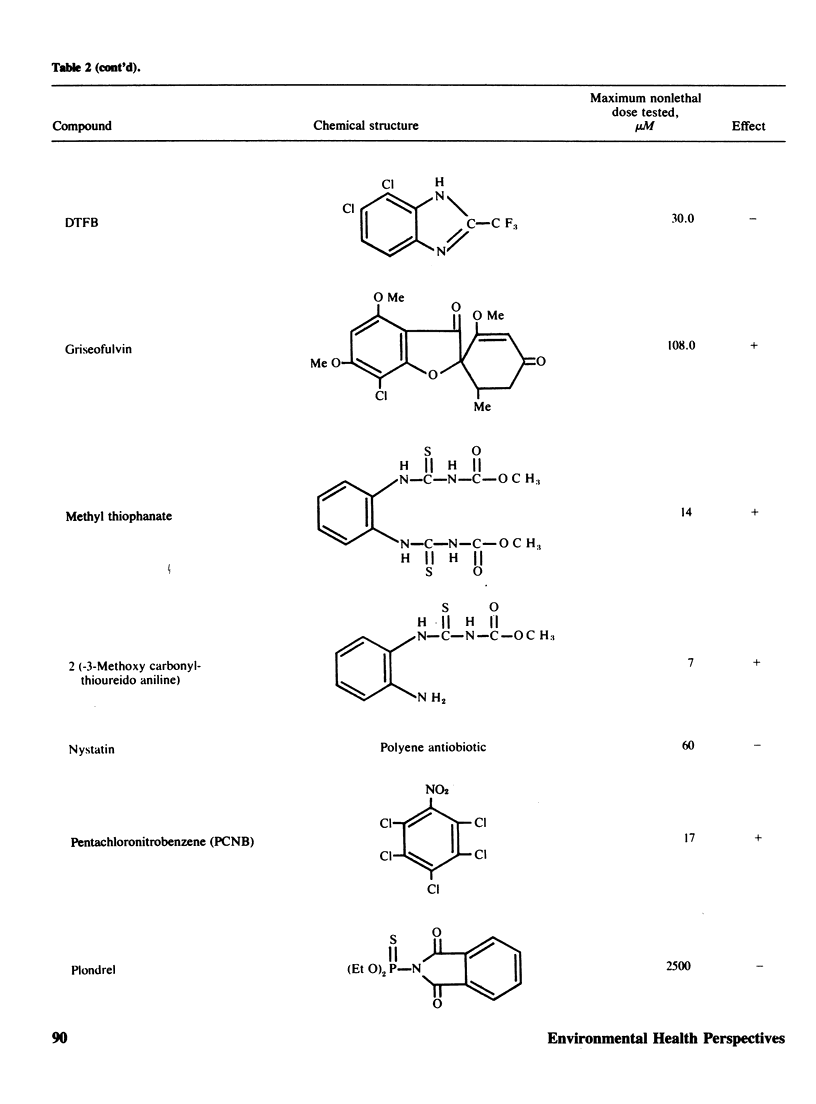
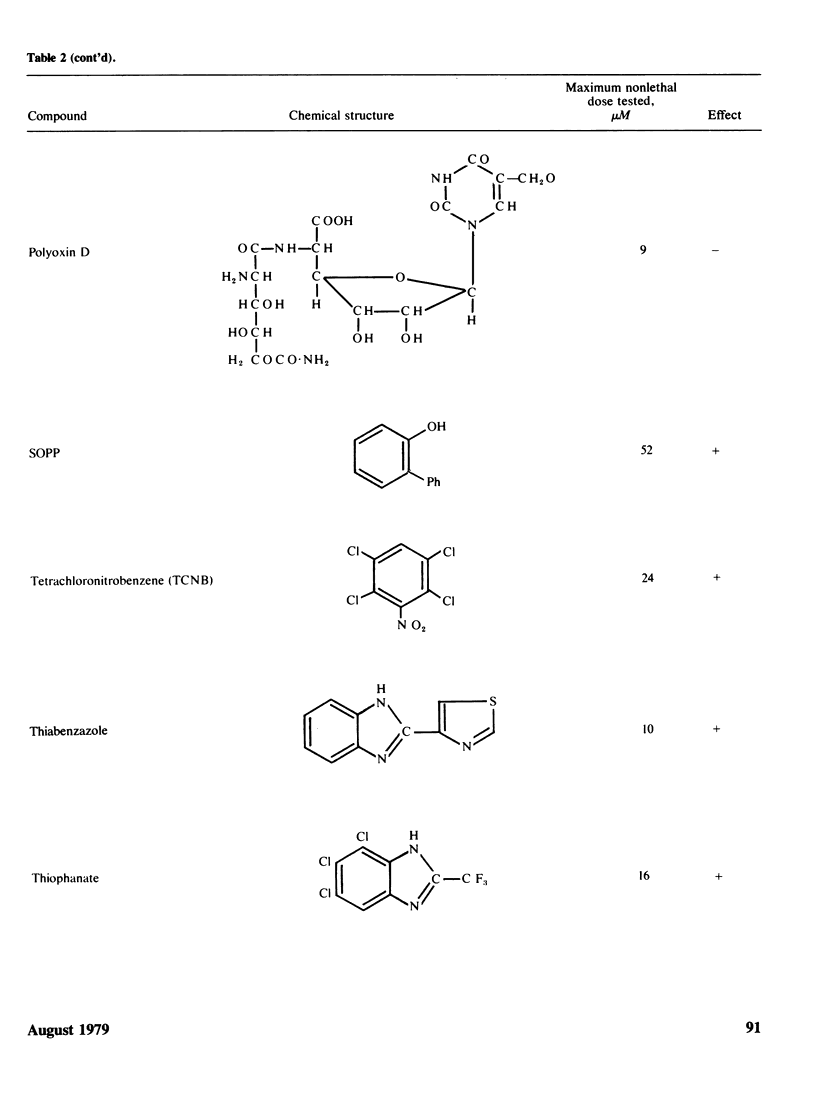

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bignami M., Aulicino F., Velcich A., Carere A., Morpurgo G. Mutagenic and recombinogenic action of pesticides in Aspergillus nidulans. Mutat Res. 1977 Dec;46(6):395–402. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(77)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratello B, Morpurgo G, Sermonti G. Induced Somatic Segregation in Aspergillus Nidulans. Genetics. 1960 Jun;45(6):785–800. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.6.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAFER E. The processes of spontaneous recombination in vegetative nuclei of Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1961 Dec;46:1581–1609. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.12.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morpurgo G. Induction of Mitotic Crossing-over in Aspergillus Nidulans by Bifunctional Alkylating Agents. Genetics. 1963 Sep;48(9):1259–1263. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.9.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTECORVO G., ROPER J. A., HEMMONS L. M., MACDONALD K. D., BUFTON A. W. J. The genetics of Aspergillus nidulans. Adv Genet. 1953;5:141–238. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]