Abstract
Both environmental tobacco smoke and indoor allergens can exacerbate already established childhood albeit primarily through quite disparate mechanisms. In infancy and childhood, environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) exposure is associated with measures of decreased flow in the airways, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and increased respiratory infections, but the relationship between ETS and allergy is poorly understood. Indoor allergens from dust mite, cockroach, and cat can be associated with asthma exacerbation in children sensitized to the specific allergens. The precise role of either ETS or indoor allergens in the development of asthma is less well understood. The strong and consistent association between ETS and asthma development in young children may relate to both prenatal and postnatal influences on airway caliber or bronchial responsiveness. Dust mite allergen levels predict asthma in children sensitized to dust mite. The tendency to develop specific IgE antibodies to allergens (sensitization) is associated with and may be preceded by the development of a T-helper (Th)2 profile of cytokine release. The importance of either ETS or indoor allergens in the differentiation of T cells into a Th2-type profile of cytokine release or in the localization of immediate-type allergic responses to the lung is unknown. This article evaluates the strength of the evidence that ETS or indoor allergens influence asthma exacerbation and asthma development in children. We also selectively review data for the effectiveness of allergen reduction in reducing asthma symptoms and present a potential research agenda regarding these two broad areas of environmental exposure and their relationship to childhood asthma.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. R., Bland J. M., Patel S., Peckham C. The natural history of asthma in childhood. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1986 Jun;40(2):121–129. doi: 10.1136/jech.40.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner D. B., Perzanowski M. S., Platts-Mills T. A., Woodfolk J. A. Evaluation of different techniques for washing cats: quantitation of allergen removed from the cat and the effect on airborne Fel d 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Sep;100(3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNTON H. S., BROWN H. INSECT ALLERGY--PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF THE COCKROACH. J Allergy. 1964 Nov-Dec;35:506–513. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(64)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollinger M. E., Eggleston P. A., Flanagan E., Wood R. A. Cat antigen in homes with and without cats may induce allergic symptoms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Apr;97(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)80064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge H. A., Rogers C. A. Outdoor allergens. Environ Health Perspect. 2000 Aug;108 (Suppl 4):653–659. doi: 10.1289/ehp.00108s4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call R. S., Smith T. F., Morris E., Chapman M. D., Platts-Mills T. A. Risk factors for asthma in inner city children. J Pediatr. 1992 Dec;121(6):862–866. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey V. J., Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Leeder S. R., Speizer F. E. Airways responsiveness, wheeze onset, and recurrent asthma episodes in young adolescents. The East Boston Childhood Respiratory Disease Cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Jan;153(1):356–361. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.153.1.8542143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell F., Birmingham K., Oliver J., Crewes A., Weeks J. The respiratory effects of reduction of mite allergen in the bedrooms of asthmatic children--a double-blind controlled trial. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996 Apr;26(4):386–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Li W. X. The effect of passive smoking on children's pulmonary function in Shanghai. Am J Public Health. 1986 May;76(5):515–518. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.5.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Li W. X., Yu S. Z., Qian W. H. Chang-Ning epidemiological study of children's health: I: Passive smoking and children's respiratory diseases. Int J Epidemiol. 1988 Jun;17(2):348–355. doi: 10.1093/ije/17.2.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Rennie D. C., Dosman J. A. Influence of environmental tobacco smoke on asthma in nonallergic and allergic children. Epidemiology. 1996 Sep;7(5):536–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew G. L., Burge H. A., Dockery D. W., Muilenberg M. L., Weiss S. T., Gold D. R. Limitations of a home characteristics questionnaire as a predictor of indoor allergen levels. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 May;157(5 Pt 1):1536–1541. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.157.5.9708011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew G. L., Higgins K. M., Milton D. K., Burge H. A. The effects of carpet fresheners and other additives on the behaviour of indoor allergen assays. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 Apr;29(4):470–477. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilmonczyk B. A., Knight G. J., Palomaki G. E., Pulkkinen A. J., Williams J., Haddow J. E. Environmental tobacco smoke exposure during infancy. Am J Public Health. 1990 Oct;80(10):1205–1208. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.10.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark N. M., Brown R. W., Parker E., Robins T. G., Remick D. G., Jr, Philbert M. A., Keeler G. J., Israel B. A. Childhood asthma. Environ Health Perspect. 1999 Jun;107 (Suppl 3):421–429. doi: 10.1289/ehp.99107s3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. H., Moessinger A. C., Kleinerman J., Bassi J., Rosso P., Collins A. M., James L. S., Blanc W. A. Fetal lung hypoplasia associated with maternal smoking: a morphometric analysis. Pediatr Res. 1985 Apr;19(4):408–412. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198519040-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croner S., Kjellman N. I. Natural history of bronchial asthma in childhood. A prospective study from birth up to 12-14 years of age. Allergy. 1992 Apr;47(2 Pt 2):150–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1992.tb00956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham J., Dockery D. W., Speizer F. E. Maternal smoking during pregnancy as a predictor of lung function in children. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Jun 15;139(12):1139–1152. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham J., Dockery D. W., Speizer F. E. Race, asthma, and persistent wheeze in Philadelphia schoolchildren. Am J Public Health. 1996 Oct;86(10):1406–1409. doi: 10.2105/ajph.86.10.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Custovic A., Simpson A., Pahdi H., Green R. M., Chapman M. D., Woodcock A. Distribution, aerodynamic characteristics, and removal of the major cat allergen Fel d 1 in British homes. Thorax. 1998 Jan;53(1):33–38. doi: 10.1136/thx.53.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Andrade A. D., Birnbaum J., Magalon C., Magnol J. P., Lanteaume A., Charpin D., Vervloet D. Fel d I levels in cat anal glands. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996 Feb;26(2):178–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1996.tb00077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybendal T., Elsayed S. Dust from carpeted and smooth floors. VI. Allergens in homes compared with those in schools in Norway. Allergy. 1994 Apr;49(4):210–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1994.tb02651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston P. A., Buckley T. J., Breysse P. N., Wills-Karp M., Kleeberger S. R., Jaakkola J. J. The environment and asthma in U.S. inner cities. Environ Health Perspect. 1999 Jun;107 (Suppl 3):439–450. doi: 10.1289/ehp.99107s3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnert B., Lau-Schadendorf S., Weber A., Buettner P., Schou C., Wahn U. Reducing domestic exposure to dust mite allergen reduces bronchial hyperreactivity in sensitive children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Jul;90(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(06)80024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D., Levison M. J., Feldman C. H., Clark N. M., Wasilewski Y., Levin B., Mellins R. B. The impact of passive smoking on emergency room visits of urban children with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Mar;135(3):567–572. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelber L. E., Seltzer L. H., Bouzoukis J. K., Pollart S. M., Chapman M. D., Platts-Mills T. A. Sensitization and exposure to indoor allergens as risk factors for asthma among patients presenting to hospital. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Mar;147(3):573–578. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.3.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold D. R., Burge H. A., Carey V., Milton D. K., Platts-Mills T., Weiss S. T. Predictors of repeated wheeze in the first year of life: the relative roles of cockroach, birth weight, acute lower respiratory illness, and maternal smoking. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999 Jul;160(1):227–236. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.160.1.9807104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold D. R., Rotnitzky A., Damokosh A. I., Ware J. H., Speizer F. E., Ferris B. G., Jr, Dockery D. W. Race and gender differences in respiratory illness prevalence and their relationship to environmental exposures in children 7 to 14 years of age. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jul;148(1):10–18. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen M., Stern D. A., Wright A. L., Taussig L. M., Martinez F. D. Alternaria as a major allergen for asthma in children raised in a desert environment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Apr;155(4):1356–1361. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.155.4.9105079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen M., Stern D., Lyle S., Wright A., Taussig L., Martinez F. D. Relationship of total serum IgE levels in cord and 9-month sera of infants. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 Mar;21(2):235–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb00836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanrahan J. P., Tager I. B., Segal M. R., Tosteson T. D., Castile R. G., Van Vunakis H., Weiss S. T., Speizer F. E. The effect of maternal smoking during pregnancy on early infant lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 May;145(5):1129–1135. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.5.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesselmar B., Aberg N., Aberg B., Eriksson B., Björkstén B. Does early exposure to cat or dog protect against later allergy development? Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 May;29(5):611–617. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
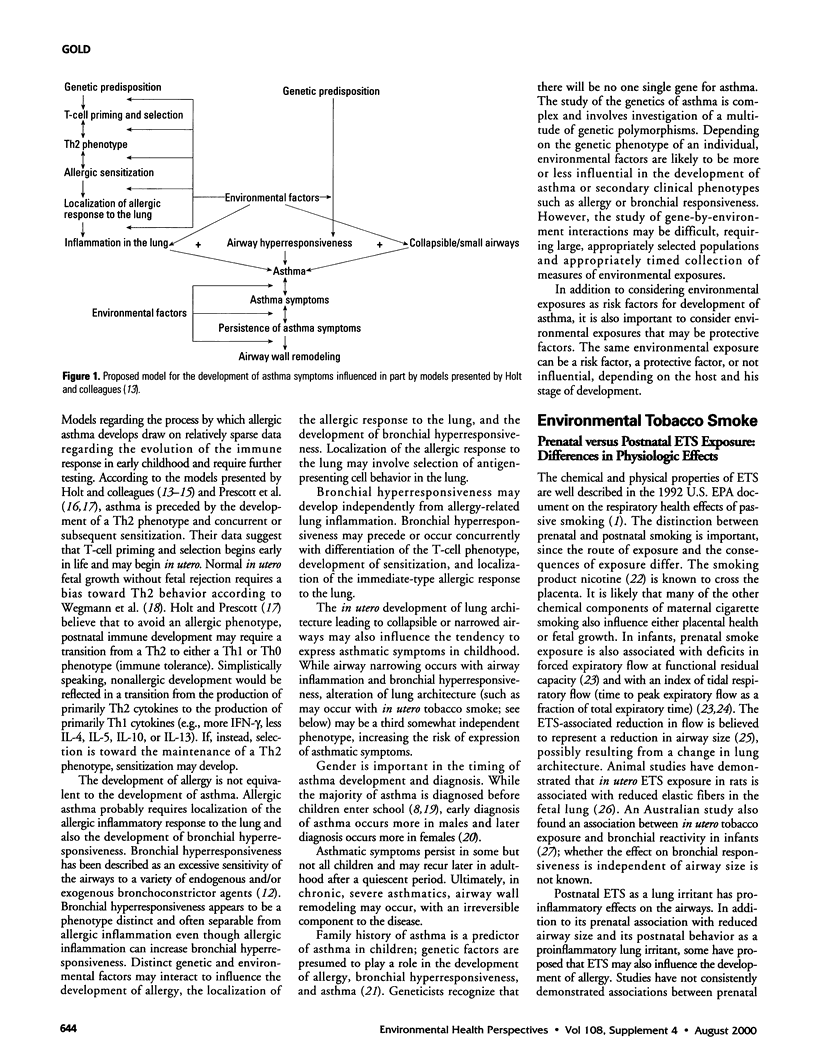
- Holt P. G., Macaubas C., Sly P. D. Strategic targets for primary prevention of allergic disease in childhood. Allergy. 1998;53(45 Suppl):72–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb04944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. Potential role of environmental factors in the etiology and pathogenesis of atopy: a working model. Environ Health Perspect. 1999 Jun;107 (Suppl 3):485–487. doi: 10.1289/ehp.99107s3485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Sly P. D. Allergic respiratory disease: strategic targets for primary prevention during childhood. Thorax. 1997 Jan;52(1):1–4. doi: 10.1136/thx.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram J. M., Sporik R., Rose G., Honsinger R., Chapman M. D., Platts-Mills T. A. Quantitative assessment of exposure to dog (Can f 1) and cat (Fel d 1) allergens: relation to sensitization and asthma among children living in Los Alamos, New Mexico. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995 Oct;96(4):449–456. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(95)70286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. A., Hopper J. L., Bowes G., Carlin J. B., Flander L. B., Giles G. G. Factors in childhood as predictors of asthma in adult life. BMJ. 1994 Jul 9;309(6947):90–93. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6947.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordanov J. S. Cotinine concentrations in amniotic fluid and urine of smoking, passive smoking and non-smoking pregnant women at term and in the urine of their neonates on 1st day of life. Eur J Pediatr. 1990 Jul;149(10):734–737. doi: 10.1007/BF01959534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang B. Study on cockroach antigen as a probable causative agent in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Sep;58(3):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellman N. I. Effect of parental smoking on IgE levels in children. Lancet. 1981 May 2;1(8227):993–994. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91749-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehr J., Frischer T., Meinert R., Barth R., Forster J., Schraub S., Urbanek R., Karmaus W. Mite allergen exposure is a risk for the incidence of specific sensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Jul;94(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Richards D., Bynner J., Butler N., Britton J. Prospective study of risk factors for early and persistent wheezing in childhood. Eur Respir J. 1995 Mar;8(3):349–356. doi: 10.1183/09031936.95.08030349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litonjua A. A., Sparrow D., Weiss S. T., O'Connor G. T., Long A. A., Ohman J. L., Jr Sensitization to cat allergen is associated with asthma in older men and predicts new-onset airway hyperresponsiveness. The Normative Aging Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Jul;156(1):23–27. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.156.1.9608072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson C. G. Maternal smoking influences cord serum IgE and IgD levels and increases the risk for subsequent infant allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Nov;78(5 Pt 1):898–904. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez F. D., Wright A. L., Taussig L. M., Holberg C. J., Halonen M., Morgan W. J. Asthma and wheezing in the first six years of life. The Group Health Medical Associates. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jan 19;332(3):133–138. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199501193320301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F. B., Bousquet J., Greillier P., Robinet-Levy M., Coulomb Y. Comparison of cord blood immunoglobulin E concentrations and maternal allergy for the prediction of atopic diseases in infancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Jun;65(6):422–430. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel O., Ginanni R., Duchateau J., Vertongen F., Le Bon B., Sergysels R. Domestic endotoxin exposure and clinical severity of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 Jul;21(4):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb01684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel O., Kips J., Duchateau J., Vertongen F., Robert L., Collet H., Pauwels R., Sergysels R. Severity of asthma is related to endotoxin in house dust. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Dec;154(6 Pt 1):1641–1646. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.154.6.8970348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molfino N. A., Slutsky A. S., Zamel N. The effects of air pollution on allergic bronchial responsiveness. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Jul;22(7):667–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb00189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molfino N. A., Wright S. C., Katz I., Tarlo S., Silverman F., McClean P. A., Szalai J. P., Raizenne M., Slutsky A. S., Zamel N. Effect of low concentrations of ozone on inhaled allergen responses in asthmatic subjects. Lancet. 1991 Jul 27;338(8761):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90346-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. B., Morrison B. J. Passive smoking by asthmatics: its greater effect on boys than on girls and on older than on younger children. Pediatrics. 1989 Sep;84(3):451–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman P. S., Ohman J. L., Jr, Long A. A., Creticos P. S., Gefter M. A., Shaked Z., Wood R. A., Eggleston P. A., Hafner K. B., Rao P. Treatment of cat allergy with T-cell reactive peptides. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Dec;154(6 Pt 1):1623–1628. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.154.6.8970345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor G. T., Gold D. R. Cockroach allergy and asthma in a 30-year-old man. Environ Health Perspect. 1999 Mar;107(3):243–247. doi: 10.1289/ehp.99107243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor G. T., Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Speizer F. E. The effect of passive smoking on pulmonary function and nonspecific bronchial responsiveness in a population-based sample of children and young adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Apr;135(4):800–804. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.4.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odhiambo J. A., Ng'ang'a L. W., Mungai M. W., Gicheha C. M., Nyamwaya J. K., Karimi F., Macklem P. T., Becklake M. R. Urban-rural differences in questionnaire-derived markers of asthma in Kenyan school children. Eur Respir J. 1998 Nov;12(5):1105–1112. doi: 10.1183/09031936.98.12051105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peat J. K., Tovey E., Mellis C. M., Leeder S. R., Woolcock A. J. Importance of house dust mite and Alternaria allergens in childhood asthma: an epidemiological study in two climatic regions of Australia. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993 Oct;23(10):812–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb00258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peat J. K., Tovey E., Toelle B. G., Haby M. M., Gray E. J., Mahmic A., Woolcock A. J. House dust mite allergens. A major risk factor for childhood asthma in Australia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Jan;153(1):141–146. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.153.1.8542107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piacentini G. L., Martinati L., Fornari A., Comis A., Carcereri L., Boccagni P., Boner A. L. Antigen avoidance in a mountain environment: influence on basophil releasability in children with allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Nov;92(5):644–650. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills T. A., Woodfolk J. A., Chapman M. D., Heymann P. W. Changing concepts of allergic disease: the attempt to keep up with real changes in lifestyles. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Dec;98(6 Pt 3):S297–S306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollart S. M., Chapman M. D., Fiocco G. P., Rose G., Platts-Mills T. A. Epidemiology of acute asthma: IgE antibodies to common inhalant allergens as a risk factor for emergency room visits. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 May;83(5):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollart S. M., Smith T. F., Morris E. C., Gelber L. E., Platts-Mills T. A., Chapman M. D. Environmental exposure to cockroach allergens: analysis with monoclonal antibody-based enzyme immunoassays. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Feb;87(2):505–510. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90009-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. L., Macaubas C., Holt B. J., Smallacombe T. B., Loh R., Sly P. D., Holt P. G. Transplacental priming of the human immune system to environmental allergens: universal skewing of initial T cell responses toward the Th2 cytokine profile. J Immunol. 1998 May 15;160(10):4730–4737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. L., Macaubas C., Smallacombe T., Holt B. J., Sly P. D., Holt P. G. Development of allergen-specific T-cell memory in atopic and normal children. Lancet. 1999 Jan 16;353(9148):196–200. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)05104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Eggleston P., Kattan M., Baker D., Slavin R. G., Gergen P., Mitchell H., McNiff-Mortimer K., Lynn H., Ownby D. The role of cockroach allergy and exposure to cockroach allergen in causing morbidity among inner-city children with asthma. N Engl J Med. 1997 May 8;336(19):1356–1363. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199705083361904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowntree S., Cogswell J. J., Platts-Mills T. A., Mitchell E. B. Development of IgE and IgG antibodies to food and inhalant allergens in children at risk of allergic disease. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Aug;60(8):727–735. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.8.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarpong S. B., Hamilton R. G., Eggleston P. A., Adkinson N. F., Jr Socioeconomic status and race as risk factors for cockroach allergen exposure and sensitization in children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Jun;97(6):1393–1401. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schou C. Defining allergens of mammalian origin. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993 Jan;23(1):7–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb02477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Burrows B., Flannery E. M., Herbison G. P., Hewitt C. J., Holdaway M. D. Relation between airway responsiveness and serum IgE in children with asthma and in apparently normal children. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 10;325(15):1067–1071. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110103251504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Herbison G. P., Holdaway M. D., Hewitt C. J., Flannery E. M., Silva P. A. The relative risks of sensitivity to grass pollen, house dust mite and cat dander in the development of childhood asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 Jul;19(4):419–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman C. B., Tosteson T. D., Tager I. B., Speizer F. E., Weiss S. T. Early childhood predictors of asthma. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Jul;132(1):83–95. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicherer S. H., Wood R. A., Eggleston P. A. Determinants of airway responses to cat allergen: comparison of environmental challenge to quantitative nasal and bronchial allergen challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Jun;99(6 Pt 1):798–805. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. U., Grotzer M., Nikolaizik W. H., Blaser K., Schöni M. H. High altitude climate therapy reduces peripheral blood T lymphocyte activation, eosinophilia, and bronchial obstruction in children with house-dust mite allergic asthma. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1994 May;17(5):304–311. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950170507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporik R., Holgate S. T., Platts-Mills T. A., Cogswell J. J. Exposure to house-dust mite allergen (Der p I) and the development of asthma in childhood. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 23;323(8):502–507. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008233230802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporik R., Ingram J. M., Price W., Sussman J. H., Honsinger R. W., Platts-Mills T. A. Association of asthma with serum IgE and skin test reactivity to allergens among children living at high altitude. Tickling the dragon's breath. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 May;151(5):1388–1392. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.5.7735590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stick S. M., Burton P. R., Gurrin L., Sly P. D., LeSouëf P. N. Effects of maternal smoking during pregnancy and a family history of asthma on respiratory function in newborn infants. Lancet. 1996 Oct 19;348(9034):1060–1064. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)04446-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan D. P., Cook D. G. Health effects of passive smoking. 6. Parental smoking and childhood asthma: longitudinal and case-control studies. Thorax. 1998 Mar;53(3):204–212. doi: 10.1136/thx.53.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand V., Rak S., Svartengren M., Bylin G. Nitrogen dioxide exposure enhances asthmatic reaction to inhaled allergen in subjects with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Mar;155(3):881–887. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.155.3.9117021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanes C., Jarvis D., Chinn S., Burney P. Childhood environment and adult atopy: results from the European Community Respiratory Health Survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999 Mar;103(3 Pt 1):415–420. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager I. B. Smoking and childhood asthma-where do we stand? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Aug;158(2):349–351. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.2.ed05-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanto T., Koivikko A. Dog hypersensitivity in asthmatic children. A clinical study with special reference to the relationship between the exposure to dogs and the occurrence of hypersensitivity symptoms. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Jul;72(4):571–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. A. Environmental allergen exposure in homes and schools. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992 Dec;22(12):1044–1045. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1992.tb00127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann T. G., Lin H., Guilbert L., Mosmann T. R. Bidirectional cytokine interactions in the maternal-fetal relationship: is successful pregnancy a TH2 phenomenon? Immunol Today. 1993 Jul;14(7):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90235-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Muñoz A., Speizer F. E. The relationship of respiratory infections in early childhood to the occurrence of increased levels of bronchial responsiveness and atopy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):573–578. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickman M., Korsgaard J. Transient sensitization to house-dust mites: a study on the influence of mite exposure and sex. Allergy. 1996 Jul;51(7):511–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1996.tb04658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers N. J., Low L., Holgate S. T., Clough J. B. The natural history of respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adolescents. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Aug;158(2):352–357. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.2.9705079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. A., Johnson E. F., Van Natta M. L., Chen P. H., Eggleston P. A. A placebo-controlled trial of a HEPA air cleaner in the treatment of cat allergy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Jul;158(1):115–120. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.1.9712110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yemaneberhan H., Bekele Z., Venn A., Lewis S., Parry E., Britton J. Prevalence of wheeze and asthma and relation to atopy in urban and rural Ethiopia. Lancet. 1997 Jul 12;350(9071):85–90. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Le Souëf P. N., Geelhoed G. C., Stick S. M., Turner K. J., Landau L. I. The influence of a family history of asthma and parental smoking on airway responsiveness in early infancy. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 25;324(17):1168–1173. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104253241704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Blay F., Sanchez J., Hedelin G., Perez-Infante A., Vérot A., Chapman M., Pauli G. Dust and airborne exposure to allergens derived from cockroach (Blattella germanica) in low-cost public housing in Strasbourg (France). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Jan;99(1 Pt 1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide S., van Aalderen W. M., Kauffman H. F., Dubois A. E., de Monchy J. G. Clinical effects of air cleaners in homes of asthmatic children sensitized to pet allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999 Aug;104(2 Pt 1):447–451. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(99)70391-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Mutius E., Martinez F. D., Fritzsch C., Nicolai T., Roell G., Thiemann H. H. Prevalence of asthma and atopy in two areas of West and East Germany. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Feb;149(2 Pt 1):358–364. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.2.8306030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


