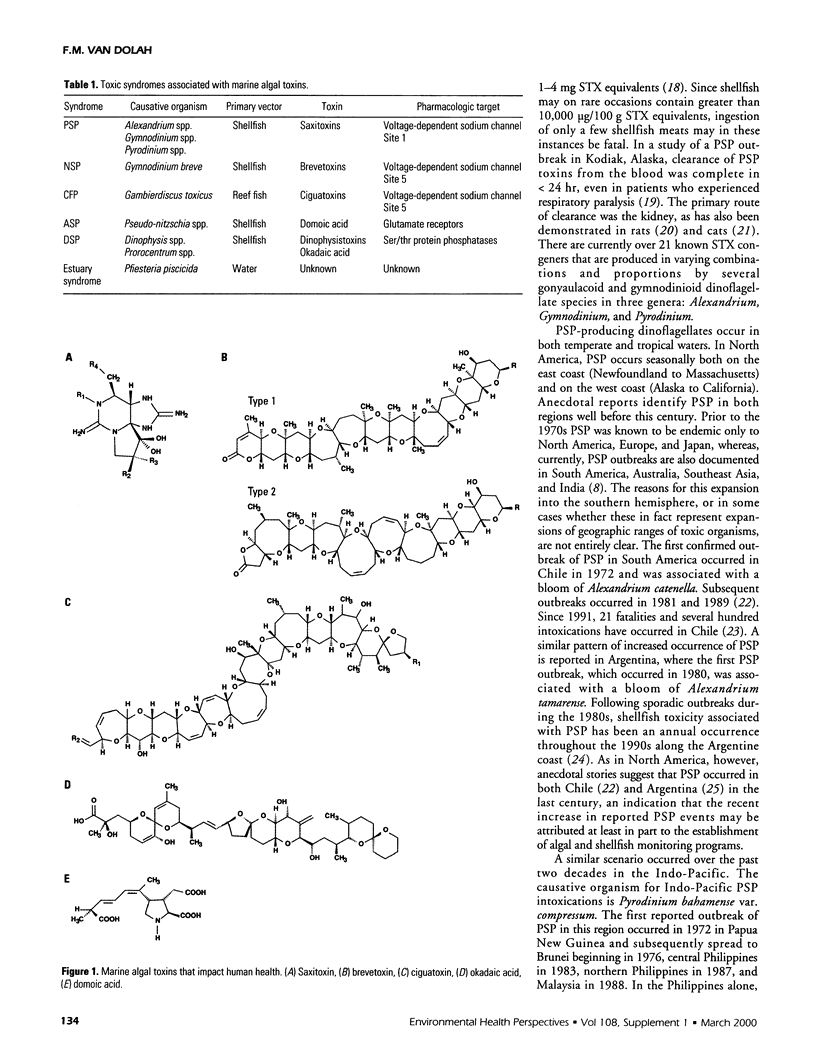
Abstract
Certain marine algae produce potent toxins that impact human health through the consumption of contaminated shellfish and finfish and through water or aerosol exposure. Over the past three decades, the frequency and global distribution of toxic algal incidents appear to have increased, and human intoxications from novel algal sources have occurred. This increase is of particular concern, since it parallels recent evidence of large-scale ecologic disturbances that coincide with trends in global warming. The extent to which human activities have contributed to their increase therefore comes into question. This review summarizes the origins and health effects of marine algal toxins, as well as changes in their current global distribution, and examines possible causes for the recent increase in their occurrence.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrinolo D., Michea L. F., Lagos N. Toxic effects, pharmacokinetics and clearance of saxitoxin, a component of paralytic shellfish poison (PSP), in cats. Toxicon. 1999 Mar;37(3):447–464. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(98)00173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagu J. R., Sykes B. D., Craig M. M., Holmes C. F. A molecular basis for different interactions of marine toxins with protein phosphatase-1. Molecular models for bound motuporin, microcystins, okadaic acid, and calyculin A. J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 21;272(8):5087–5097. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.8.5087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossart G. D., Baden D. G., Ewing R. Y., Roberts B., Wright S. D. Brevetoxicosis in manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris) from the 1996 epizootic: gross, histologic, and immunohistochemical features. Toxicol Pathol. 1998 Mar-Apr;26(2):276–282. doi: 10.1177/019262339802600214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder J. M., Noga E. J., Hobbs C. H., Glasgow H. B., Jr, Smith S. A. New 'phantom' dinoflagellate is the causative agent of major estuarine fish kills. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):407–410. doi: 10.1038/358407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cariton J. T., Geller J. B. Ecological roulette: the global transport of nonindigenous marine organisms. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.261.5117.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton E. C., Peng Y. G., Means L. W., Ramsdell J. S. Working memory deficits induced by single but not repeated exposures to domoic acid. Toxicon. 1999 Jul;37(7):1025–1039. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(98)00230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R. Global climate and infectious disease: the cholera paradigm. Science. 1996 Dec 20;274(5295):2025–2031. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5295.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechraoui M. Y., Naar J., Pauillac S., Legrand A. M. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon. 1999 Jan;37(1):125–143. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(98)00169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds J. S., McCarthy R. A., Ramsdell J. S. Ciguatoxin reduces larval survivability in finfish. Toxicon. 1999 Dec;37(12):1827–1832. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(99)00119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. R. Climate and health. Science. 1999 Jul 16;285(5426):347–348. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5426.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki H., Suganuma M., Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Takagi K., Uda N., Wakamatsu K., Yamada K., Murata M., Yasumoto T. Diarrhetic shellfish toxin, dinophysistoxin-1, is a potent tumor promoter on mouse skin. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Oct;79(10):1089–1093. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss C. M., Sheppeck J. E., 2nd, Nairn A. C., Chamberlin R. A molecular modeling analysis of the binding interactions between the okadaic acid class of natural product inhibitors and the Ser-Thr phosphatases, PP1 and PP2A. Bioorg Med Chem. 1997 Sep;5(9):1751–1773. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(97)00145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawley R. E., Rein K. S., Jeglitsch G., Adams D. J., Theodorakis E. A., Tiebes J., Nicolaou K. C., Baden D. G. The relationship of brevetoxin 'length' and A-ring functionality to binding and activity in neuronal sodium channels. Chem Biol. 1995 Aug;2(8):533–541. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner B. D., Bell P., Doucette G. J., Moczydlowski E., Poli M. A., Van Dolah F., Hall S. Hypertension and identification of toxin in human urine and serum following a cluster of mussel-associated paralytic shellfish poisoning outbreaks. Toxicon. 1997 May;35(5):711–722. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(96)00154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grattan L. M., Oldach D., Perl T. M., Lowitt M. H., Matuszak D. L., Dickson C., Parrott C., Shoemaker R. C., Kauffman C. L., Wasserman M. P. Learning and memory difficulties after environmental exposure to waterways containing toxin-producing Pfiesteria or Pfiesteria-like dinoflagellates. Lancet. 1998 Aug 15;352(9127):532–539. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)02132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson D. R., Huang X. P., Wells J. W., Walter J. A., Wright J. L. Interaction of domoic acid and several derivatives with kainic acid and AMPA binding sites in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 21;218(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90140-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson D. R., Manalo J. L. The activation of glutamate receptors by kainic acid and domoic acid. Nat Toxins. 1998;6(3-4):153–158. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1522-7189(199805/08)6:3/4<153::aid-nt16>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvell C. D., Kim K., Burkholder J. M., Colwell R. R., Epstein P. R., Grimes D. J., Hofmann E. E., Lipp E. K., Osterhaus A. D., Overstreet R. M. Emerging marine diseases--climate links and anthropogenic factors. Science. 1999 Sep 3;285(5433):1505–1510. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5433.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines H. B., Naseem S. M., Wannemacher R. W., Jr [3H]-saxitoxinol metabolism and elimination in the rat. Toxicon. 1993 Jul;31(7):905–908. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(93)90226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson F., Truelove J., Nera E., Tryphonas L., Campbell J., Lok E. Domoic acid poisoning and mussel-associated intoxication: preliminary investigations into the response of mice and rats to toxic mussel extract. Food Chem Toxicol. 1989 Jun;27(6):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(89)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean J. M., Chan C. K., Fleming G. R., Owens T. G. Excitation transport and trapping on spectrally disordered lattices. Biophys J. 1989 Dec;56(6):1203–1215. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82767-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeglitsch G., Rein K., Baden D. G., Adams D. J. Brevetoxin-3 (PbTx-3) and its derivatives modulate single tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in rat sensory neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Feb;284(2):516–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn R. L., Berlin K. D., Hawkins W. E., Ostrander G. K. Relationships among petroleum refining, water and sediment contamination, and fish health. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1995 Sep;46(1):101–116. doi: 10.1080/15287399509532020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. J., Holmes M. J. Origin and transfer of toxins involved in ciguatera. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1993 Nov;106(3):615–628. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(93)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka K. Eutrophication process recorded in dinoflagellate cyst assemblages--a case of Yokohama Port, Tokyo Bay, Japan. Sci Total Environ. 1999 Jun 15;231(1):17–35. doi: 10.1016/s0048-9697(99)00087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl M. L., Fischer M., McCauley D. L., Valea F. A., Chalas E. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation as an adjunct for controlling chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in gynecologic oncology patients. Cancer Nurs. 1999 Aug;22(4):307–311. doi: 10.1097/00002820-199908000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles P. J., Schramm D. N., Turner E. L., Kron R. G. The evolution of the universe. Sci Am. 1994 Oct;271(4):52–57. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1094-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y. G., Taylor T. B., Finch R. E., Switzer R. C., Ramsdell J. S. Neuroexcitatory and neurotoxic actions of the amnesic shellfish poison, domoic acid. Neuroreport. 1994 Apr 14;5(8):981–985. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199404000-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl T. M., Bédard L., Kosatsky T., Hockin J. C., Todd E. C., Remis R. S. An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 21;322(25):1775–1780. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006213222504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli M. A., Mende T. J., Baden D. G. Brevetoxins, unique activators of voltage-sensitive sodium channels, bind to specific sites in rat brain synaptosomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;30(2):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston E., Hynie I. Transfer constants for blood-brain barrier permeation of the neuroexcitatory shellfish toxin, domoic acid. Can J Neurol Sci. 1991 Feb;18(1):39–44. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100031279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes L., Scholin C., Garthwaite I. Pseudo-nitzschia in New Zealand and the role of DNA probes and immunoassays in refining marine biotoxin monitoring programmes. Nat Toxins. 1998;6(3-4):105–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudarsanam S., Virca G. D., March C. J., Srinivasan S. An approach to computer-aided inhibitor design: application to cathepsin L. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1992 Jun;6(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00123378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Hirota M., Nakayasu M., Ojika M., Wakamatsu K., Yamada K., Sugimura T. Okadaic acid: an additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1768–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainer V. L., Baden D. G., Catterall W. A. Identification of peptide components of the brevetoxin receptor site of rat brain sodium channels. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19904–19909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernoux J. P., Lewis R. J. Isolation and characterisation of Caribbean ciguatoxins from the horse-eye jack (Caranx latus). Toxicon. 1997 Jun;35(6):889–900. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(96)00191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wera S., Hemmings B. A. Serine/threonine protein phosphatases. Biochem J. 1995 Oct 1;311(Pt 1):17–29. doi: 10.1042/bj3110017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi D., Ramsdell J. S. Glutamate receptors and calcium entry mechanisms for domoic acid in hippocampal neurons. Neuroreport. 1996 Apr 26;7(6):1115–1120. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199604260-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Zhao S., Long F., Zhang L., Bai G., Shima H., Nagao M., Lee E. Y. A mutant of protein phosphatase-1 that exhibits altered toxin sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):16997–17000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]