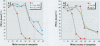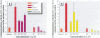Abstract
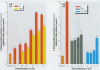
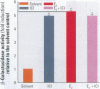
Environmental chemicals with estrogenic activities have been suggested to be associated with deleterious effects in animals and humans. To characterize estrogenic chemicals and their mechanisms of action, we established in vitro and cell culture assays that detect human estrogen receptor [alpha] (hER[alpha])-mediated estrogenicity. First, we assayed chemicals to determine their ability to modulate direct interaction between the hER[alpha] and the steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) and in a competition binding assay to displace 17ss-estradiol (E(2)). Second, we tested the chemicals for estrogen-associated transcriptional activity in the yeast estrogen screen and in the estrogen-responsive MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. The chemicals investigated in this study were o,p'-DDT (racemic mixture and enantiomers), nonylphenol mixture (NPm), and two poorly analyzed compounds in the environment, namely, tris-4-(chlorophenyl)methane (Tris-H) and tris-4-(chlorophenyl)methanol (Tris-OH). In both yeast and MCF-7 cells, we determined estrogenic activity via the estrogen receptor (ER) for o,p'-DDT, NPm, and for the very first time, Tris-H and Tris-OH. However, unlike estrogens, none of these xenobiotics seemed to be able to induce ER/SRC-1 interactions, most likely because the conformation of the activated receptor would not allow direct contacts with this coactivator. However, these compounds were able to inhibit [(3)H]-E(2) binding to hER, which reveals a direct interaction with the receptor. In conclusion, the test compounds are estrogen mimics, but their molecular mechanism of action appears to be different from that of the natural hormone as revealed by the receptor/coactivator interaction analysis.
Full text
PDF


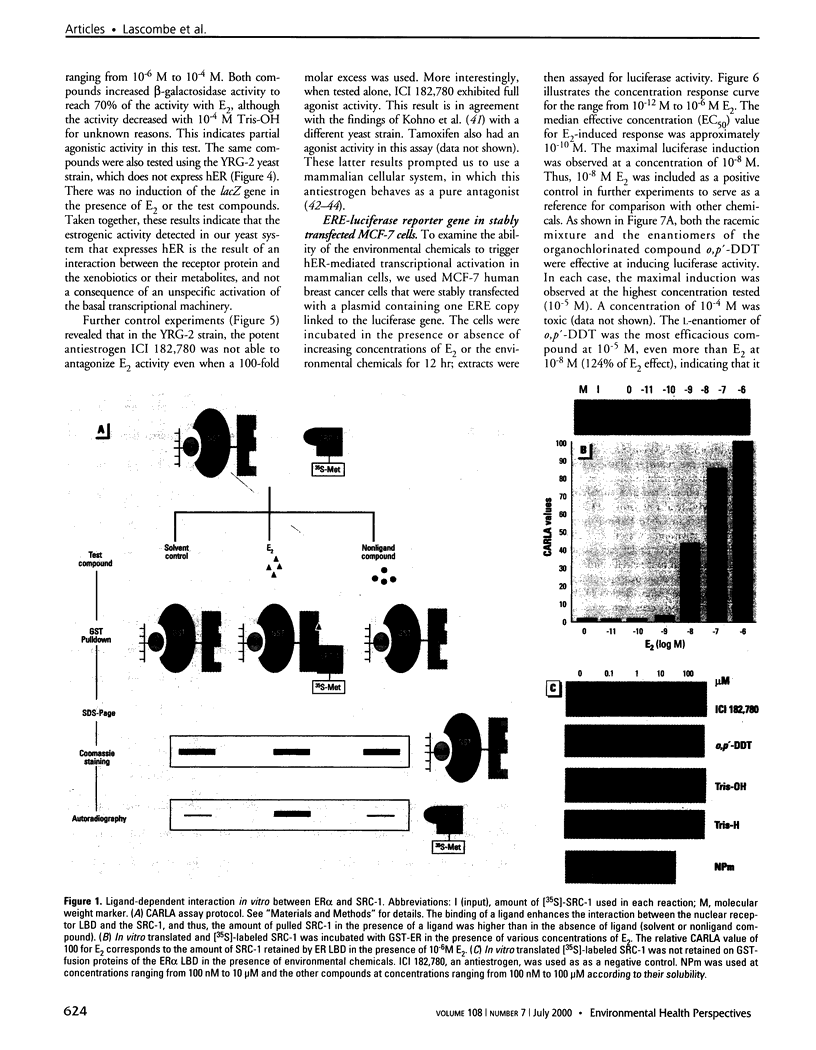
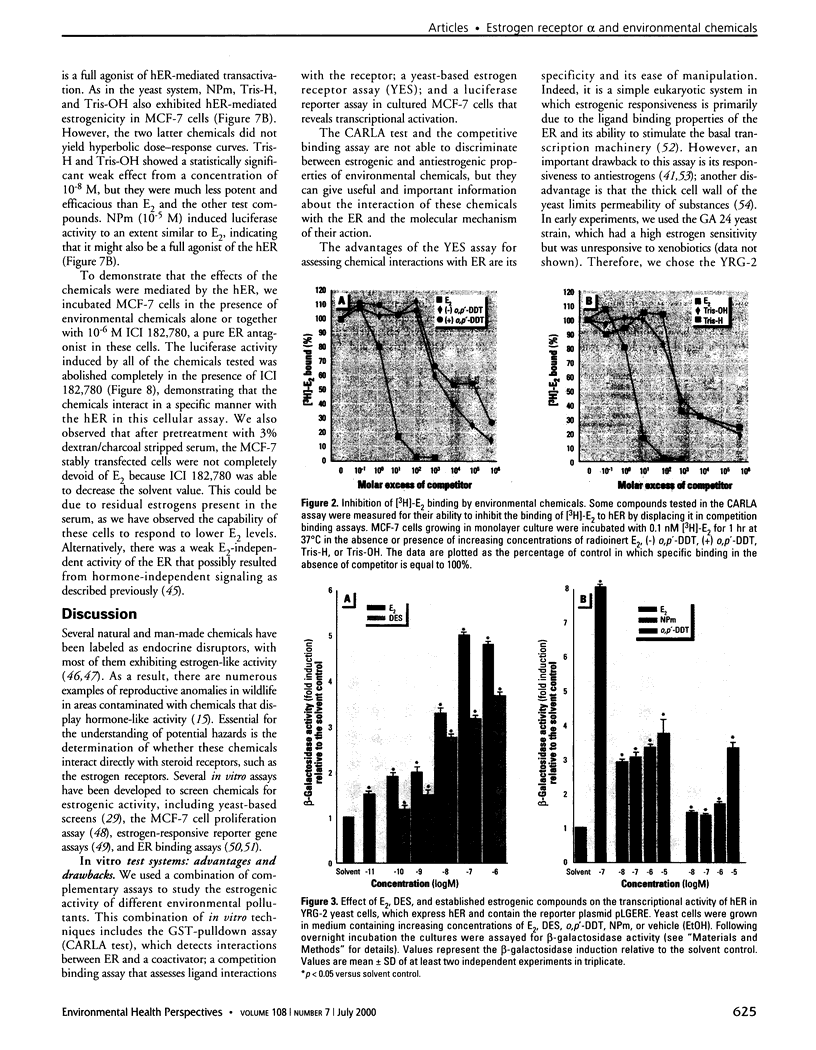
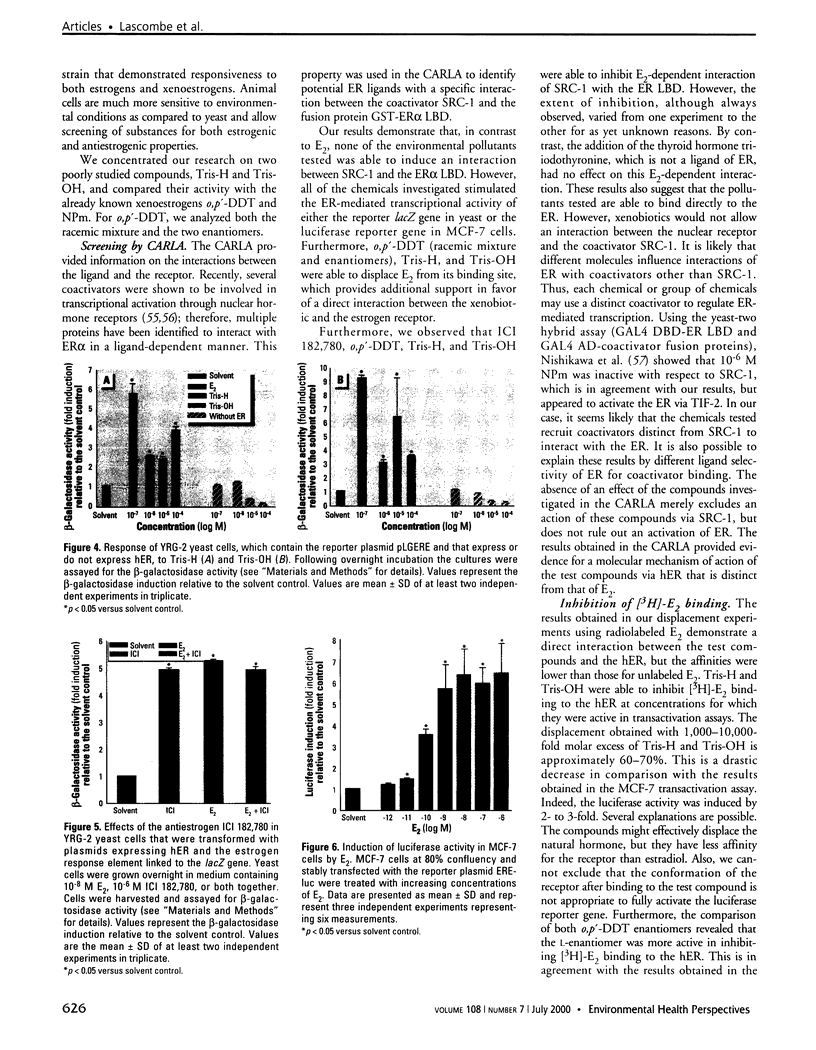
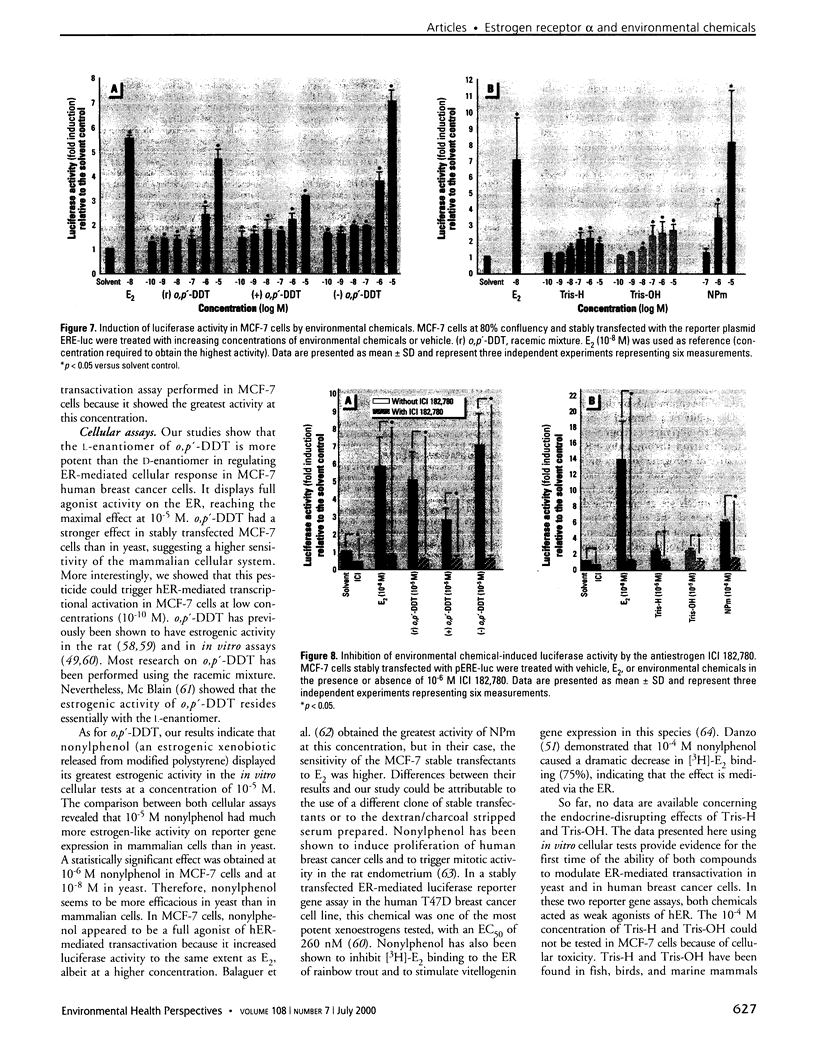


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitman J., Cecil H. C. Estrogenic activity of DDT analogs and polychlorinated biphenyls. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 Nov-Dec;18(6):1108–1112. doi: 10.1021/jf60172a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colborn T., vom Saal F. S., Soto A. M. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Oct;101(5):378–384. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couse J. F., Korach K. S. Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev. 1999 Jun;20(3):358–417. doi: 10.1210/edrv.20.3.0370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley S. M., Hoare S., Mosselman S., Parker M. G. Estrogen receptors alpha and beta form heterodimers on DNA. J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 8;272(32):19858–19862. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.32.19858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzo B. J. Environmental xenobiotics may disrupt normal endocrine function by interfering with the binding of physiological ligands to steroid receptors and binding proteins. Environ Health Perspect. 1997 Mar;105(3):294–301. doi: 10.1289/ehp.97105294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. L., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Physical properties of estrogen receptor complexes in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Differences with anti-estrogen and estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8840–8846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagne D., Balaguer P., Demirpence E., Chabret C., Trousse F., Nicolas J. C., Pons M. Stable luciferase transfected cells for studying steroid receptor biological activity. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1994 May-Jun;9(3):201–209. doi: 10.1002/bio.1170090314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaido K. W., Leonard L. S., Lovell S., Gould J. C., Babaï D., Portier C. J., McDonnell D. P. Evaluation of chemicals with endocrine modulating activity in a yeast-based steroid hormone receptor gene transcription assay. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997 Mar;143(1):205–212. doi: 10.1006/taap.1996.8069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson M. K., Nemmers L. A., Beckman W. C., Jr, Davis V. L., Curtis S. W., Korach K. S. The mechanism of ICI 164,384 antiestrogenicity involves rapid loss of estrogen receptor in uterine tissue. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):2000–2010. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H. Control of transcription activation by steroid hormone receptors. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2524–2529. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1592204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Jackson T. A., Bain D. L., Richer J. K., Takimoto G. S., Tung L. Nuclear receptor coactivators and corepressors. Mol Endocrinol. 1996 Oct;10(10):1167–1177. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.10.9121485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høyer A. P., Grandjean P., Jørgensen T., Brock J. W., Hartvig H. B. Organochlorine exposure and risk of breast cancer. Lancet. 1998 Dec 5;352(9143):1816–1820. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)04504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iafrati M. D., Karas R. H., Aronovitz M., Kim S., Sullivan T. R., Jr, Lubahn D. B., O'Donnell T. F., Jr, Korach K. S., Mendelsohn M. E. Estrogen inhibits the vascular injury response in estrogen receptor alpha-deficient mice. Nat Med. 1997 May;3(5):545–548. doi: 10.1038/nm0597-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V. Steroid hormone antagonists. Summary and future challenges. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Jun 12;761:1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb31364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobling S., Reynolds T., White R., Parker M. G., Sumpter J. P. A variety of environmentally persistent chemicals, including some phthalate plasticizers, are weakly estrogenic. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Jun;103(6):582–587. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan V. C., Mittal S., Gosden B., Koch R., Lieberman M. E. Structure-activity relationships of estrogens. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Sep;61:97–110. doi: 10.1289/ehp.856197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen J. A., O'Malley B. W., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Tripartite steroid hormone receptor pharmacology: interaction with multiple effector sites as a basis for the cell- and promoter-specific action of these hormones. Mol Endocrinol. 1996 Feb;10(2):119–131. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.2.8825552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelce W. R., Stone C. R., Laws S. C., Gray L. E., Kemppainen J. A., Wilson E. M. Persistent DDT metabolite p,p'-DDE is a potent androgen receptor antagonist. Nature. 1995 Jun 15;375(6532):581–585. doi: 10.1038/375581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz D. M., Beckman B. S., Hill S. M., McLachlan J. A., Walters M. R., Arnold S. F. Identification of environmental chemicals with estrogenic activity using a combination of in vitro assays. Environ Health Perspect. 1996 Oct;104(10):1084–1089. doi: 10.1289/ehp.961041084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno H., Gandini O., Curtis S. W., Korach K. S. Anti-estrogen activity in the yeast transcription system: estrogen receptor mediated agonist response. Steroids. 1994 Oct;59(10):572–578. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(94)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krey G., Braissant O., L'Horset F., Kalkhoven E., Perroud M., Parker M. G., Wahli W. Fatty acids, eicosanoids, and hypolipidemic agents identified as ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors by coactivator-dependent receptor ligand assay. Mol Endocrinol. 1997 Jun;11(6):779–791. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.6.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan A. V., Stathis P., Permuth S. F., Tokes L., Feldman D. Bisphenol-A: an estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2279–2286. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper G. G., Enmark E., Pelto-Huikko M., Nilsson S., Gustafsson J. A. Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 11;93(12):5925–5930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.12.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper G. G., Lemmen J. G., Carlsson B., Corton J. C., Safe S. H., van der Saag P. T., van der Burg B., Gustafsson J. A. Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta. Endocrinology. 1998 Oct;139(10):4252–4263. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.10.6216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler J., van den Brink C. E., Brouwer A., Murk A. J., van der Saag P. T., Vethaak A. D., van der Burg B. Development of a stably transfected estrogen receptor-mediated luciferase reporter gene assay in the human T47D breast cancer cell line. Toxicol Sci. 1999 Mar;48(1):55–66. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/48.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyttle C. R., Damian-Matsumura P., Juul H., Butt T. R. Human estrogen receptor regulation in a yeast model system and studies on receptor agonists and antagonists. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Aug;42(7):677–685. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90108-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani S. K., Allen J. M., Clark J. H., Blaustein J. D., O'Malley B. W. Convergent pathways for steroid hormone- and neurotransmitter-induced rat sexual behavior. Science. 1994 Aug 26;265(5176):1246–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.7915049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBlain W. A. The levo enantiomer of o,p'-DDT inhibits the binding of 17 beta-estradiol to the estrogen receptor. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 12;40(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna N. J., Lanz R. B., O'Malley B. W. Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr Rev. 1999 Jun;20(3):321–344. doi: 10.1210/edrv.20.3.0366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan J. A. Functional toxicology: a new approach to detect biologically active xenobiotics. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Oct;101(5):386–387. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moosmann B., Behl C. The antioxidant neuroprotective effects of estrogens and phenolic compounds are independent from their estrogenic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Aug 3;96(16):8867–8872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.16.8867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosselman S., Polman J., Dijkema R. ER beta: identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett. 1996 Aug 19;392(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00782-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa J., Saito K., Goto J., Dakeyama F., Matsuo M., Nishihara T. New screening methods for chemicals with hormonal activities using interaction of nuclear hormone receptor with coactivator. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1999 Jan 1;154(1):76–83. doi: 10.1006/taap.1998.8557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oñate S. A., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1995 Nov 24;270(5240):1354–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit F., Le Goff P., Cravédi J. P., Valotaire Y., Pakdel F. Two complementary bioassays for screening the estrogenic potency of xenobiotics: recombinant yeast for trout estrogen receptor and trout hepatocyte cultures. J Mol Endocrinol. 1997 Dec;19(3):321–335. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0190321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Khursheed B., Garabedian M. J., Fortin M. G., Lindquist S., Yamamoto K. R. Reduced levels of hsp90 compromise steroid receptor action in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):166–168. doi: 10.1038/348166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safe S. H. Environmental and dietary estrogens and human health: is there a problem? Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Apr;103(4):346–351. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe R. M., Skakkebaek N. E. Are oestrogens involved in falling sperm counts and disorders of the male reproductive tract? Lancet. 1993 May 29;341(8857):1392–1395. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90953-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar P. V., Werdell J., Basrur V. S. Environmental estrogen stimulation of growth and estrogen receptor function in preneoplastic and cancerous human breast cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997 Dec 3;89(23):1774–1782. doi: 10.1093/jnci/89.23.1774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto A. M., Chung K. L., Sonnenschein C. The pesticides endosulfan, toxaphene, and dieldrin have estrogenic effects on human estrogen-sensitive cells. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Apr;102(4):380–383. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. M., Blanchard B., Zava D. T. A simple method to determine whole cell uptake of radiolabelled oestrogen and progesterone and their subcellular localization in breast cancer cell lines in monolayer culture. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 May;20(5):1083–1088. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay G. B., Tremblay A., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Labrie F., Giguère V. Cloning, chromosomal localization, and functional analysis of the murine estrogen receptor beta. Mol Endocrinol. 1997 Mar;11(3):353–365. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.3.9902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai-Pflugfelder M., Gasser S. M., Wahli W. Functional interaction between the estrogen receptor and CTF1: analysis of the vitellogenin gene B1 promoter in yeast. Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Oct;12(10):1525–1541. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.10.0182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakeling A. E., Bowler J. Novel antioestrogens without partial agonist activity. J Steroid Biochem. 1988 Oct;31(4B):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(88)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Jobling S., Hoare S. A., Sumpter J. P., Parker M. G. Environmentally persistent alkylphenolic compounds are estrogenic. Endocrinology. 1994 Jul;135(1):175–182. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.1.8013351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zysk J. R., Johnson B., Ozenberger B. A., Bingham B., Gorski J. Selective uptake of estrogenic compounds by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a mechanism for antiestrogen resistance in yeast expressing the mammalian estrogen receptor. Endocrinology. 1995 Mar;136(3):1323–1326. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.3.7867588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vom Saal F. S., Nagel S. C., Palanza P., Boechler M., Parmigiani S., Welshons W. V. Estrogenic pesticides: binding relative to estradiol in MCF-7 cells and effects of exposure during fetal life on subsequent territorial behaviour in male mice. Toxicol Lett. 1995 May;77(1-3):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(95)03316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]