Abstract
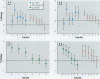
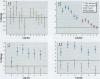
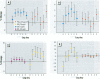
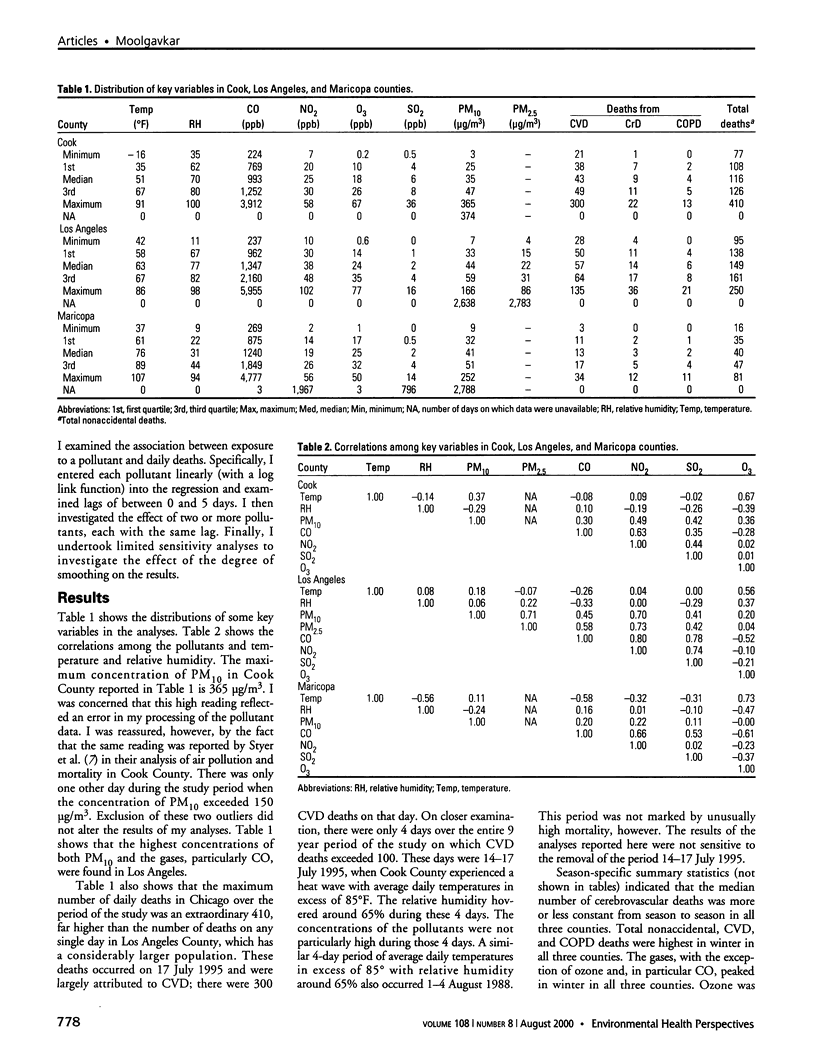
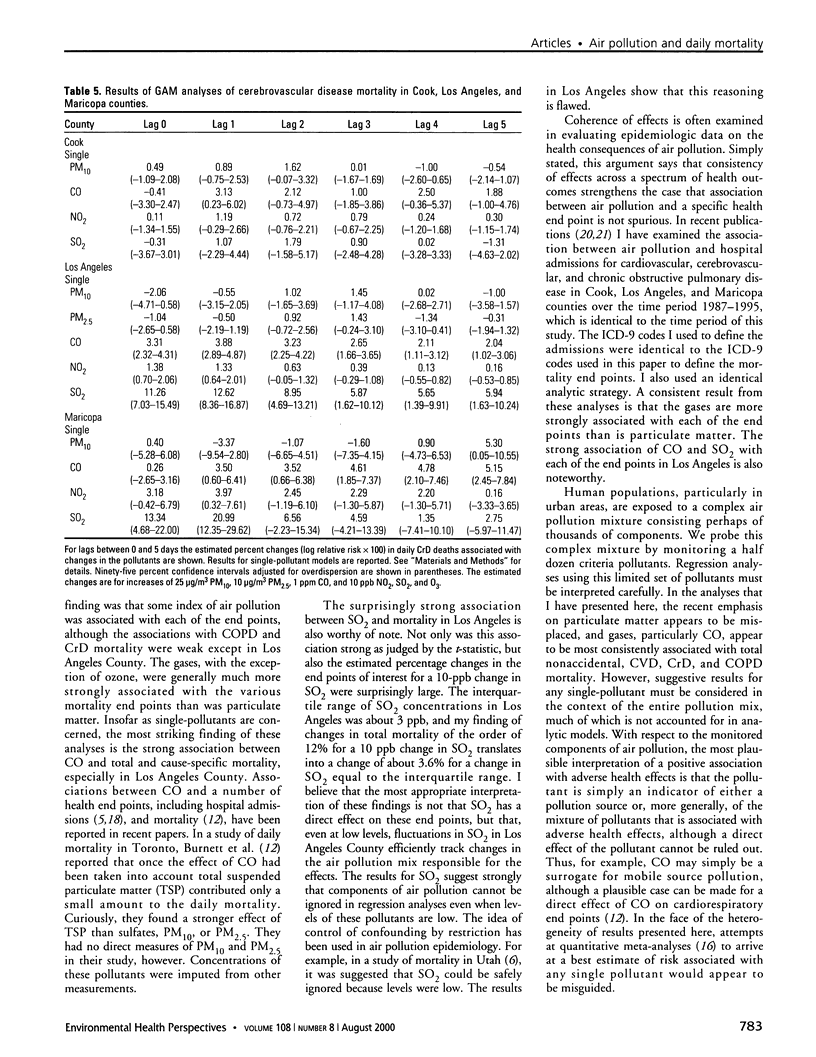
I used generalized additive models to analyze the time-series of daily total nonaccidental and cause-specific (cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) deaths over the period 1987-1995 in three major U.S. metropolitan areas: Cook County, Los Angeles County, and Maricopa County. In all three counties I had monitoring information on particulate matter [less than/equal to] 10 microm (PM(10)), carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone. In Los Angeles, monitoring information on particulate matter [less than/equal to] 2.5 microm (PM(2.5)) was available as well. I present the results of both single and multi-pollutant analyses. Air pollution was associated with each of the mortality end points. With respect to the individual components of the pollution mix, the results indicate considerable heterogeneity of air pollution effects in the different geographic locations. In general, the gases, particularly CO, but not ozone, were much more strongly associated with mortality than was particulate matter. This association was particularly striking in Los Angeles County.
Full text
PDF
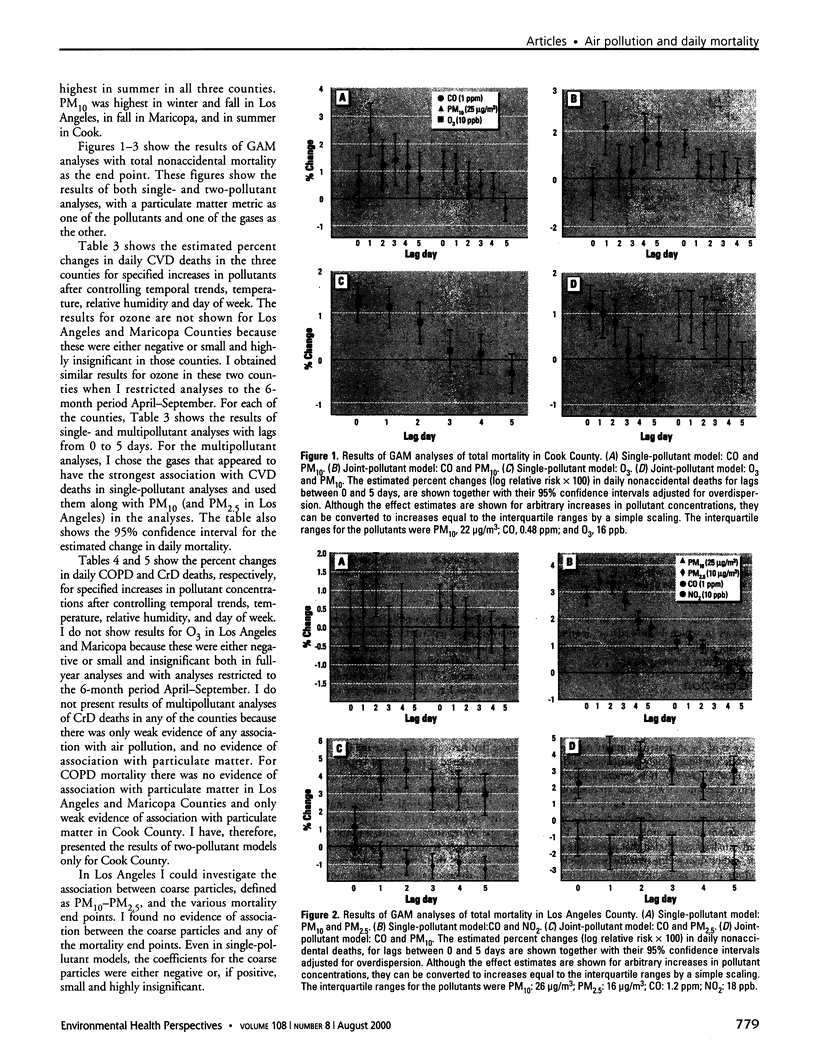
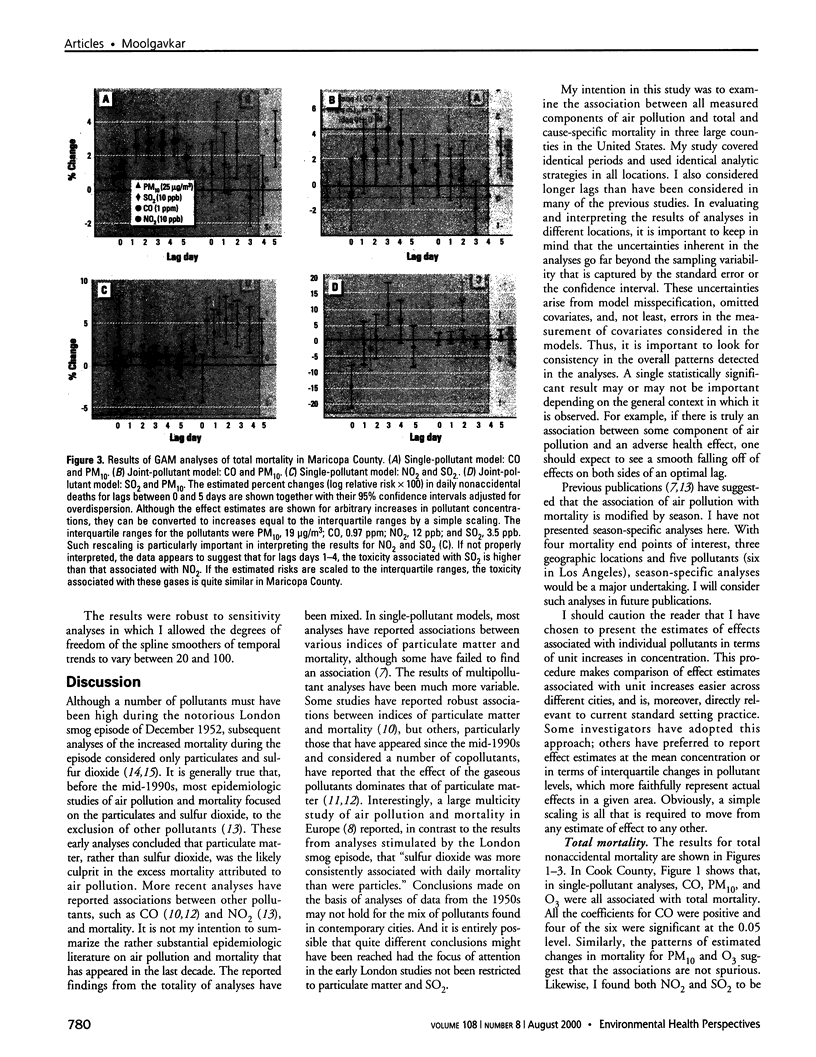
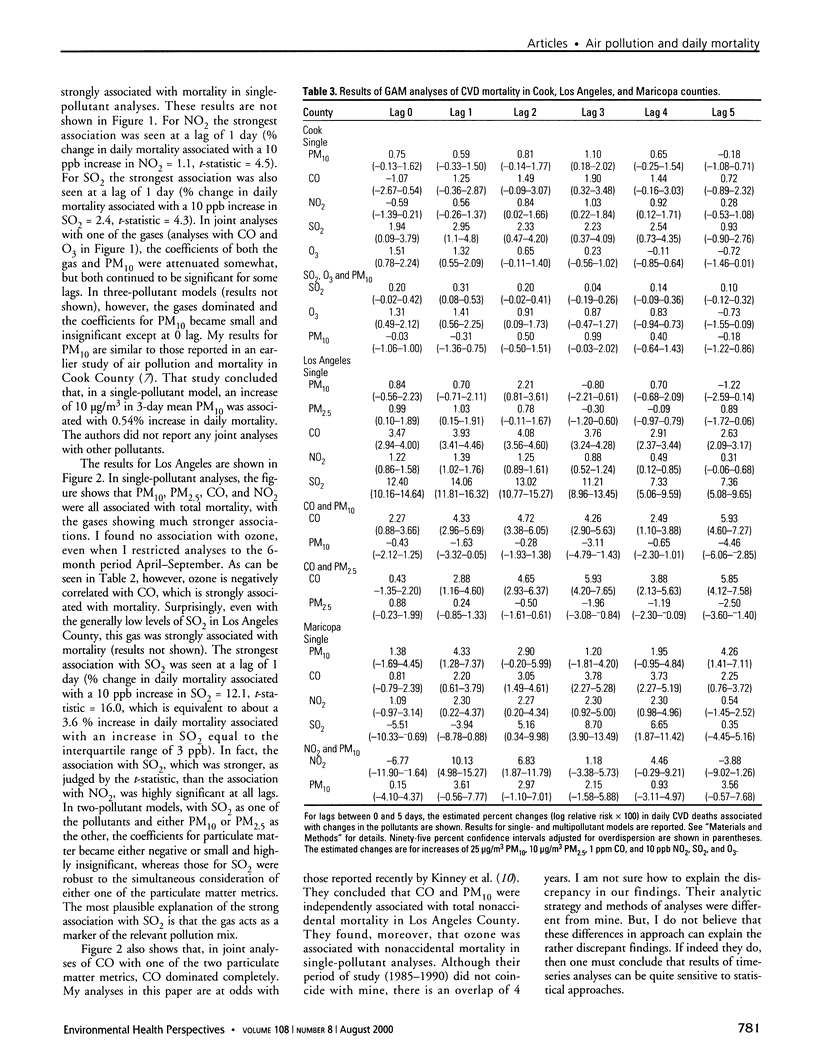
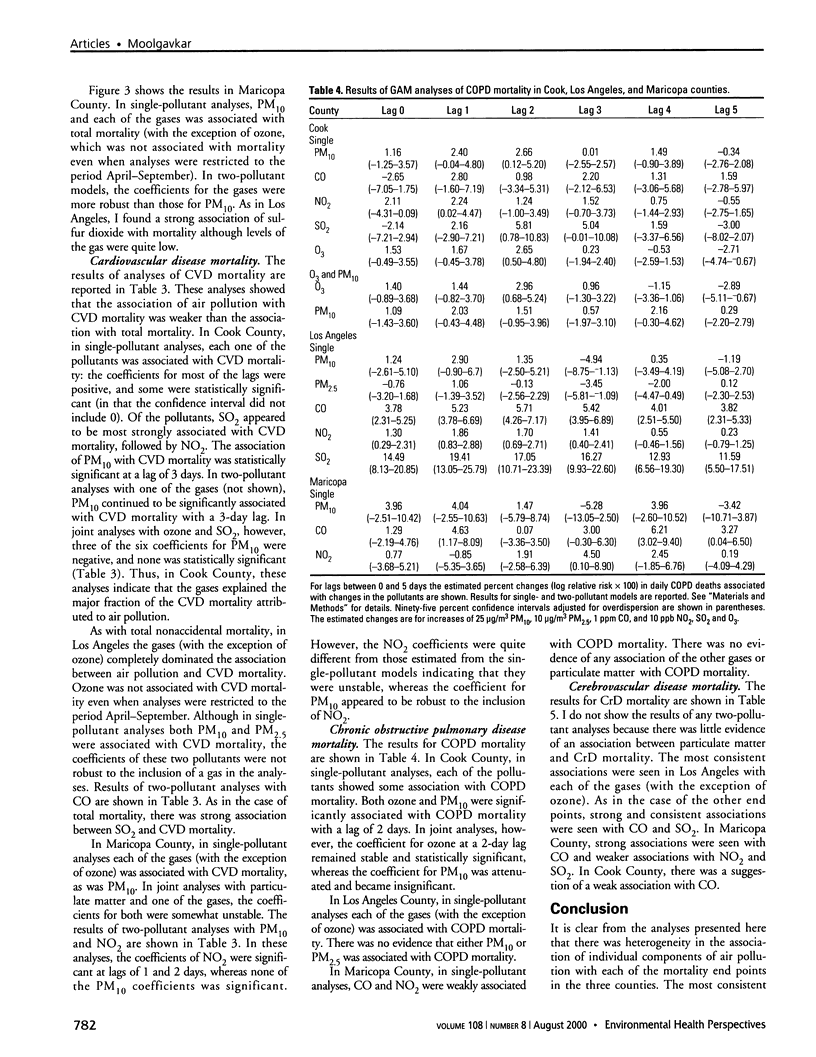

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnett R. T., Cakmak S., Brook J. R., Krewski D. The role of particulate size and chemistry in the association between summertime ambient air pollution and hospitalization for cardiorespiratory diseases. Environ Health Perspect. 1997 Jun;105(6):614–620. doi: 10.1289/ehp.97105614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett R. T., Cakmak S., Brook J. R. The effect of the urban ambient air pollution mix on daily mortality rates in 11 Canadian cities. Can J Public Health. 1998 May-Jun;89(3):152–156. doi: 10.1007/BF03404464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett R. T., Cakmak S., Raizenne M. E., Stieb D., Vincent R., Krewski D., Brook J. R., Philips O., Ozkaynak H. The association between ambient carbon monoxide levels and daily mortality in Toronto, Canada. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 1998 Aug;48(8):689–700. doi: 10.1080/10473289.1998.10463718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett R. T., Dales R. E., Brook J. R., Raizenne M. E., Krewski D. Association between ambient carbon monoxide levels and hospitalizations for congestive heart failure in the elderly in 10 Canadian cities. Epidemiology. 1997 Mar;8(2):162–167. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199703000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockery D. W., Speizer F. E., Stram D. O., Ware J. H., Spengler J. D., Ferris B. G., Jr Effects of inhalable particles on respiratory health of children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):587–594. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney P. L., Ozkaynak H. Associations of daily mortality and air pollution in Los Angeles County. Environ Res. 1991 Apr;54(2):99–120. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(05)80094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumdar S., Schimmel H., Higgins I. T. Relation of daily mortality to air pollution: an analysis of 14 London winters, 1958/59-1971/72. Arch Environ Health. 1982 Jul-Aug;37(4):213–220. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1982.10667567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolgavkar S. H., Luebeck E. G. A critical review of the evidence on particulate air pollution and mortality. Epidemiology. 1996 Jul;7(4):420–428. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199607000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolgavkar S. H., Luebeck E. G., Anderson E. L. Air pollution and hospital admissions for respiratory causes in Minneapolis-St. Paul and Birmingham. Epidemiology. 1997 Jul;8(4):364–370. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199707000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. A., 3rd, Schwartz J., Ransom M. R. Daily mortality and PM10 pollution in Utah Valley. Arch Environ Health. 1992 May-Jun;47(3):211–217. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1992.9938351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. Air pollution and daily mortality: a review and meta analysis. Environ Res. 1994 Jan;64(1):36–52. doi: 10.1006/enrs.1994.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Marcus A. Mortality and air pollution in London: a time series analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Jan;131(1):185–194. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Slater D., Larson T. V., Pierson W. E., Koenig J. Q. Particulate air pollution and hospital emergency room visits for asthma in Seattle. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):826–831. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard L., Levy D., Norris G., Larson T. V., Koenig J. Q. Effects of ambient air pollution on nonelderly asthma hospital admissions in Seattle, Washington, 1987-1994. Epidemiology. 1999 Jan;10(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styer P., McMillan N., Gao F., Davis J., Sacks J. Effect of outdoor airborne particulate matter on daily death counts. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 May;103(5):490–497. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. H., Ferris B. G., Jr, Dockery D. W., Spengler J. D., Stram D. O., Speizer F. E. Effects of ambient sulfur oxides and suspended particles on respiratory health of preadolescent children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):834–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmirou D., Schwartz J., Saez M., Zanobetti A., Wojtyniak B., Touloumi G., Spix C., Ponce de León A., Le Moullec Y., Bacharova L. Time-series analysis of air pollution and cause-specific mortality. Epidemiology. 1998 Sep;9(5):495–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]