Abstract
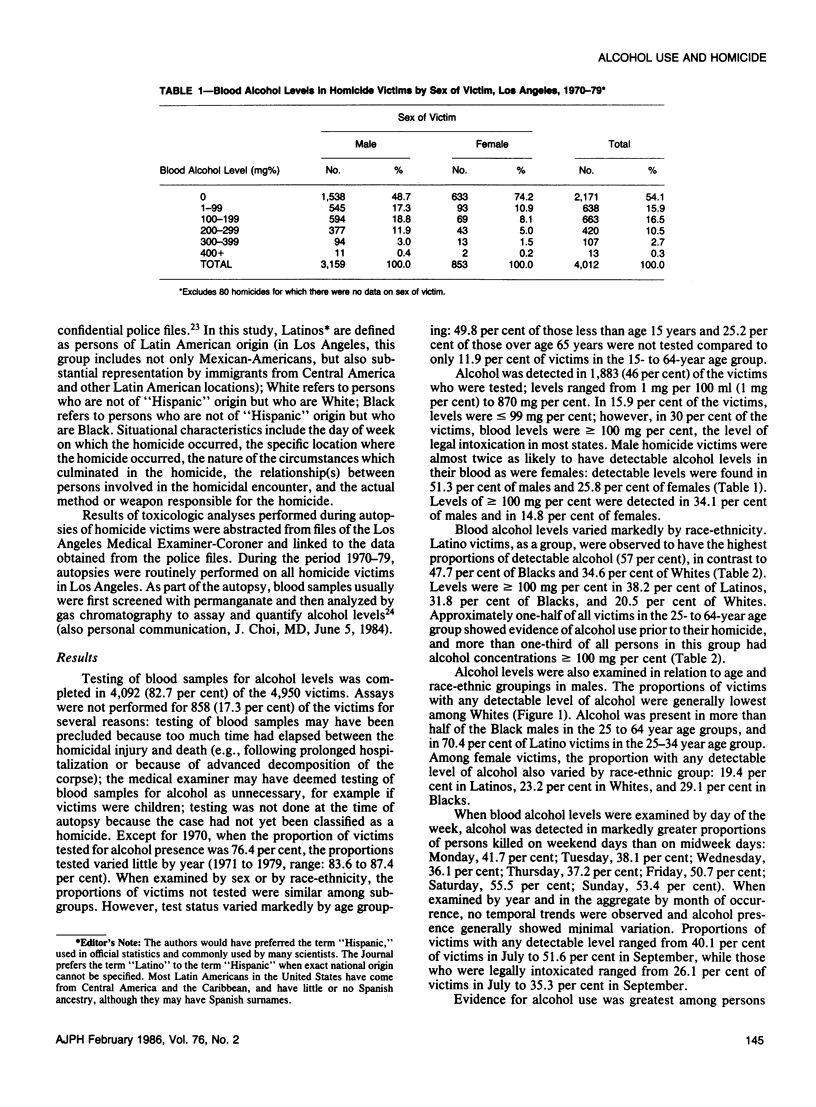
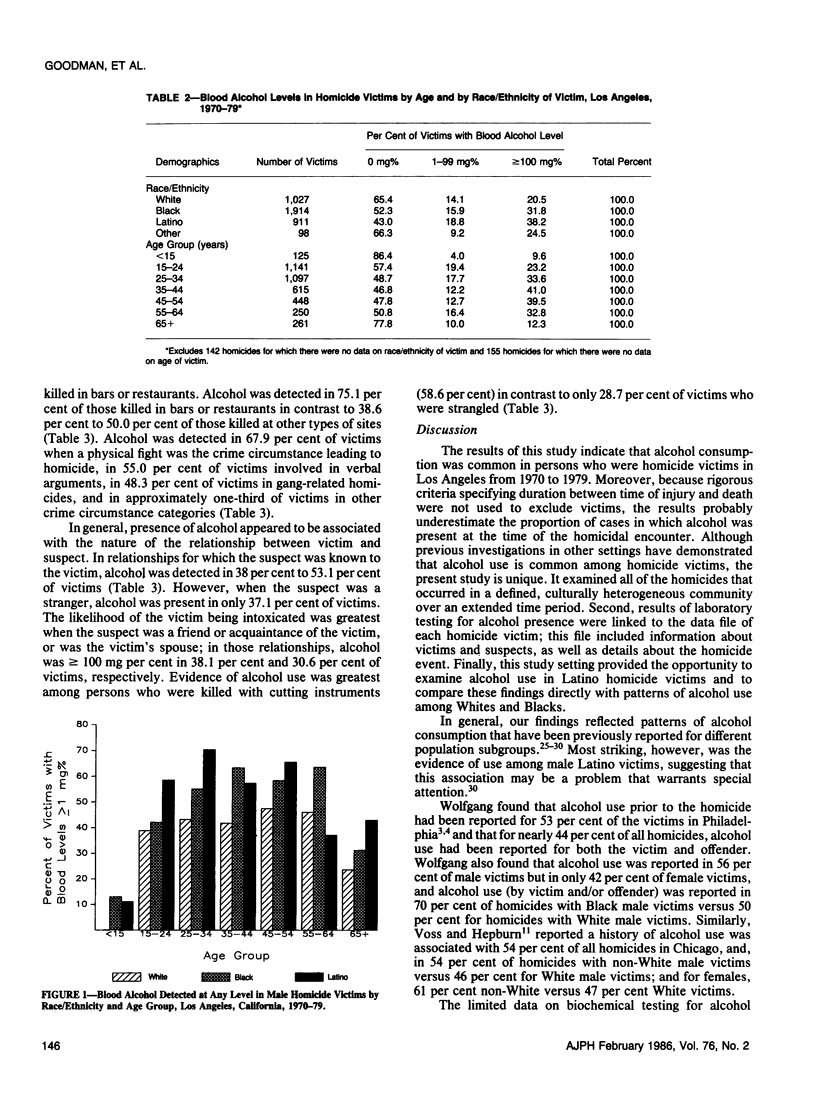
To characterize the relationship between alcohol use and homicide victimization, we used data from the Los Angeles City Police Department and the Los Angeles Medical Examiner's Office to study 4,950 victims of criminal homicides in Los Angeles in the period 1970-79. Alcohol was detected in the blood of 1,883 (46 per cent) of the 4,092 victims who were tested. In 30 per cent of those tested, the blood alcohol level was greater than or equal to 100 mg/100 ml, the level of legal intoxication in most states. Blood alcohol was present most commonly in victims who were male, young, and Latino, categories where rates have been increasing at an alarming pace. Alcohol was also detected most commonly in victims killed during weekends, when homicides occurred in bars or restaurants, when homicides resulted from physical fights or verbal arguments, when victims were friends or acquaintances of offenders, and when homicides resulted from stabbings. The evidence for alcohol use by homicide victims focuses attention on the need for controlled epidemiologic studies of the role played by alcohol as a risk factor in homicide and on the importance of considering situational variables in developing approaches to homicide prevention.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argeriou M. Daily alcohol consumption patterns in Boston: some findings and a partial test of the Tuesday hypothesis. J Stud Alcohol. 1975 Nov;36(11):1578–1583. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1975.36.1578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. P., Robertson L. S., Spitz W. U. Tattoos, alcohol, and violent death. J Forensic Sci. 1971 Apr;16(2):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Buss A. H., Carpenter J. A. Alcohol and human physical aggression. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1969 Dec;30(4):870–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyatzis R. E. The predisposition toward alcohol-related interpersonal aggression in men. J Stud Alcohol. 1975 Sep;36(9):1196–1207. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1975.36.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantino J. P., Kuller L. H., Perper J. A., Cypess R. H. An epidemiologic study of homicides in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Oct;106(4):314–324. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine E. W., Steer R. A., Scoles P. E. Relationship between blood alcohol concentration and self-reported drinking behavior. J Stud Alcohol. 1978 Mar;39(3):466–472. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1978.39.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham K., La Rocque L., Yetman R., Ross T. J., Guistra E. Aggression and barroom environments. J Stud Alcohol. 1980 Mar;41(3):277–292. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1980.41.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harford T. C., Gerstel E. K. Age-related patterns of daily alcohol consumption in metropolitan Boston. J Stud Alcohol. 1981 Nov;42(11):1062–1066. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1981.42.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEROUX L. C., SMITH L. S. VIOLENT DEATHS AND ALCOHOLIC INTOXICATION. J Forensic Med. 1964 Oct-Dec;11:131–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROHM R. B., WOLFGANG M. E. The relationship between alcohol and criminal homicide. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1956 Sep;17(3):411–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. P., Gammon C. B., Capasso D. R. Aggression as a function of the interaction of alcohol and threat. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1976 Nov;34(5):938–941. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.34.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. P., Gammon C. B. Effects of type and dose of alcohol on human physical aggression. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1975 Jul;32(1):169–175. doi: 10.1037/h0076812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F. Feasibility of determining blood alcohol concentrations in social drinking settings. J Stud Alcohol. 1978 Jan;39(1):201–206. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1978.39.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichner A., Pihl R. O. Effects of alcohol and instigator intent on human aggression. J Stud Alcohol. 1980 Mar;41(3):265–276. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1980.41.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



