Abstract
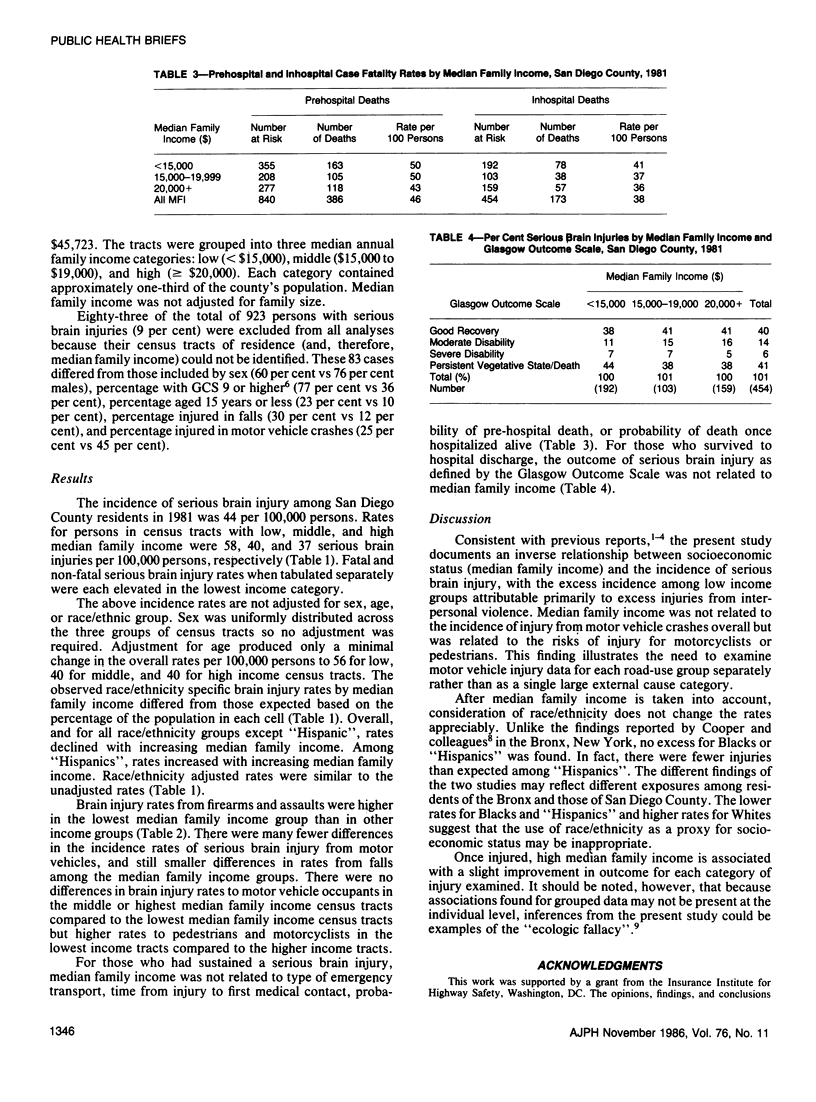
Among residents of San Diego County, California the incidence and external causes of serious brain injury were related to the median family income of the census tract of residency. Low income tracts had high incidence rates--a finding not changed by adjustment for age and race/ethnicity. For those injured, the type of emergency transport, time from injury to treatment, and outcome of treatment were not related to the median income of the census tract of residency.
Full text
PDF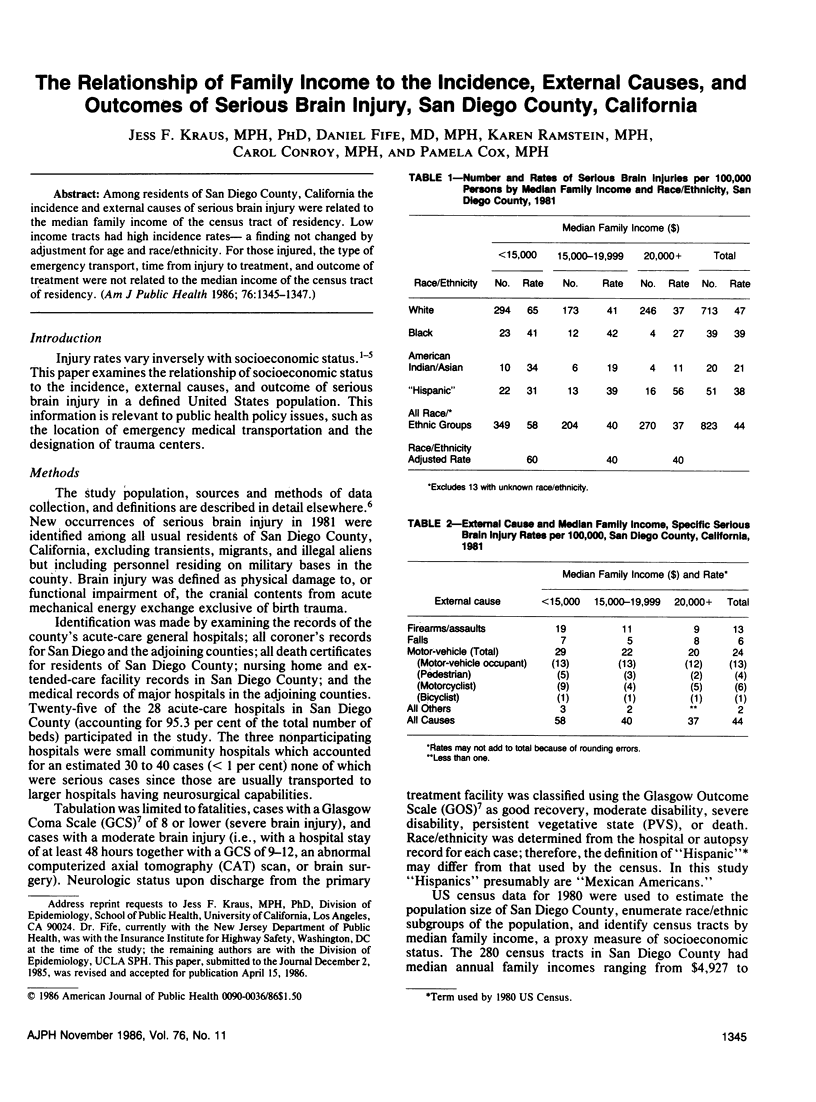

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kraus J. F., Black M. A., Hessol N., Ley P., Rokaw W., Sullivan C., Bowers S., Knowlton S., Marshall L. The incidence of acute brain injury and serious impairment in a defined population. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Feb;119(2):186–201. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierley M. C., Baker S. P. Fatal house fires in an urban population. JAMA. 1983 Mar 18;249(11):1466–1468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman S., Coonley-Hoganson R., Desai B. T. Comparative head trauma experiences in two socioeconomically different Chicago-area communities: a population study. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Apr;119(4):570–580. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



