Abstract
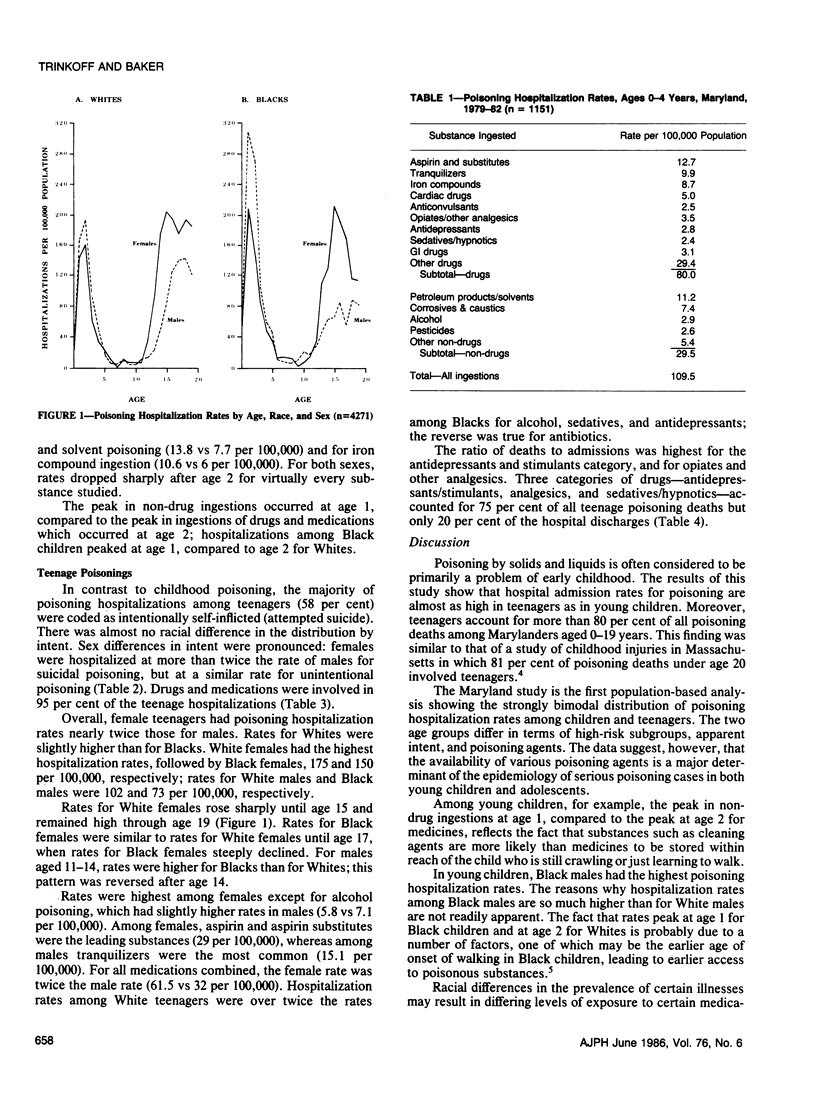
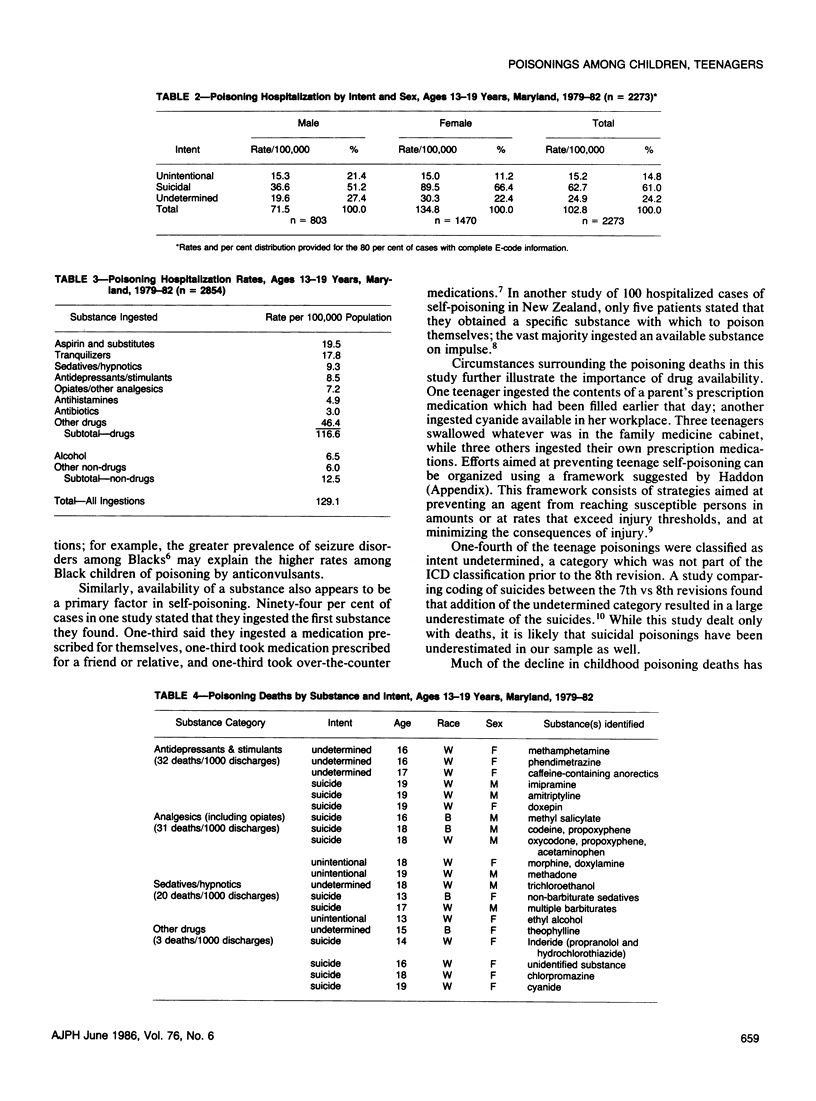
Twenty-four deaths and 4,271 hospital admissions due to poisoning occurred in the 0-19 year age group in Maryland during 1979-82. Four-fifths of the deaths (83 per cent) and two-thirds of the admissions involved teenagers. Among teenagers, four out of five admissions and deaths were of suicidal or undetermined intent. Black males had the highest hospitalization rate among young children, and White females among teenagers. The most common poisons ingested by children aged 0-4 years were aspirin, solvents and petroleum products, tranquilizers, and iron compounds. Among teenagers, aspirin, tranquilizers, sedatives, and antidepressants were the most common substances ingested, with antidepressants and stimulants most common among the fatalities. Reducing the availability and toxicity of the most hazardous drugs is important if morbidity and mortality from poisoning are to be prevented.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. P. Childhood injuries: the community approach to prevention. J Public Health Policy. 1981 Sep;2(3):235–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capute A. J., Shapiro B. K., Palmer F. B., Ross A., Wachtel R. C. Normal gross motor development: the influences of race, sex and socio-economic status. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1985 Oct;27(5):635–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1985.tb14136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. S., Guyer B., Kotelchuck M., Bass J., Lovejoy F. H., Jr, McLoughlin E., Mehta K. A strategy for the reduction of childhood injuries in Massachusetts: SCIPP. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 14;307(16):1015–1019. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210143071613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. I. Self-poisoning with drugs: the past 20 years in Sheffield. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 1;1(6052):28–29. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6052.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large R. G., Epston A., Kirker J. M., Kydd R. R. Self poisoning: who supplies the drugs? 100 examples. N Z Med J. 1980 Mar 26;91(656):218–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton W. W. An evaluation of the Poison Prevention Packaging Act. Pediatrics. 1982 Mar;69(3):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshauer M. E., Monk M. Problems in suicide statistics for whites and blacks. Am J Public Health. 1978 Apr;68(4):383–388. doi: 10.2105/ajph.68.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



