Abstract
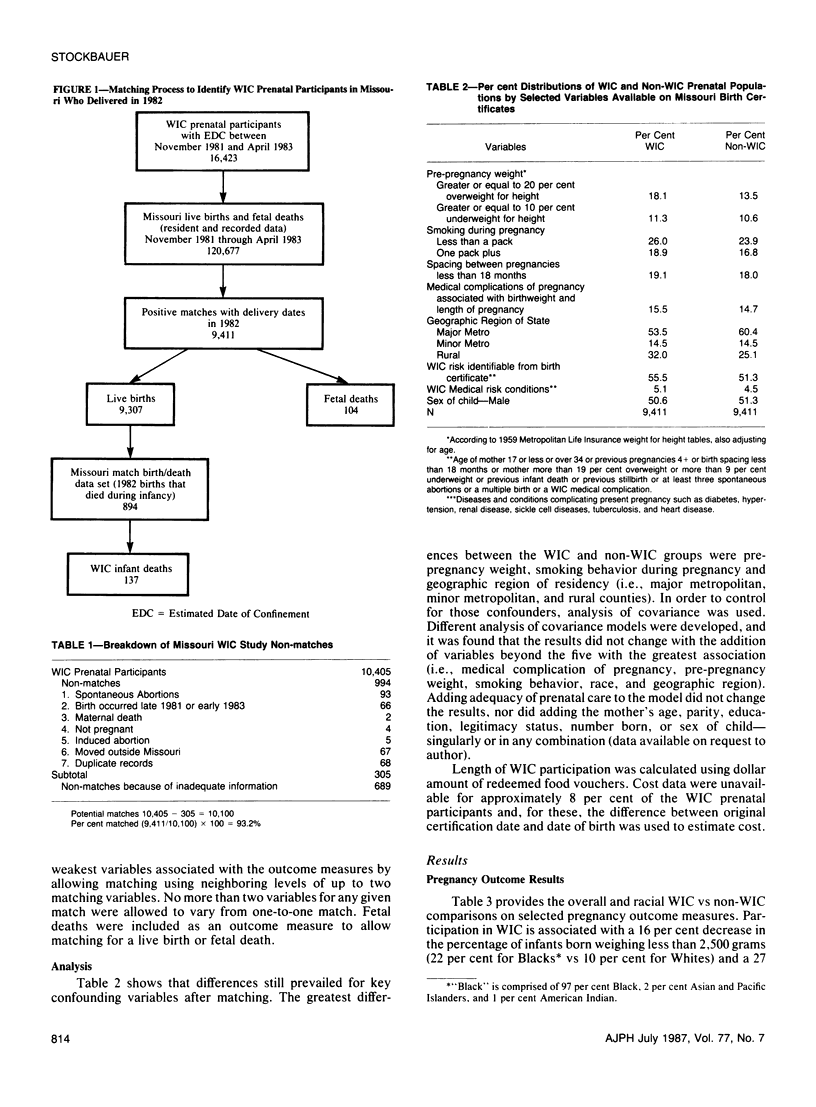
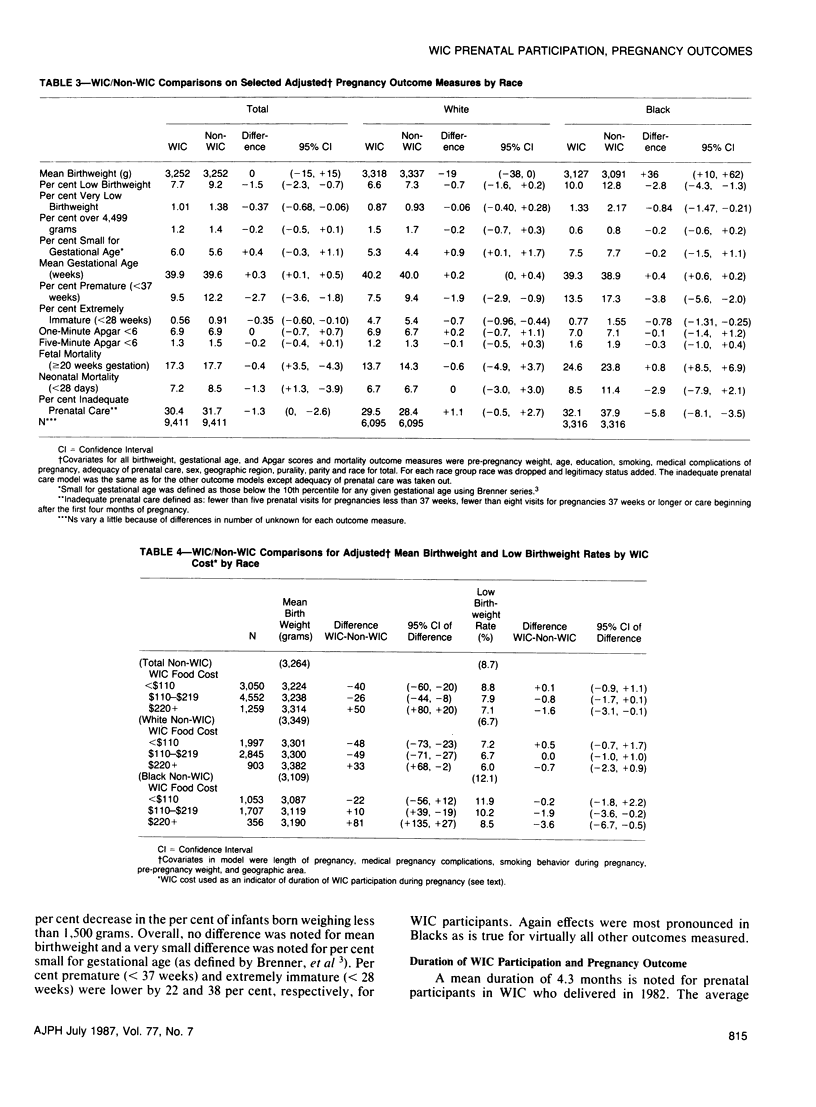
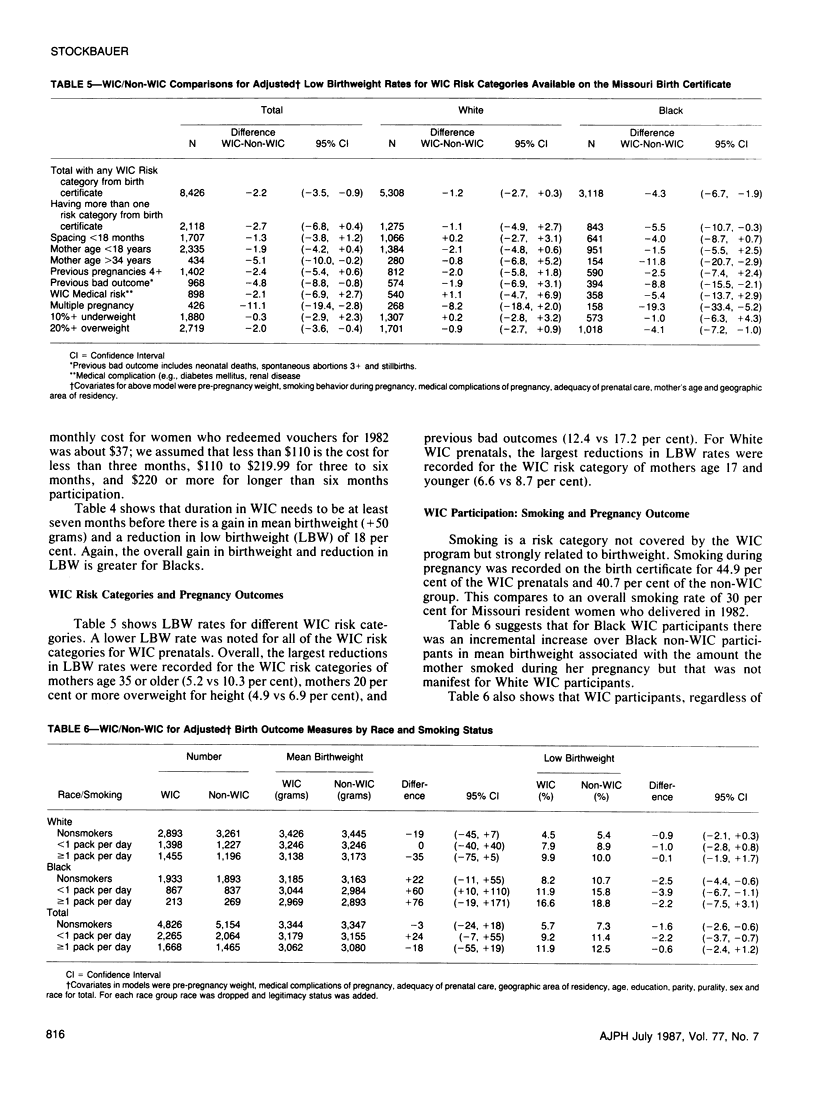
We studied the association of WIC prenatal supplementation with pregnancy outcome using Missouri WIC participants who delivered in 1982 linked with their offspring's birth/fetal death certificates. A 93 per cent match rate resulted in a final study population of 9,411 pregnancies. A control population of like number was acquired by matching on key demographic characteristics. The majority of the results generally confirm the results of a 1980 Missouri study; WIC participation was associated with decreases in low birthweight (7.8 vs 9.2 per cent), prematurity (9.7 vs 12.0 per cent) and inadequate prenatal care (30.5 vs 31.7 per cent), and an increase in mean gestational age (39.9 vs 39.6 weeks). Low birthweight rates were lower for infants of WIC participants in each of the risk categories reviewed. As noted in the 1980 study, duration of WIC of at least seven months was needed before improvements in birthweight outcomes measures were noted.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner W. E., Edelman D. A., Hendricks C. H. A standard of fetal growth for the United States of America. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Nov 1;126(5):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(76)90748-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edozien J. C., Switzer B. R., Bryan R. B. Medical evaluation of the special supplemental food program for women, infants, and children. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Mar;32(3):677–692. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.3.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth J. C., Ellestad-Sayed J. J., King J., Dilling L. A. Fetal growth retardation in cigarette-smoking mothers is not due to decreased maternal food intake. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Jul 15;137(6):719–723. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(15)33248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. T., Gershoff S., Reed R., Austin J. E. Evaluation of the effect of WIC supplemental feeding on birth weight. J Am Diet Assoc. 1982 Mar;80(3):220–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotelchuck M., Schwartz J. B., Anderka M. T., Finison K. S. WIC participation and pregnancy outcomes: Massachusetts Statewide Evaluation Project. Am J Public Health. 1984 Oct;74(10):1086–1092. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.10.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm W. F. WIC prenatal participation and its relationship to newborn Medicaid costs in Missouri: a cost/benefit analysis. Am J Public Health. 1985 Aug;75(8):851–857. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.8.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm W. Smoking and pregnancy outcome. Mo Med. 1980 Oct;77(10):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A., Moar V., Ounsted M. The relative contributions of different maternal factors in small-for-gestational-age pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1981 Sep;12(3):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(81)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockbauer J. W. Evaluation of the Missouri WIC program: prenatal components. J Am Diet Assoc. 1986 Jan;86(1):61–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


