Abstract
A controlled study of mechanical ventilation has been performed in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. 168 infants in respiratory failure were ventilated and 53 similar infants were not.
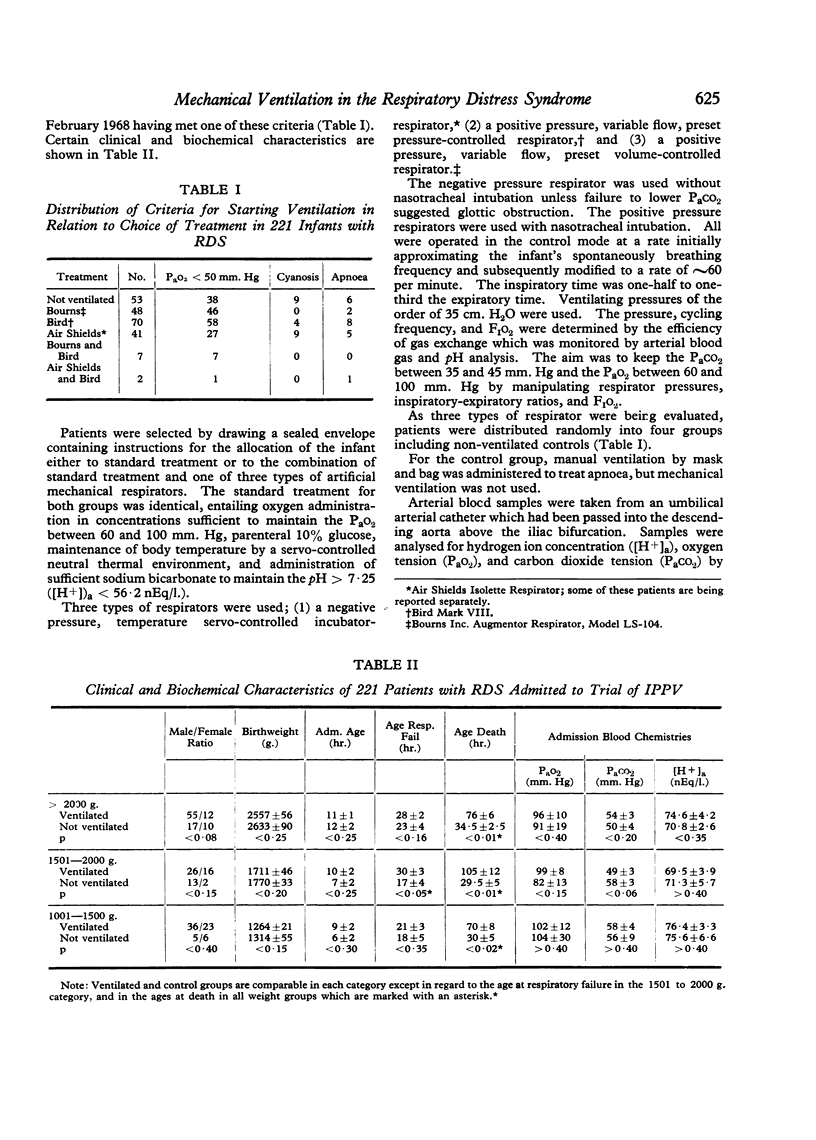
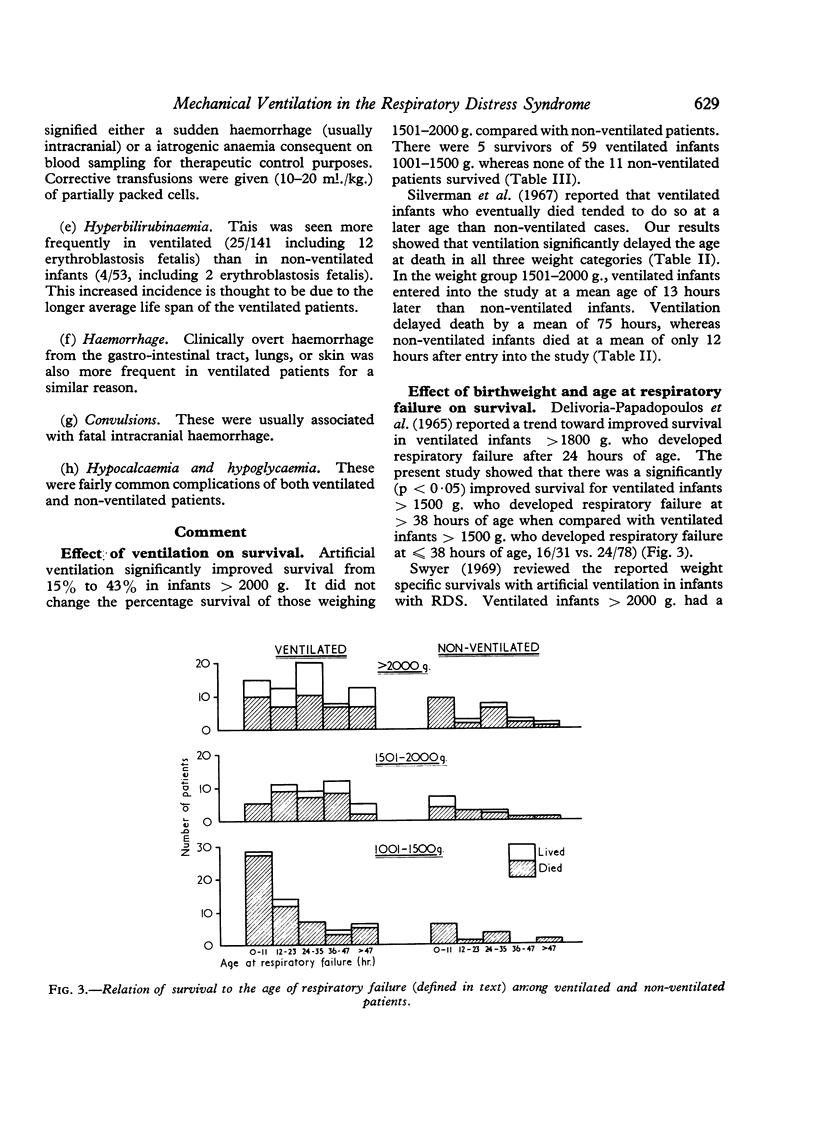
Artificial mechanical ventilation improved survival in infants weighing more than 2000 g. from 15% to 43% (4/27 vs. 29/67, p < 0·025).
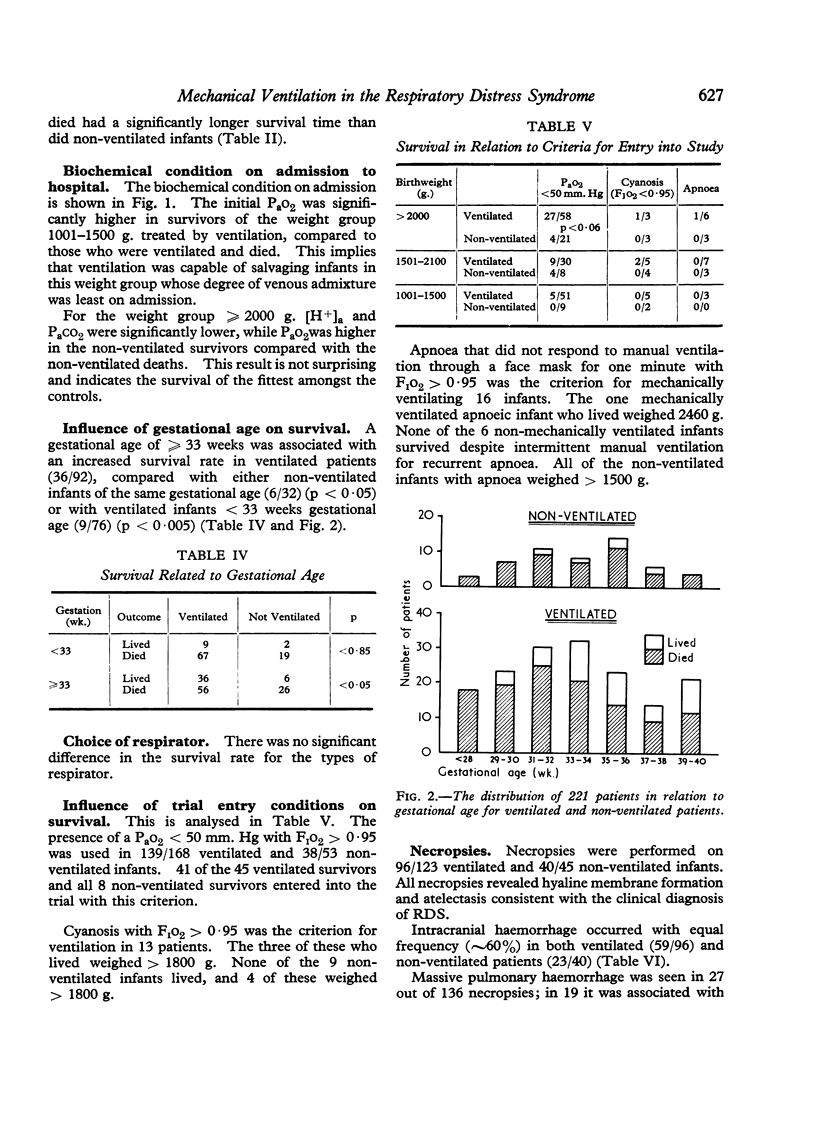
Infants who weighed more than 1500 g. and developed respiratory failure at less than 38 hours of age had an improved survival (16/31) on ventilatory treatment, as compared with infants more than 1500 g. ventilated at more than 38 hours of age (24/78) (p < 0·05).
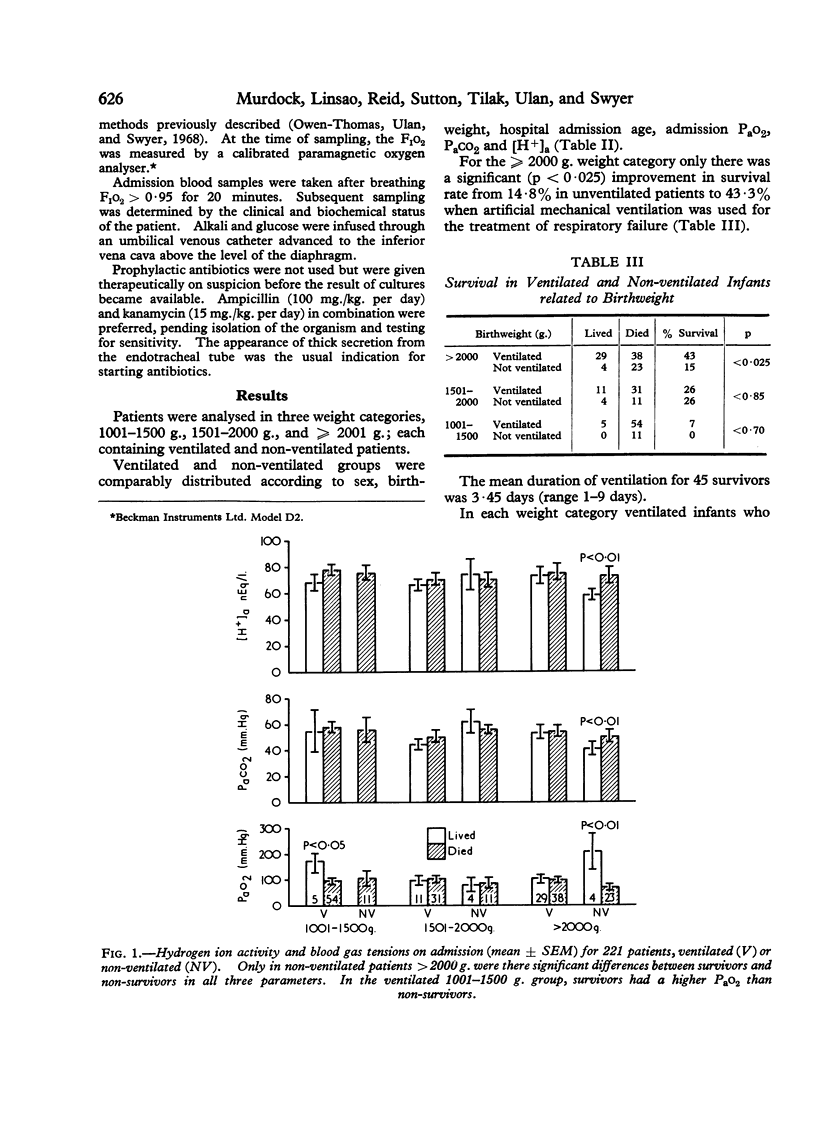
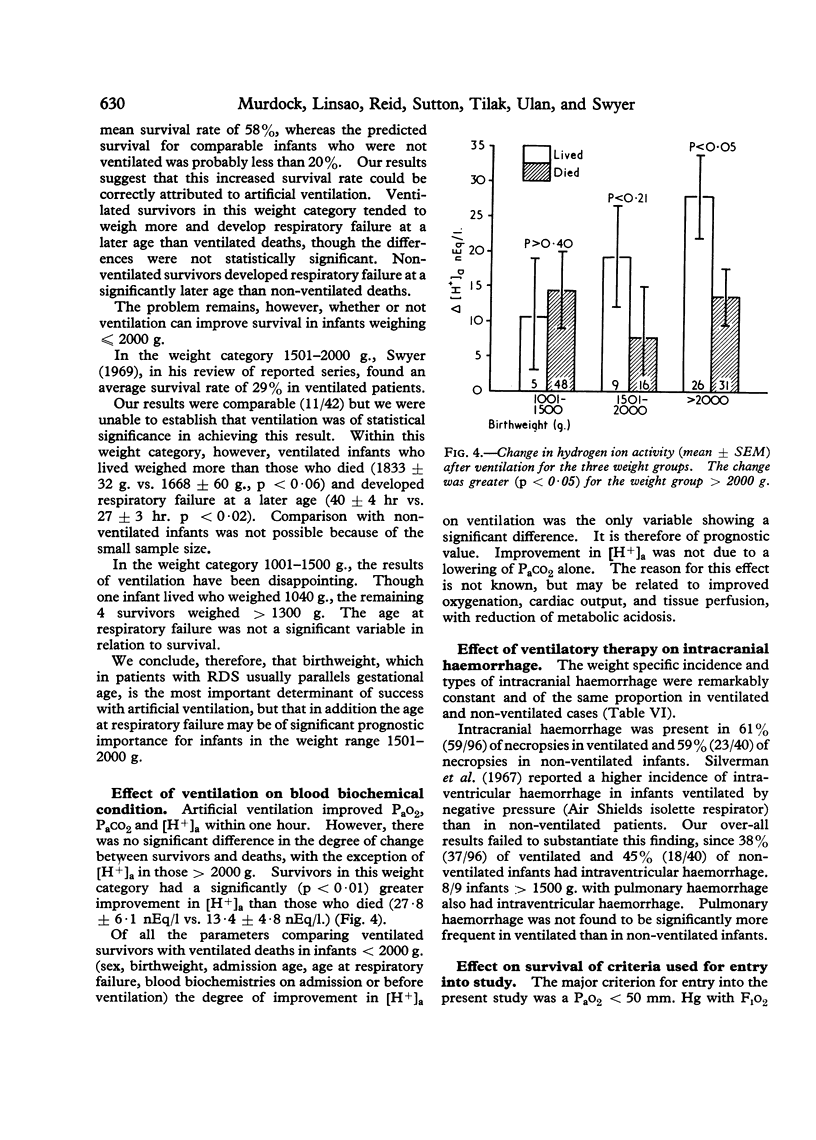
Artificial ventilation improved Pao2, Paco2, and [H+]a within one hour, but it was only the change in [H+]a in infants more than 2000 g. which was of prognostic significance.
Survival rates were similar for each of the three types of respirator used.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson T. M., Collins L. M., Dehan M., Hawker J. M., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Mechanical ventilation in newborn infants with respiratory railure. Lancet. 1968 Aug 3;2(7562):227–231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCK J. B., MCCORMACK W. C. A NASAL MASK FOR PREMATURE INFANTS. J Pediatr. 1965 Jan;66:123–125. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80348-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boston R. W., Geller F., Smith C. A. Arterial blood gas tensions and acid-base balance in the management of the respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1966 Jan;68(1):74–89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELIVORIA-PAPADOPOULOS M., SWYER P. R. ASSISTED VENTILATION IN TERMINAL HYALINE MEMBRANE DISEASE. Arch Dis Child. 1964 Oct;39:481–484. doi: 10.1136/adc.39.207.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALD I., KERR M. M., MACDONALD I. R. Respiratory phenomena in the newborn; experiments in their measurement and assistance. Scott Med J. 1958 Apr;3(4):151–164. doi: 10.1177/003693305800300401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
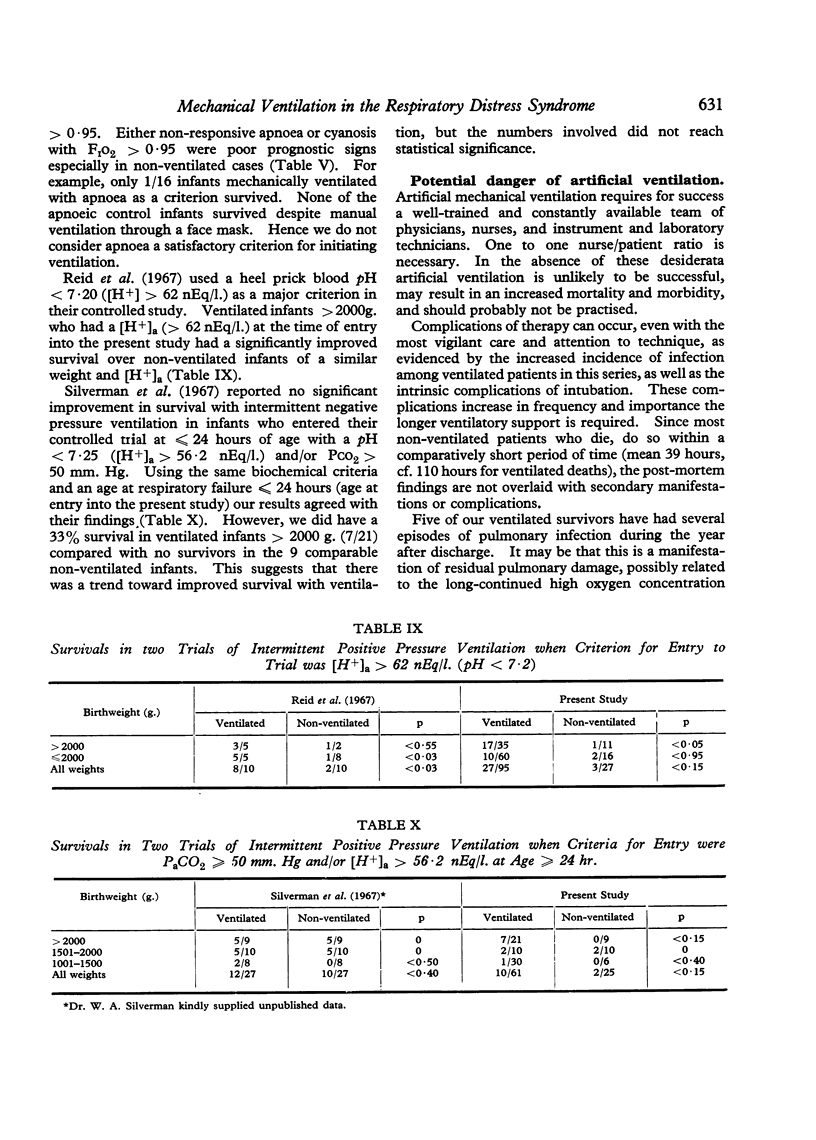
- Delivoria-Papadopoulos M., Levison H., Swyer P. R. Intermittent positive pressure respiration as a treatment in severe respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1965 Oct;40(213):474–479. doi: 10.1136/adc.40.213.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez P. C., Noakes M., Barrie H. A prognostic score for use in the respiratory-distress syndrome. Lancet. 1969 Apr 19;1(7599):808–810. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEESE H. D., WITTMANN W., MALAN A. F. The management of the respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn with positive-pressure respiration. S Afr Med J. 1963 Jan 19;37:123–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsao L. S., Levison H., Swyer P. R. Negative pressure artificial respiration: use in treatment of respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn. Can Med Assoc J. 1970 Mar 28;102(6):602–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn M. A., Tilak K. S., Swyer P. R. A controlled trial of assisted ventilation using an oro-nasal mask. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Aug;45(242):453–459. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.242.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Thomas J. B., Ulan O. A., Swyer P. R. The effect of varying inspiratory gas flow rate on arterial oxygenation during IPPV in the respiratory distress syndrome. Br J Anaesth. 1968 Jul;40(7):493–502. doi: 10.1093/bja/40.7.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID D. H., TUNSTALL M. E. TREATMENT OF RESPIRATORY-DISTRESS SYNDROME OF NEWBORN WITH NASOTRACHEAL INTUBATION AND INTERMITTENT POSITIVE-PRESSURE RESPIRATION. Lancet. 1965 Jun 5;1(7397):1196–1197. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92724-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. H., Tunstall M. E., Mitchell R. G. A controlled trial of artificial respiration in the respiratory-distress syndrome of the newborn. Lancet. 1967 Mar 11;1(7489):532–533. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAHLMAN M. T., YOUNG W. C., GRAY J., SHEPARD F. M. THE MANAGEMENT OF RESPIRATORY FAILURE IN THE IDIOPATHIC RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME OF PREMATURITY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 24;121:930–941. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb14263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWYER P. R., LEVISON H. THE CURRENT STATUS OF THE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME OF THE NEWLY BORN. Can Med Assoc J. 1965 Aug 21;93:335–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman W. A., Sinclair J. C., Gandy G. M., Finster M., Bauman W. A., Agate F. J., Jr A controlled trial of management of respiratory distress syndrome in a body-enclosing respirator. I. Evaluation of safety. Pediatrics. 1967 May;39(5):740–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. C., Engel K., Silverman W. A. Early correction of hypoxemia and acidemia in infants of low birth weight: a controlled trial of oxygen breathing, rapid alkali infusion, and assisted ventilation. Pediatrics. 1968 Oct;42(4):565–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahlman M. T., Battersby E. J., Shepard F. M., Blankenship W. J. Prognosis in hyaline-membrane disease. Use of a linear-discriminant. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 9;276(6):303–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702092760601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L., Ramos A. D., Outerbridge E. W., Beaudry P. H. Negative pressure artificial respiration: use in treatment of respiratory failure of the newborn. Can Med Assoc J. 1970 Mar 28;102(6):595–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS D. V., FLETCHER G., SUNSHINE P., SCHAFER I. A., KLAUS M. H. PROLONGED RESPIRATOR USE IN PULMONARY INSUFFICIENCY OF NEWBORN. JAMA. 1965 Jul 19;193:183–190. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090030005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



