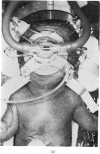
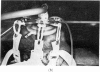
Abstract
A controlled study was performed to assess the effect of early assisted ventilation using a tight fitting face mask. Early mask ventilation reduced the number of infants requiring intubation, but did not significantly alter the survival rate.
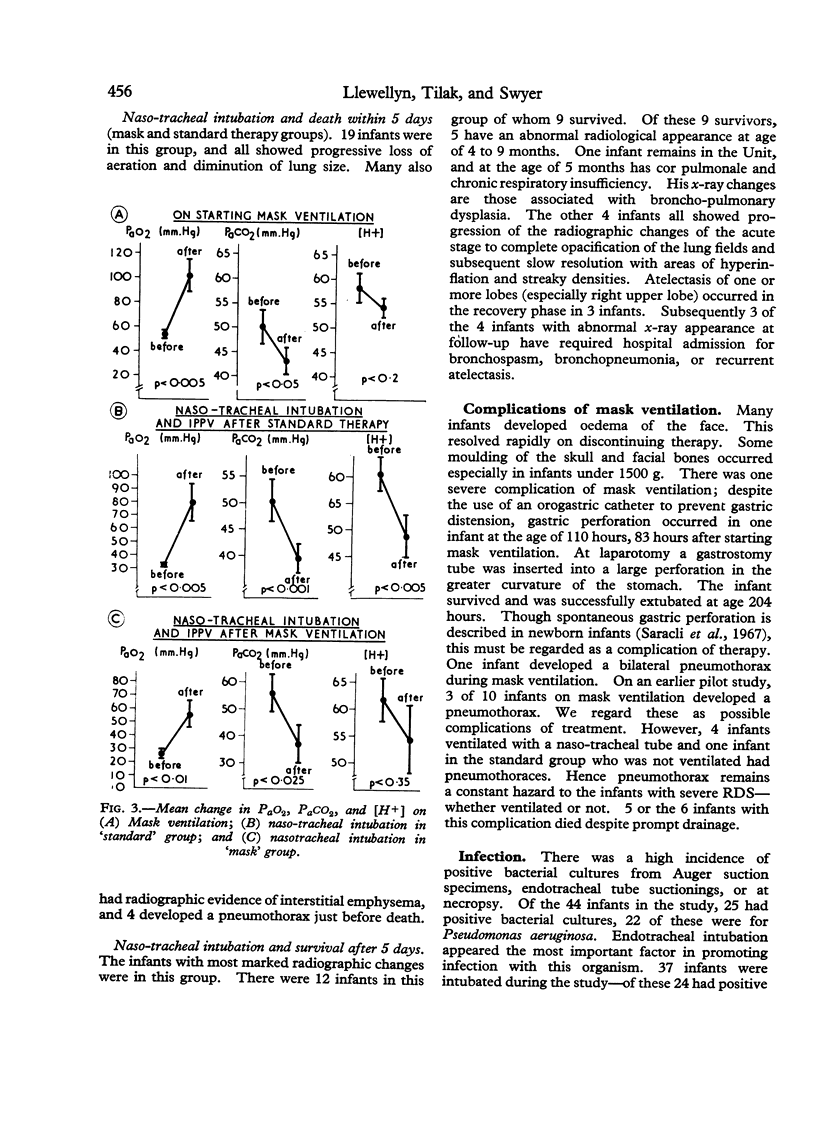
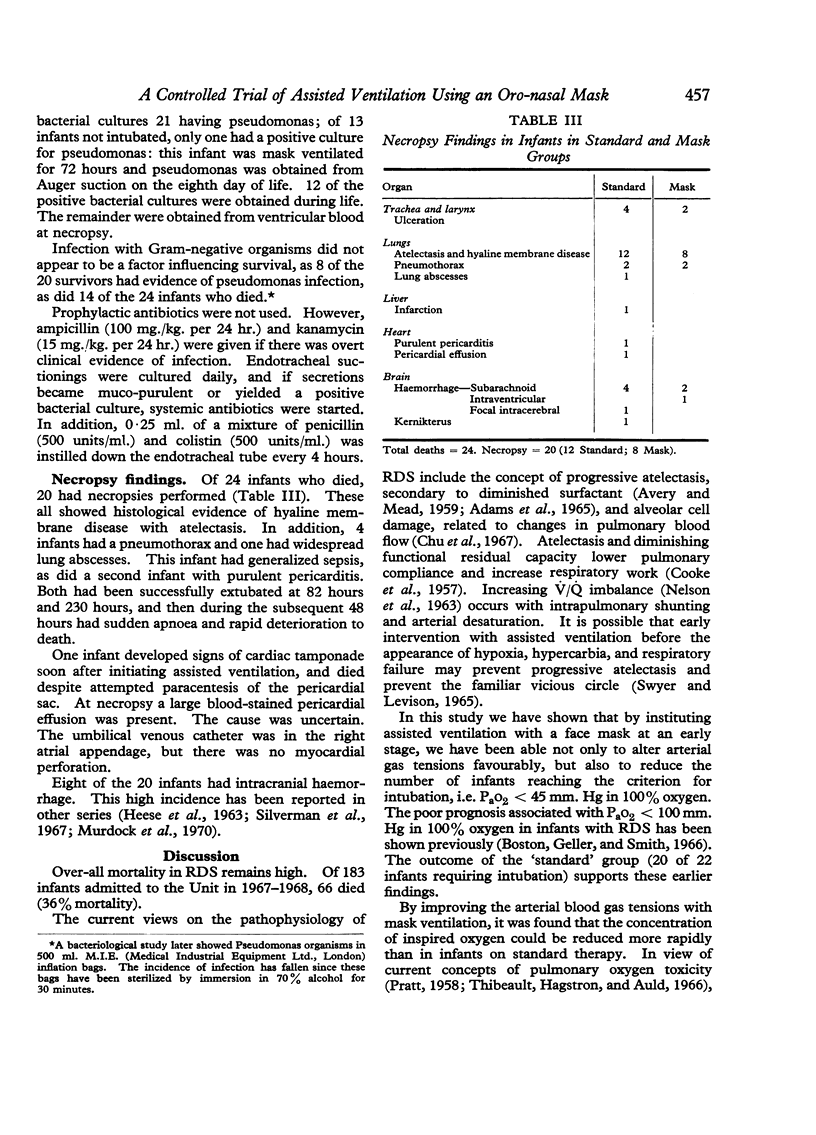
Complications were seen in infants during both mask ventilation and ventilation with a naso-tracheal tube. Persistent radiological changes were seen in 5 of 9 infants who survived after ventilation for more than 5 days..
Full text
PDF
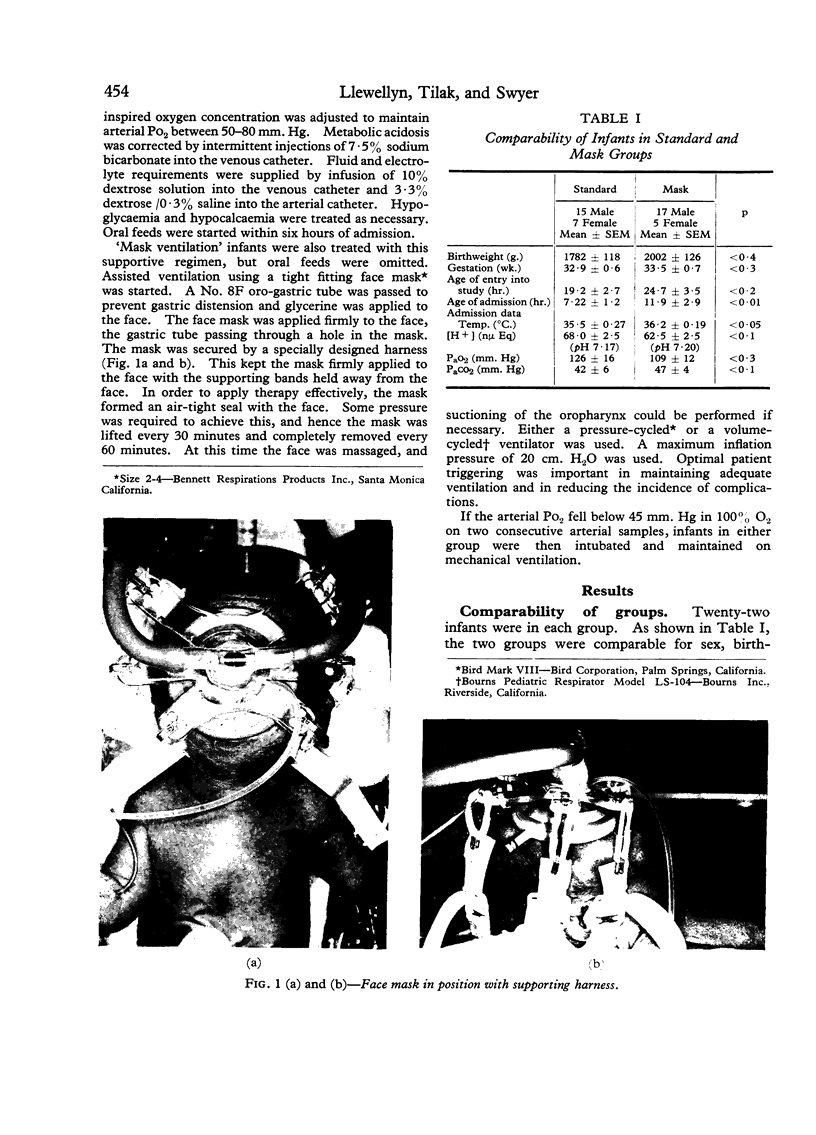
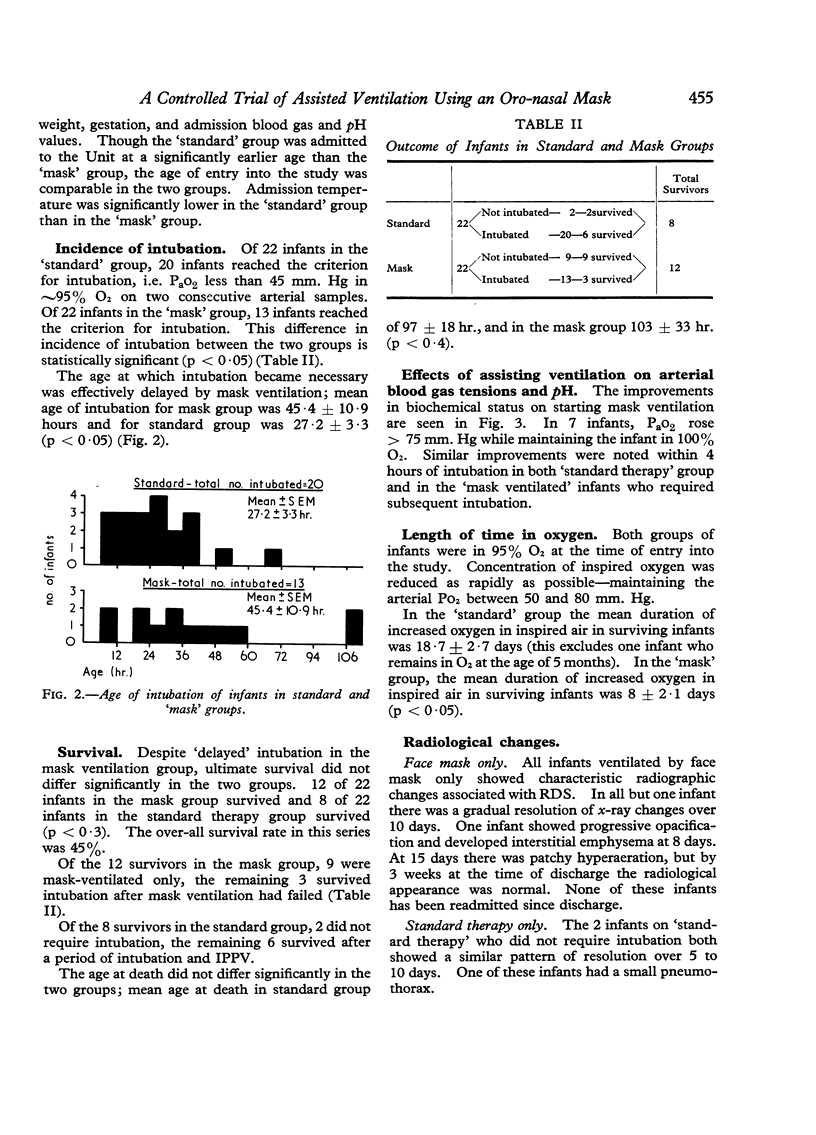


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS F. H., FUJIWARA T., EMMANOUILIDES G., SCUDDER A. SURFACE PROPERTIES AND LIPIDS FROM LUNGS OF INFANTS WITH HYALINE MEMBRANE DISEASE. J Pediatr. 1965 Feb;66:357–364. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AVERY M. E., MEAD J. Surface properties in relation to atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 1):517–523. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010519001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson T. M., Collins L. M., Dehan M., Hawker J. M., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Mechanical ventilation in newborn infants with respiratory railure. Lancet. 1968 Aug 3;2(7562):227–231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON F., CELANDER O., HAGLUND G., NILSSON L., PAULSEN L., RENCK L. Positive-pressure respirator treatment of severe pulmonary insufficiency in the newborn infant; a clinical report. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1958;2(1):37–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1958.tb05249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCK J. B., MCCORMACK W. C. A NASAL MASK FOR PREMATURE INFANTS. J Pediatr. 1965 Jan;66:123–125. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80348-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boston R. W., Geller F., Smith C. A. Arterial blood gas tensions and acid-base balance in the management of the respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1966 Jan;68(1):74–89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK C. D., SUTHERLAND J. M., SEGAL S., CHERRY R. B., MEAD J., MCILROY M. B., SMITH C. A. Studies of respiratory physiology in the newborn infant. III. Measurements of mechanics of respiration. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):440–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI103441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J., Clements J. A., Cotton E. K., Klaus M. H., Sweet A. Y., Tooley W. H., Bradley B. L., Brandorff L. C. Neonatal pulmonary ischemia. I. Clinical and physiological studies. Pediatrics. 1967 Oct;40(4 Suppl):709–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALD I., LORD J. Augmented respiration; studies in atelectasis neonatorum. Lancet. 1953 Jan 3;1(6749):9–17. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)92511-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delivoria-Papadopoulos M., Levison H., Swyer P. R. Intermittent positive pressure respiration as a treatment in severe respiratory distress syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1965 Oct;40(213):474–479. doi: 10.1136/adc.40.213.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEESE H. D., WITTMANN W., MALAN A. F. The management of the respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn with positive-pressure respiration. S Afr Med J. 1963 Jan 19;37:123–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northway W. H., Jr, Rosan R. C., Porter D. Y. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 16;276(7):357–368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702162760701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Thomas J. B., Ulan O. A., Swyer P. R. The effect of varying inspiratory gas flow rate on arterial oxygenation during IPPV in the respiratory distress syndrome. Br J Anaesth. 1968 Jul;40(7):493–502. doi: 10.1093/bja/40.7.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRATT P. C. Pulmonary capillary proliferation induced by oxygen inhalation. Am J Pathol. 1958 Nov-Dec;34(6):1033–1049. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. H., Tunstall M. E., Mitchell R. G. A controlled trial of artificial respiration in the respiratory-distress syndrome of the newborn. Lancet. 1967 Mar 11;1(7489):532–533. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWYER P. R., LEVISON H. THE CURRENT STATUS OF THE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME OF THE NEWLY BORN. Can Med Assoc J. 1965 Aug 21;93:335–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saracli T., Mann M., French D. M., Booker C. R., Scott R. B. Rupture of the stomach in the newborn infant. Report of three cases and review of the world literature. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1967 Oct;6(10):583–588. doi: 10.1177/000992286700601014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman W. A., Sinclair J. C., Gandy G. M., Finster M., Bauman W. A., Agate F. J., Jr A controlled trial of management of respiratory distress syndrome in a body-enclosing respirator. I. Evaluation of safety. Pediatrics. 1967 May;39(5):740–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L., Ramos A. D., Outerbridge E. W., Beaudry P. H. Negative pressure artificial respiration: use in treatment of respiratory failure of the newborn. Can Med Assoc J. 1970 Mar 28;102(6):595–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS D. V., FLETCHER G., SUNSHINE P., SCHAFER I. A., KLAUS M. H. PROLONGED RESPIRATOR USE IN PULMONARY INSUFFICIENCY OF NEWBORN. JAMA. 1965 Jul 19;193:183–190. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090030005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]