Abstract
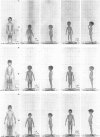
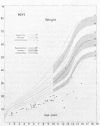
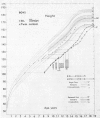
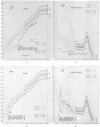
(1) Human growth hormone (HGH) has been given for one whole year or longer to 100 patients, aged 1·5 to 19 years, participating in the Medical Research Council Clinical Trial of HGH. Each patient was measured 3-monthly for a control year before treatment, and the majority for a control year after the first treatment year. All measurements were made by one anthropometrist. Radiographic measurements of widths of bone, muscle, and fat in calf and upper arm were made. Methods and standards for assessing the significance of a given height acceleration are presented.
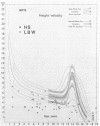
(2) The characteristics at diagnosis are given of 35 patients with isolated GH deficiency or hyposomatotrophism (HS), 18 with craniopharyngiomas and other CNS lesions, 3 with multiple trophic hormone deficiency, 18 with low birthweight short stature, 4 with hereditary smallness and/or delay in growth, 4 with psychosocial short stature, 1 with high resting HGH and low somatomedin, 6 with Turner's syndrome, and 11 with other diagnoses.
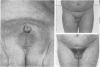
(3) 29 of the 35 HS patients were boys and 13 had an abnormally small penis and ill-developed scrotum. Only 2 were sibs. Parents averaged 40th centile for height. 4 children developed growth-suppressing antibodies, and had to cease treatment. The mean standard deviation score (SDS) for height at diagnosis was -4·7, range -2·6 to -7·3. Bone age SDS averaged -3·2, range -0·8 to -5·7. Skinfold SDS averaged +0·91. Limb muscle width SDS averaged about -3·0. GH peak in insulin hypoglycaemia averaged 4·7 ± 0·7 μU/ml, range 1 to 13.
(4) A category of partial growth hormone deficiency is defined as patients with GH peaks of 7-20 μU/ml inclusive and height velocity SDS in the year before treatment between -1 and -2. Total HS patients have GH peaks of 1 to 6 μU/ml inclusive and height velocity SDS of < -2. Partial HS patients are accelerated by HGH and should be treated; but their average acceleration is below that of total HS patients.
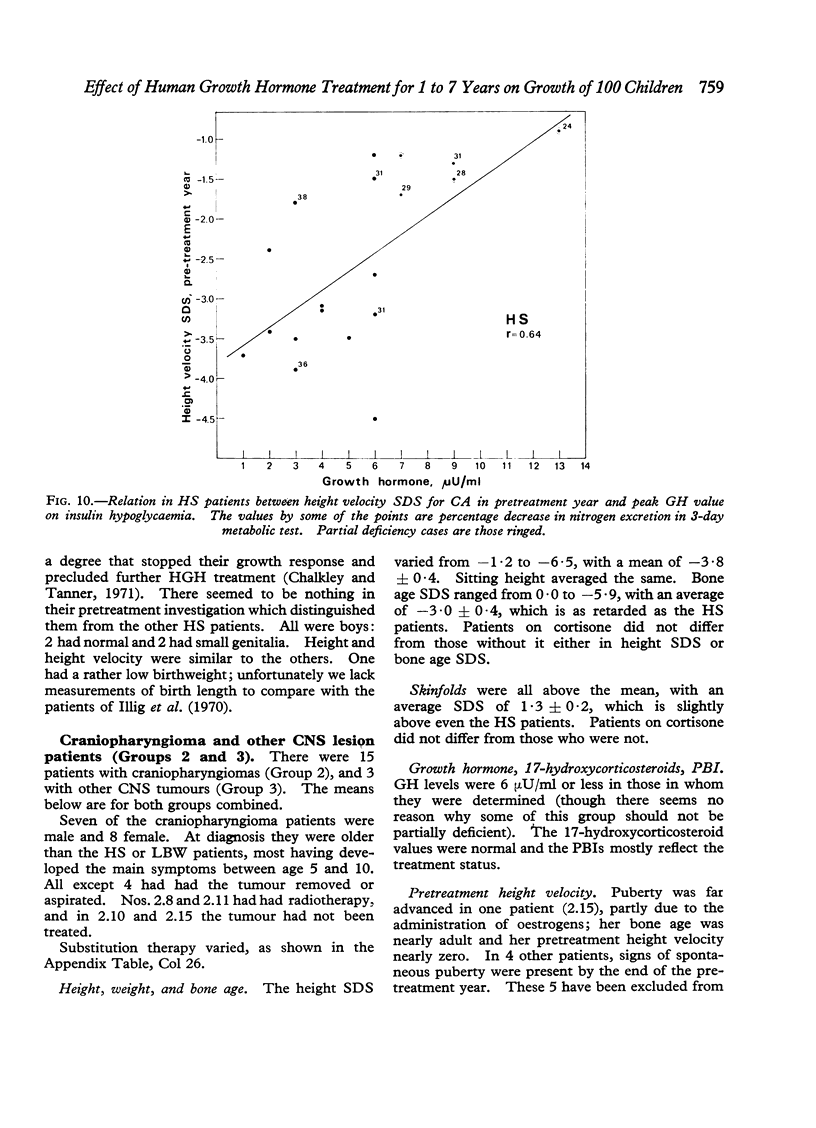
(5) There was a highly significant relation (r = -0·64) between blood GH peak level and pretreatment height velocity in the HS patients.
(6) The LBW patients were 10 boys and 7 girls; all the boys had normal genitalia. The average height SDS at diagnosis was -3·7; parents' height centile averaged 50th, bone age SDS -1·8, skinfold SDS -0·9. GH peaks were all above 30
Full text
PDF







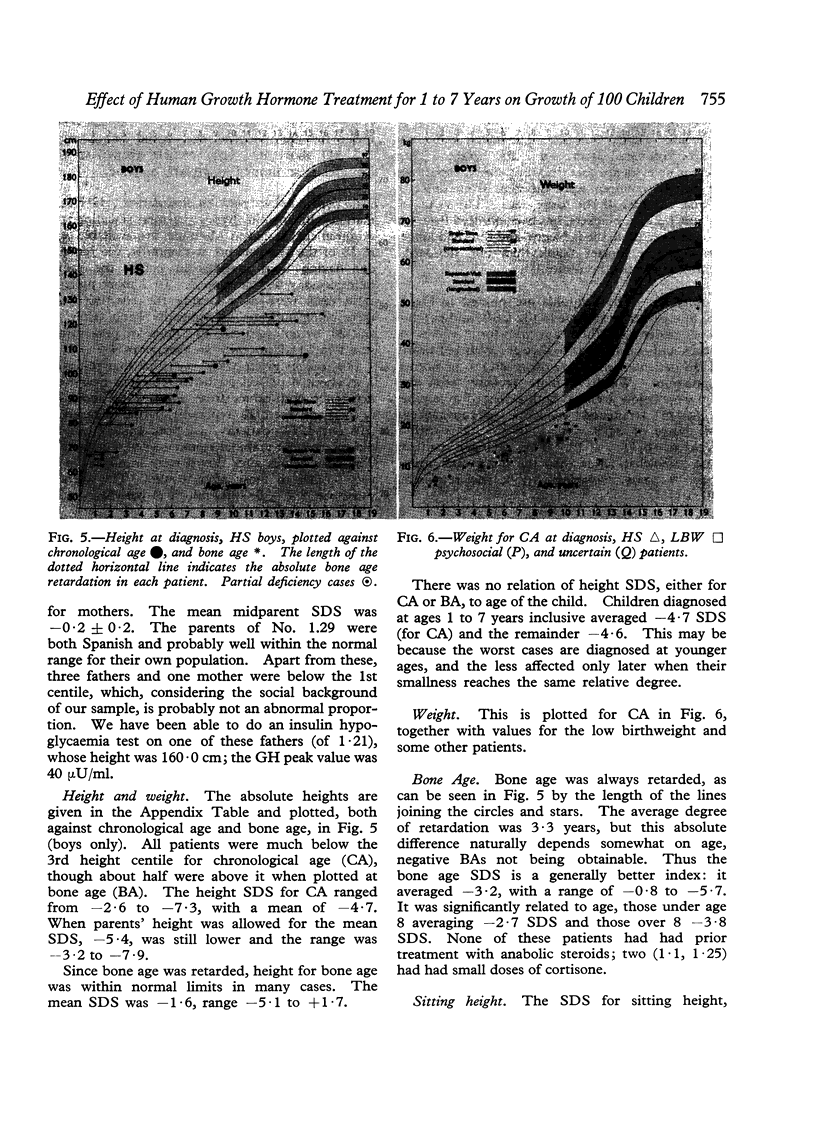
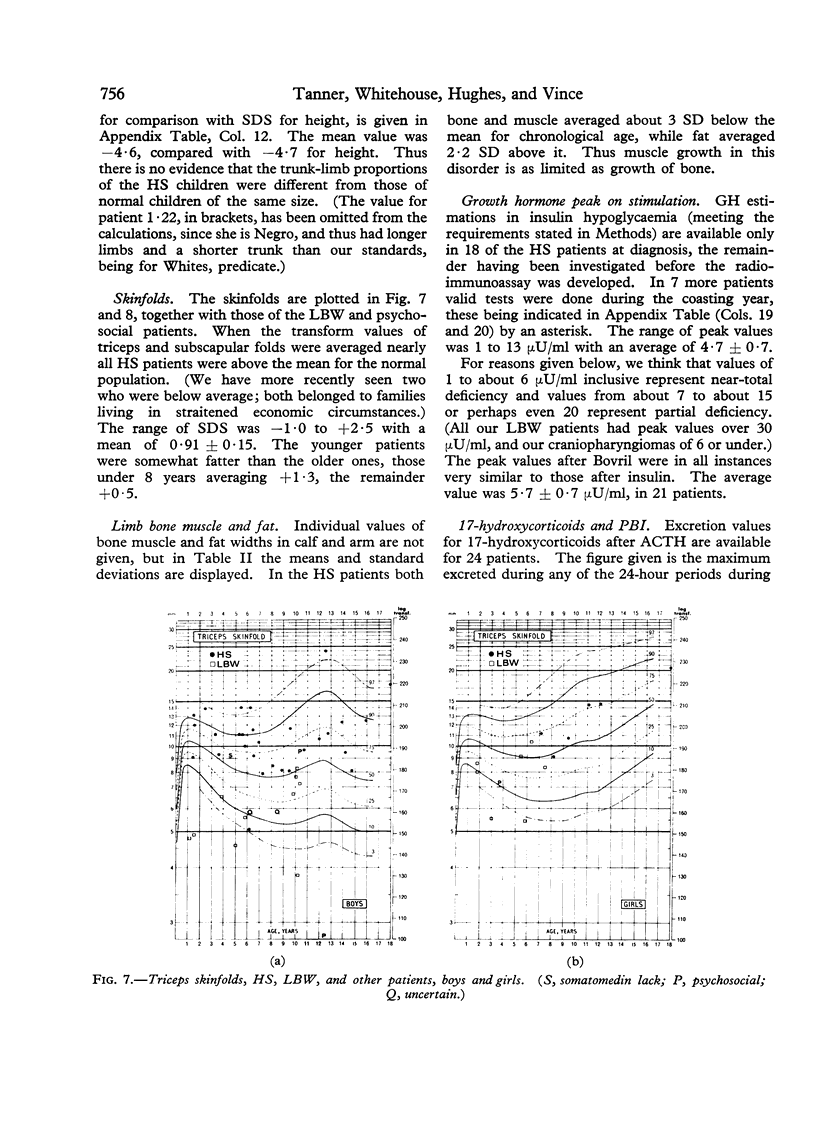
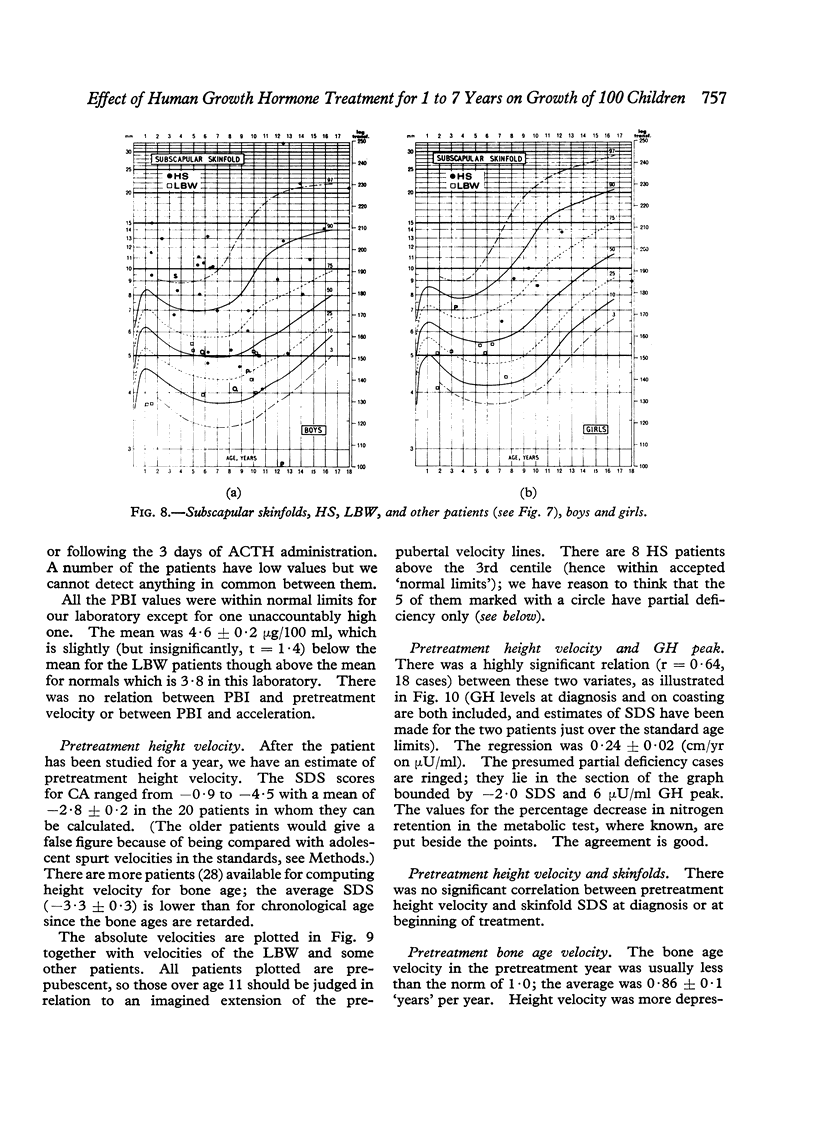
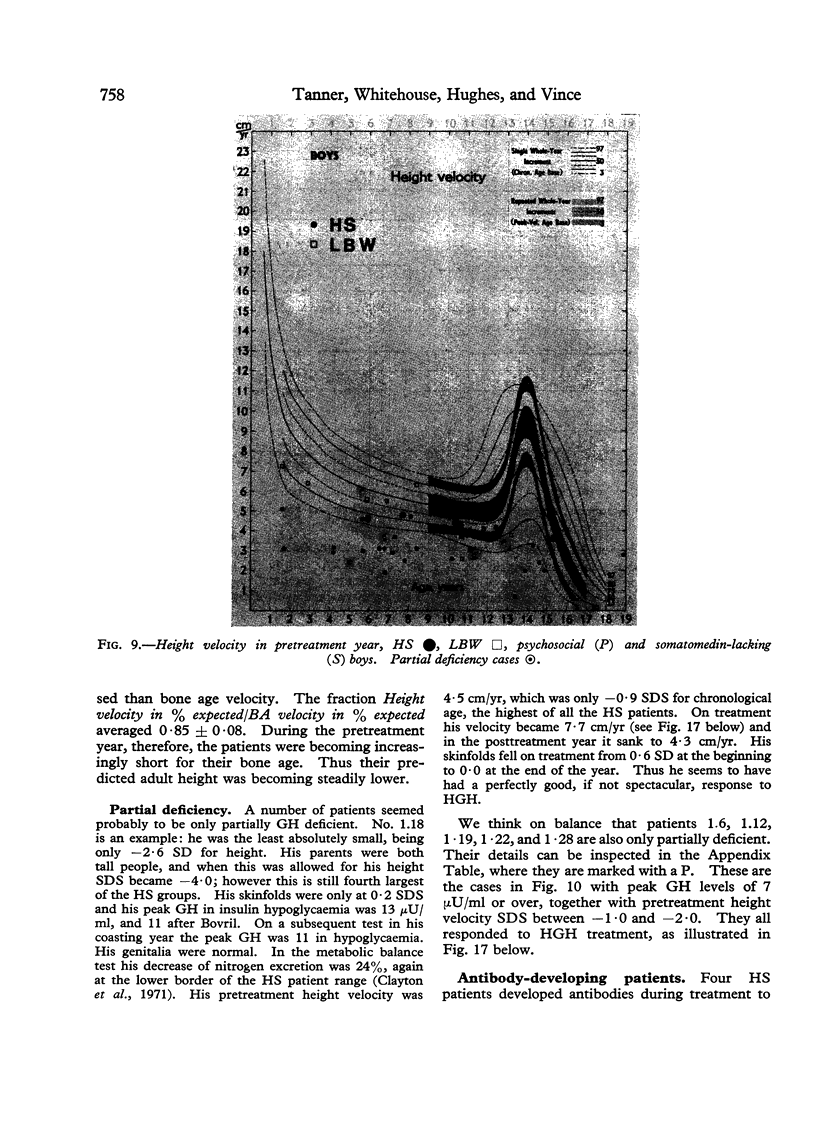




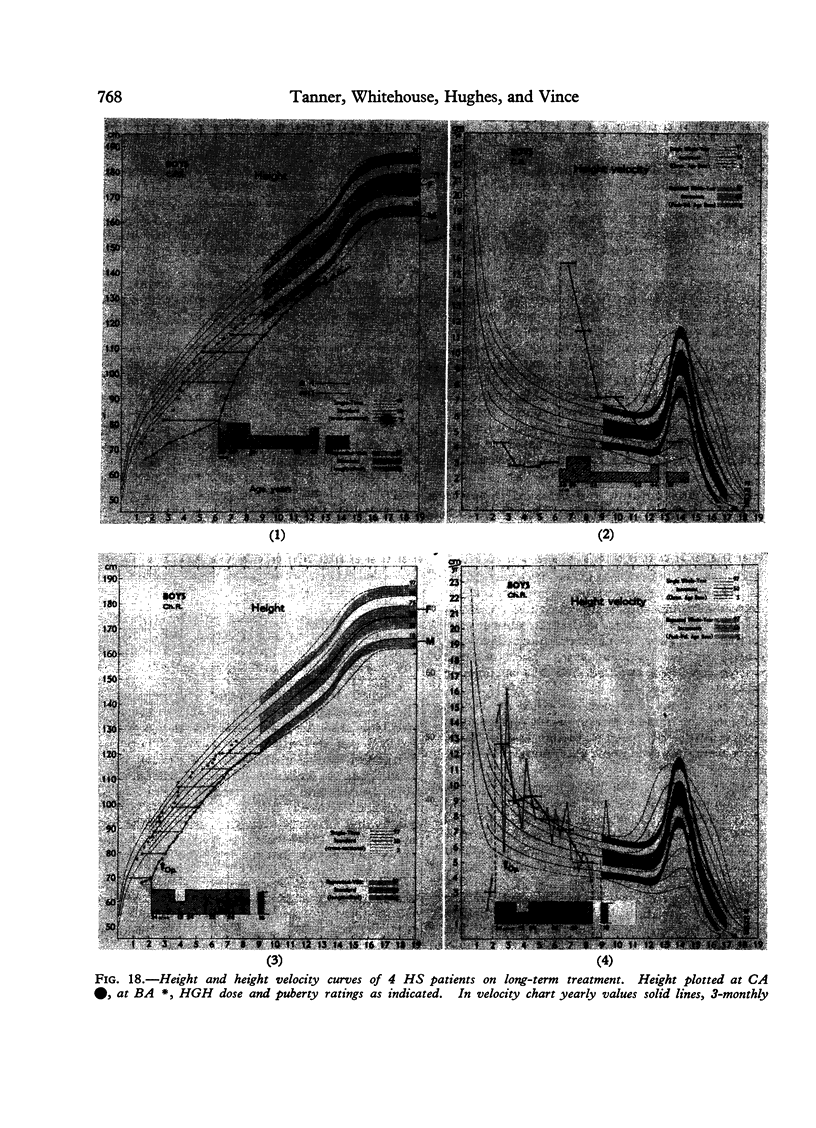
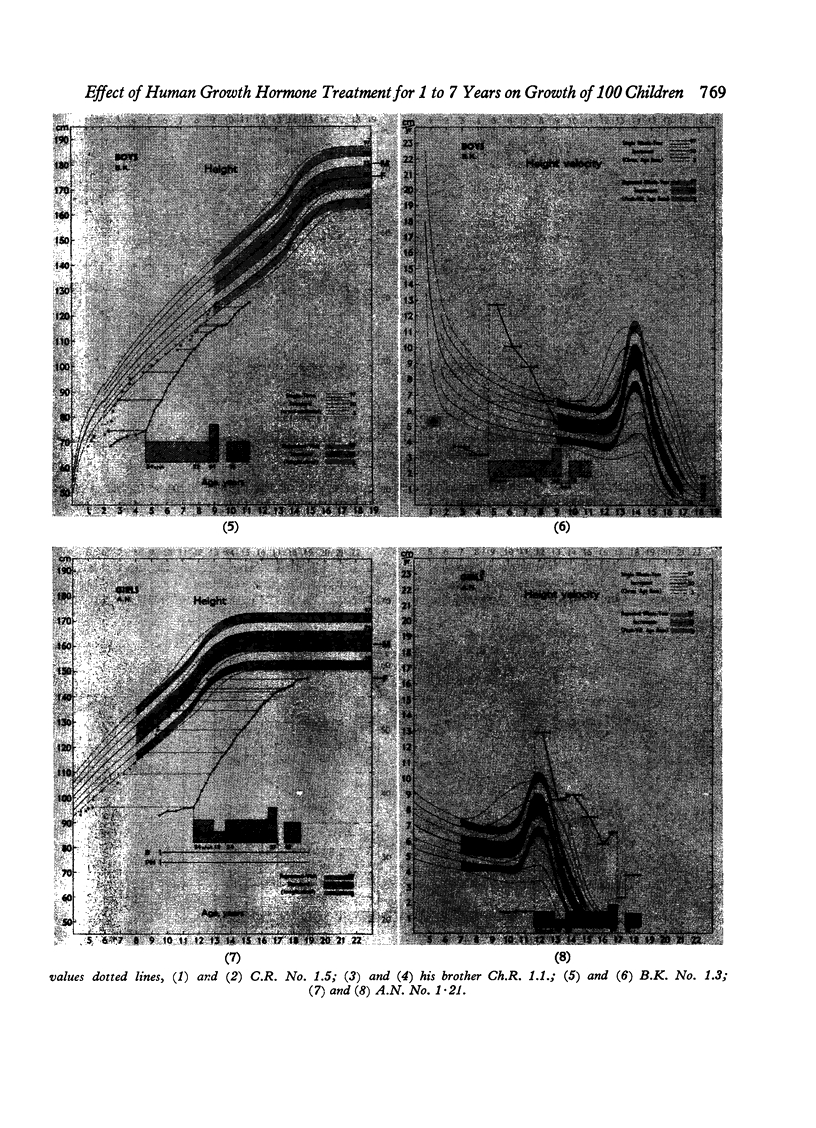
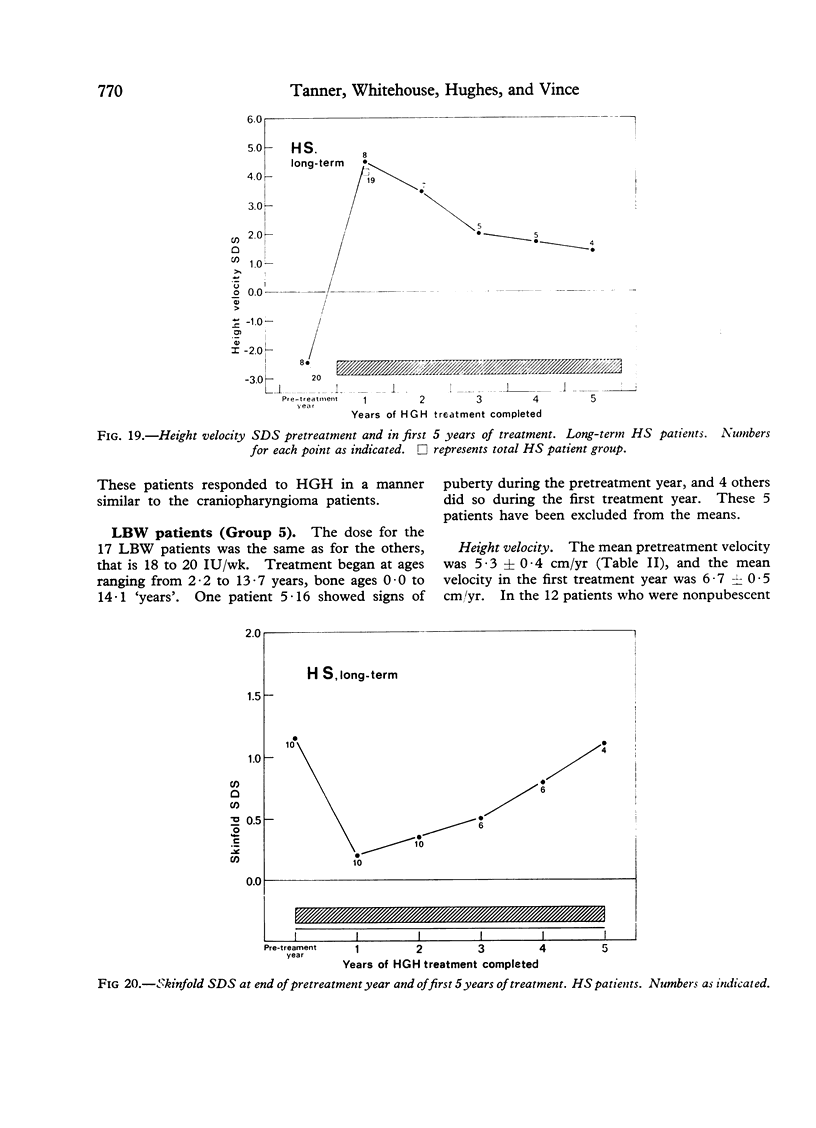
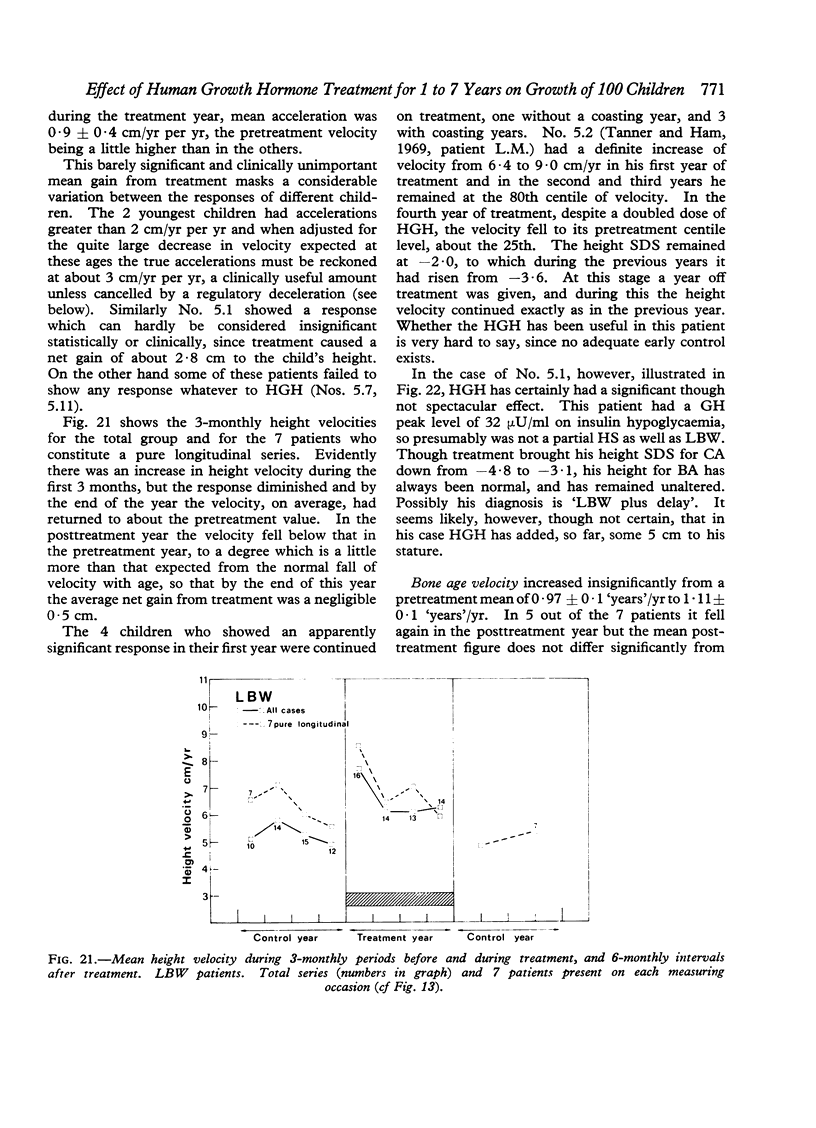











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butenandt O., Knorr D. Familiärer Hypopituitarismus. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1970 Aug;118(8):470–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON B. E., EDWARDS R. W., RENWICK A. G. Adrenal function in children. Arch Dis Child. 1963 Feb;38:49–53. doi: 10.1136/adc.38.197.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalkley S. R., Tanner J. M. Incidence and effects on growth of antibodies to human growth hormone. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Apr;46(246):160–166. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.246.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton B. E., Tanner J. M., Vince F. P. Diagnostic and prognostic value of short-term metabolic response to human growth hormone in short stature. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Aug;46(248):405–413. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.248.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deller J. J., Jr, Boulis M. W., Harriss W. E., Hutsell T. C., Garcia J. F., Linfoot J. A. Growth hormone response patterns to sex hormone administration in growth retardation. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Apr;259(4):292–297. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197004000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS D. A., HAMMOND W. H., HEALY M. J., TANNER J. M., WHITEHOUSE R. H. Design and accuracy of calipers for measuring subcutaneous tissue thickness. Br J Nutr. 1955;9(2):133–143. doi: 10.1079/bjn19550021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman C. J., Lazarus L., Stuart M. C., Casey J. H. The effect of puberty on growth hormone secretion in boys with short stature and delayed adolescence. Aust N Z J Med. 1971 May;1(2):154–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1971.tb02283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSS O. P., HANKES L., VAN SLYKE D. D. A study of the alkaline ashing method for determination of protein-bound iodine in serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1960 May;5:301–326. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(60)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrandez A., Zachmann M., Prader A., Illig R. Isolated growth hormone deficiency in prepubertal children. Influence of human growth hormone on longitudinal growth, adipose tissue, bone mass and bone maturation. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1970 Dec;25(6):566–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasier S. D., Hilburn J. M., Smith F. G. Effect of adolescence on the serum growth hormone response to hypoglycemia. J Pediatr. 1970 Sep;77(3):465–467. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Aceto T., Jr, MacGillivray M. H. Studies of growth hormone secretion in children: normal, hypopituitary and constitutionally delayed. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Oct;27(10):1409–1417. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-10-1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. B., Jackson D., Raiti S., Clayton B. E. Comparison of serum growth hormone levels after Bovril and insulin stimulation. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Aug;45(242):544–546. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.242.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree A. S. Separation and partial purification of the protein hormones from human pituitary glands. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):754–761. doi: 10.1042/bj1000754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman D. A., Colle E. Plasma growth hormone and insulin responses in short children. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jun;117(6):636–644. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100030638004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illig R., Prader A. Effect of testosterone on growth hormone secretion in patients with anorchia and delayed puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 May;30(5):615–618. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-5-615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D., Grant D. B., Clayton B. E. A simple oral test of growth-hormone secretion in children. Lancet. 1968 Aug 17;2(7564):373–375. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90592-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Abrams C. A., Bell J. J., Conte F. A., Grumbach M. M. Growth and growth hormone. I. Changes in serum level of growth hormone following hypoglycemia in 134 children with growth retardation. Pediatr Res. 1968 Jan;2(1):43–63. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196801000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Karp M. Pituitary dwarfism with high serum levels of growth hormone. Isr J Med Sci. 1968 Jul-Aug;4(4):883–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Pertzelan A., Mannheimer S. Genetic pituitary dwarfism with high serum concentation of growth hormone--a new inborn error of metabolism? Isr J Med Sci. 1966 Mar-Apr;2(2):152–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCarthy D., Booth E. M. Parental rejection and stunting of growth. J Psychosom Res. 1970 Sep;14(3):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(70)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. A. Evaluation of growth rate in height over periods of less than one year. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Aug;46(248):414–420. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.248.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. A., Tanner J. M. Variations in pattern of pubertal changes in girls. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Jun;44(235):291–303. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.235.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRADER A., ILLIG R., SZEKY J., WAGNER H. THE EFFECT OF HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE IN HYPOPITUITARY DWARFISM. Arch Dis Child. 1964 Dec;39:535–544. doi: 10.1136/adc.39.208.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRADER A., TANNER J. M., von HARNACK G. Catch-up growth following illness or starvation. An example of developmental canalization in man. J Pediatr. 1963 May;62:646–659. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell G. F., Brasel J. A., Blizzard R. M. Emotional deprivation and growth retardation simulating idiopathic hypopituitarism. I. Clinical evaluation of the syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jun 8;276(23):1271–1278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196706082762301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prader A., Zachmann M., Poley J. R., Illig R., Széky J. Long-term treatment with human growth hormone (Raben) in small doses. Evaluation of 18 hypopituitary patients. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1967 Oct;22(5):423–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABEN M. S. Treatment of a pituitary dwarf with human growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Aug;18(8):901–903. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-8-901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root A. W., Saenz-Rodriguez C., Bongiovanni A. M., Eberlein W. R. The effect of arginine infusion on plasma growth hormone and insulin in children. J Pediatr. 1969 Feb;74(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seip M., Trygstad O. Experiences with human growth hormone in pituitary dwarfism. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1966 May;55(3):287–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1966.tb17656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seip M., Van Der Hagen C. B., Trygstad O. Hereditary pituitary dwarfism with spontaneous puberty. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Feb;43(227):47–52. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.227.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shizume K., Matsuzaki F., Irie M., Osawa N. Results of long-term human growth hormone therapy for pituitary dwarfism. Endocrinol Jpn. 1970 Aug;17(4):297–306. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.17.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANNER J. M. REGULATION OF GROWTH IN SIZE IN MAMMALS. Nature. 1963 Aug 31;199:845–850. doi: 10.1038/199845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANNER J. M., WHITEHOUSE R. H. Standards for subcutaneous fat in British children. Percentiles for thickness of skinfolds over triceps and below scapula. Br Med J. 1962 Feb 17;1(5276):446–450. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5276.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Goldstein H., Whitehouse R. H. Standards for children's height at ages 2-9 years allowing for heights of parents. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Dec;45(244):755–762. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.244.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Ham T. J. Low birthweight dwarfism with asymmetry (Silver's syndrome): treatment with human growth hormone. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Apr;44(234):231–243. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.234.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Thomson A. M. Standards for birthweight as gestation periods from 32 to 42 weeks, allowing for maternal height and weight. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Aug;45(242):566–569. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.242.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H. Growth response of 26 children with short stature given human growth hormone. Br Med J. 1967 Apr 8;2(5544):69–75. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5544.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H., Takaishi M. Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity, and weight velocity: British children, 1965. II. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Dec;41(220):613–635. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.220.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. M., Whitehouse R. H. The effect of human growth hormone on subcutaneous fat thickness in hyposomatotrophic and panhypopituitary dwarfs. J Endocrinol. 1967 Oct;39(2):263–275. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trygstad O. Human growth hormone and hypopituitargrowth retardation. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1969 Jul;58(4):407–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1969.tb04738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson J. E., Barnes A. C., McKusick V. A., Scott C. I., Jones G. S. Obstetric and gynecologic considerations of dwarfism. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Nov 1;108(5):688–704. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT J. C., BRASEL J. A., ACETO T., Jr, FINKELSTEIN J. W., KENNY F. M., SPAULDING J. S., BLIZZARD R. M. STUDIES WITH HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE (HGH). Am J Med. 1965 Apr;38:499–516. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youlton R., Kaplan S. L., Grumbach M. M. Growth and growth hormone. IV. Limitations of the growth hormone response to insulin and arginine and of the immunoreactive insulin response to arginine in the assessment of growth hormone deficiency in children. Pediatrics. 1969 Jun;43(6):989–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachmann M., Prader A. Anabolic and androgenic affect of testosterone in sexually immature boys and its dependency on growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jan;30(1):85–95. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]