Abstract
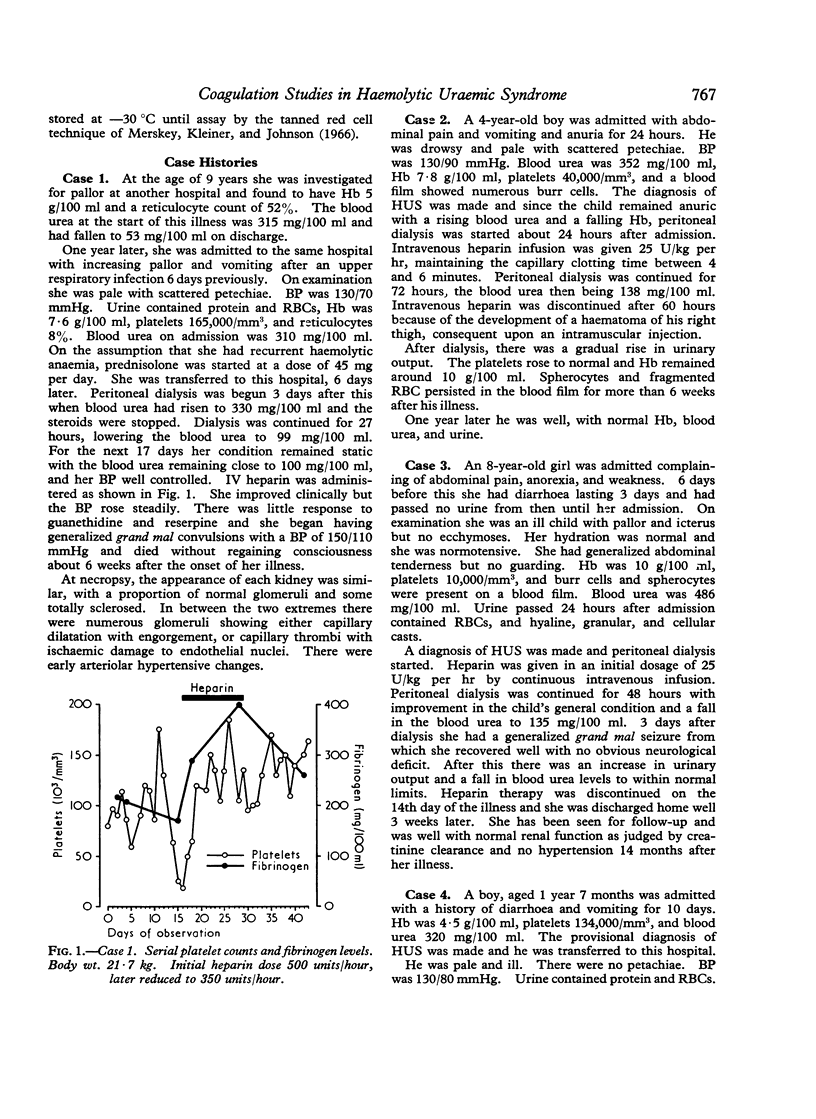
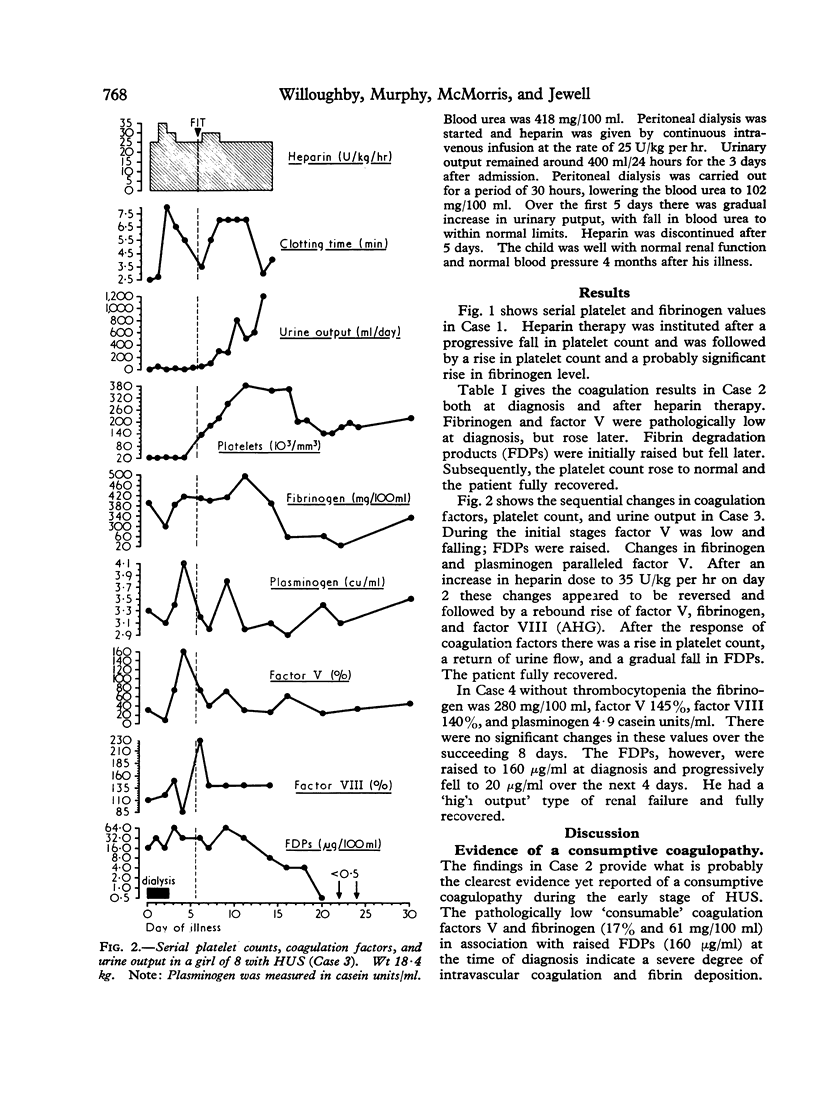
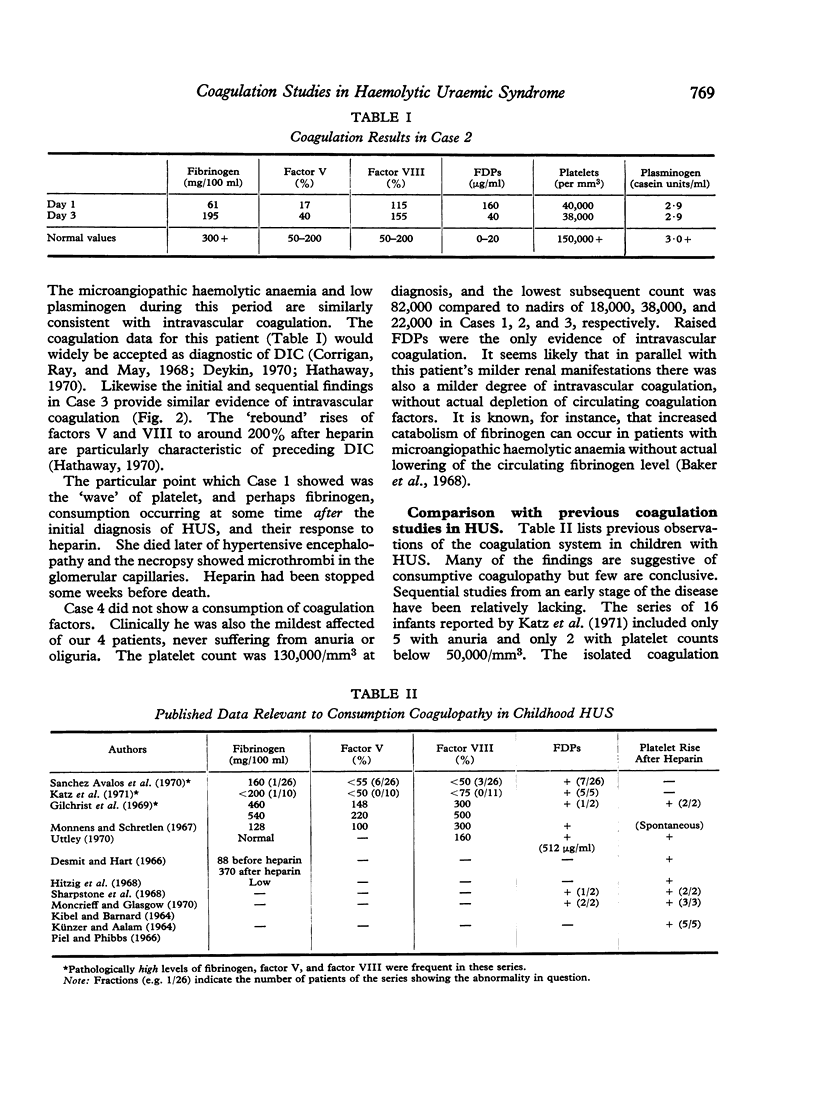
Serial coagulation investigations were performed in 4 children with the haemolytic uraemic syndrome treated with heparin by continuous infusion. 2 anuric patients showed consumption of factor V and fibrinogen early in the disease, with thrombocytopenia and raised fibrin degradation products. These changes regressed during heparin therapy and renal function fully recovered in both patients. A third patient with a mild form of the disease, normal urinary output, and only borderline thrombocytopenia did not develop demonstrable depletion of factor V or fibrinogen. In a further patient a secondary `wave' of consumption of platelets and perhaps fibrinogen was seen late in the course of the disease. These findings confirmed the occurrence of a consumptive coagulopathy in severe cases of haemolytic uraemic syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. xi-Aminocaproic acid: an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avalos J. S., Vitacco M., Molinas F., Peñalver J., Gianantonio C. Coagulation studies in the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J Pediatr. 1970 Apr;76(4):538–548. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAIN M. C., DACIE J. V., HOURIHANE D. O. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the possible role of vascular lesions in pathogenesis. Br J Haematol. 1962 Oct;8:358–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECHER G., CRONKITE E. P. Morphology and enumeration of human blood platelets. J Appl Physiol. 1950 Dec;3(6):365–377. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1950.3.6.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker L. R., Rubenberg M. L., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Fibrinogen catabolism in microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):617–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain M. C., Baker L. R., McBride J. A., Rubenberg M. L., Dacie J. V. Treatment of patients with microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia with heparin. Br J Haematol. 1968 Dec;15(6):603–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain M. C., Hourihane D. O. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the occurrence of haemolysis in experimentally produced vascular disease. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jan;13(1):135–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain M. C. The haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. Semin Hematol. 1969 Apr;6(2):162–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Rubenberg M. L., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: mechanisms of red-cell fragmentation: in vitro studies. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):643–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan J. J., Jr, Ray W. L., May N. Changes in the blood coagulation system associated with septicemia. N Engl J Med. 1968 Oct 17;279(16):851–856. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196810172791603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D. The clinical challenge of disseminated intravascular coagulation. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 17;283(12):636–644. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009172831207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist G. S., Lieberman E., Ekert H., Fine R. N., Grushkin C. Heparin therapy in the haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. Lancet. 1969 Jun 7;1(7606):1123–1126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91644-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M., MACPHERSON J. C. A one-stage factor VIII (antihaemophilic globulin) assay and its use on venous and capillary plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 May 15;7:215–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond D., Lieberman E. The hemolytic uremic syndrome. Renal cortical thrombotic microangiopathy. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):816–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway W. E. Care of the critically ill child: the problem of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Pediatrics. 1970 Nov;46(5):767–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzig W. H., Straub P. W., Lo S. S., Frick P. G. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Clinical experience with anticoagulant therapy in the management of disseminated intravascular coagulation in children. Proc R Soc Med. 1968 Nov;61(11 Pt 1):1138–1138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Lurie A., Kaplan B. S., Krawitz S., Metz J. Coagulation findings in the hemolytic-uremic syndrome of infancy: similarity to hyperacute renal allograft rejection. J Pediatr. 1971 Mar;78(3):426–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzkowsky P., McCrory W. Disseminated intravascular coagulation as a possible factor in the pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathy (hemolytic-uremic syndrome). J Pediatr. 1967 Mar;70(3):460–462. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Kleiner G. J., Johnson A. J. Quantitative estimation of split products of fibrinogen in human serum, relation to diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1966 Jul;28(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncrieff M. W., Glasgow E. F. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome treated with heparin. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 25;3(5716):188–191. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5716.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnens L., Schretlen E. Intravascular coagulation in an infant with the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1967 Jul;56(4):436–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1967.tb15403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenberg M. L., Regoeczi E., Bull B. S., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the experimental production of haemolysis and red-cell fragmentation by defibrination in vivo. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):627–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEFANINI M. New one-stage procedures for the quantitative determination of prothrombin and labile factor. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 Mar;20(3):233–240. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/20.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpstone P., Evans R. G., O'Shea M., Alexander L., Lee H. A. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome: survival after prolonged oliguria. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Dec;43(232):711–716. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.232.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttley W. S. Serum levels of fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products in the haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Aug;45(242):587–589. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.242.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


