Abstract
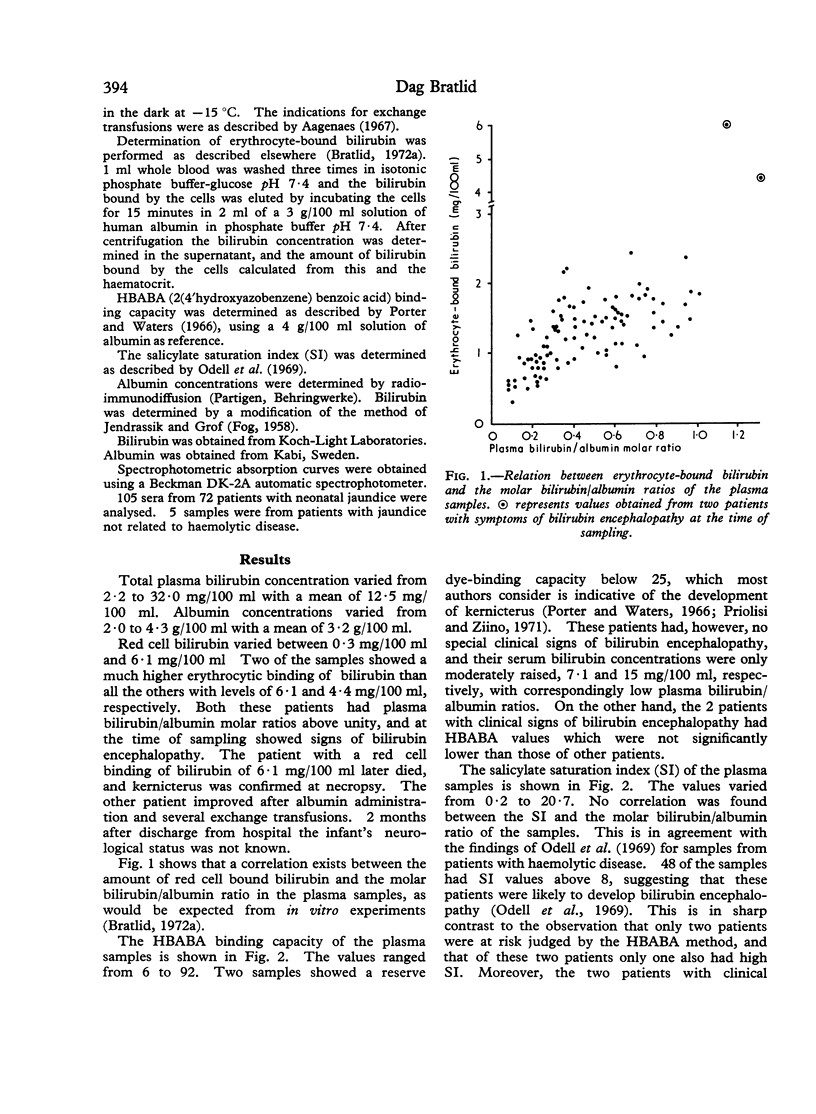
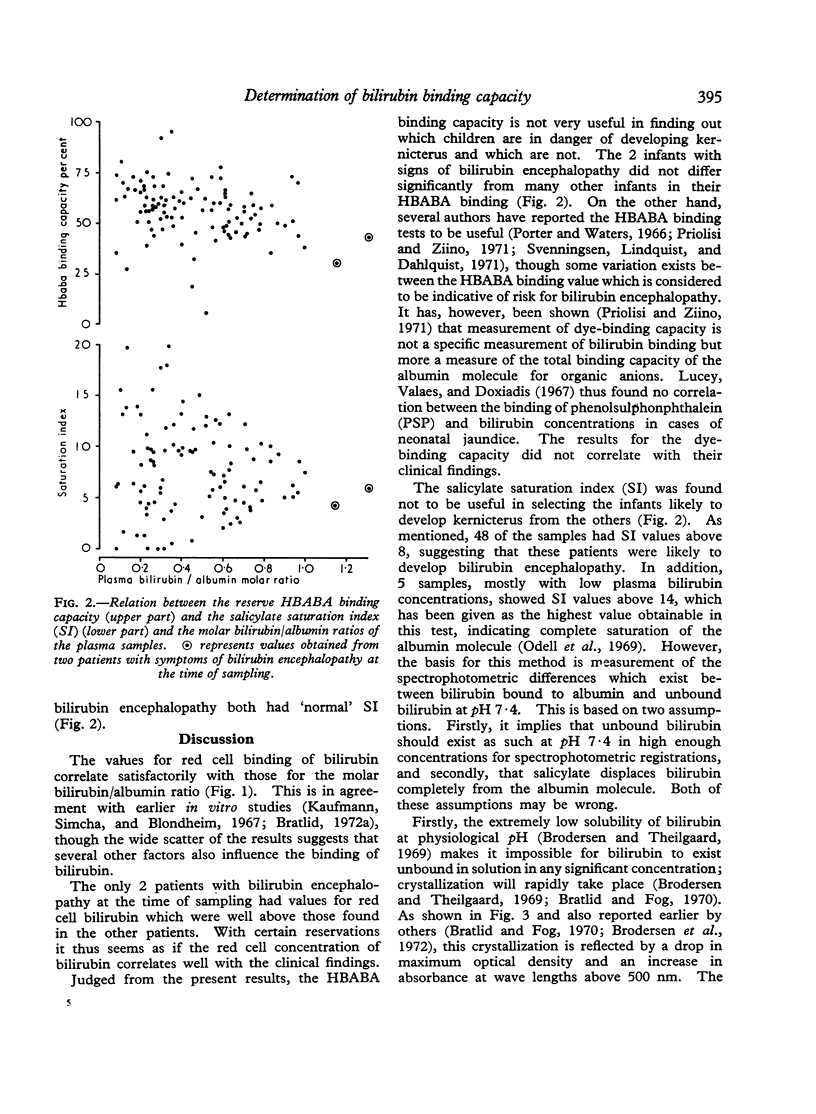
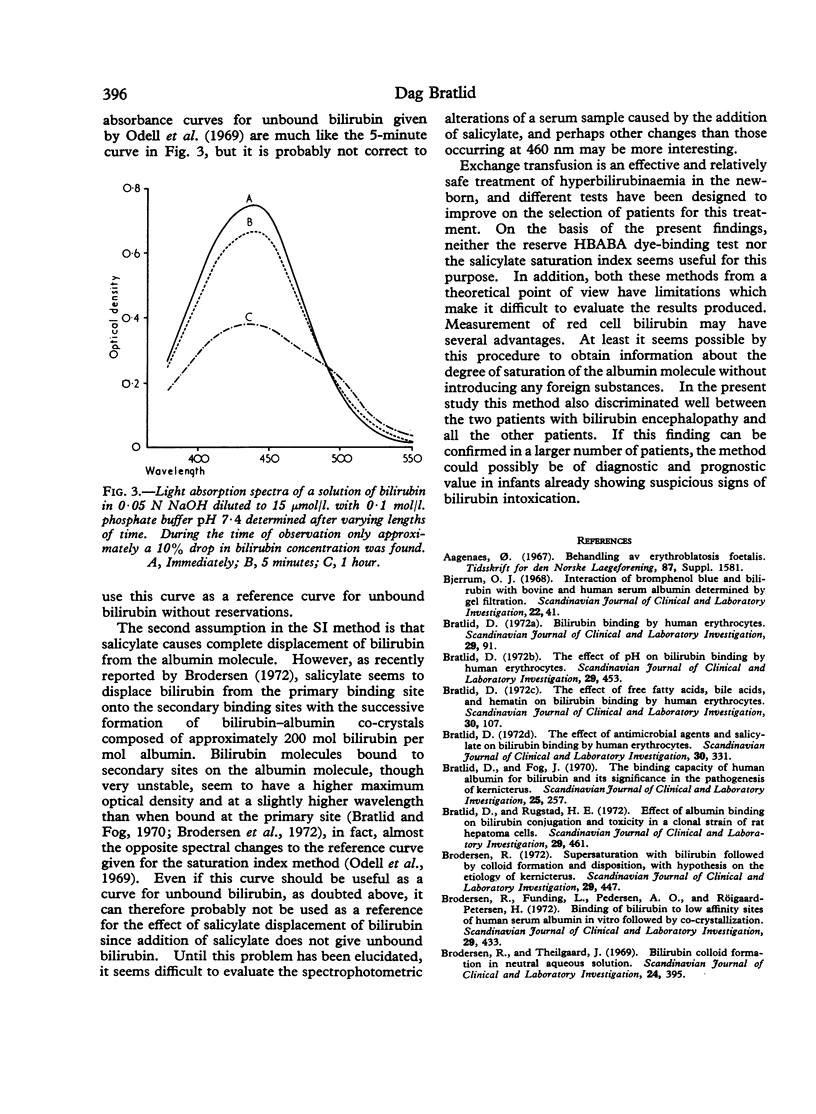
105 blood samples from 72 infants, mostly with jaundice due to haemolytic disease, were analysed for reserve albumin binding capacity (HBABA method), salicylate saturation index (SI), and red cell binding of bilirubin. 2 infants with clinical symptoms of bilirubin encephalopathy had abnormally large amounts of red cell bound bilirubin, though the HBABA binding capacity and salicylate saturation index did not suggest a risk of bilirubin encephalopathy. On the other hand, 48 of the other samples showed `risk values' for saturation index and 2 of the other samples showed such values as judged by the HBABA method. The discrepancies between these findings are discussed. It is suggested that determination of red cell bound bilirubin may have clinical value in patients with neonatal jaundice, especially in cases of suggested kernicterus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aagenaes O. Behandling av erythroblastosis foetalis. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1967 Sep 25;87(18 Suppl):1581–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J. Interaction of bromphenol blue and bilirubin with bovine and human serum albumin determined by gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;22(1):41–48. doi: 10.3109/00365516809160735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratlid D. Bilirubin binding by human erythrocytes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Feb;29(1):91–97. doi: 10.3109/00365517209081060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratlid D., Fog J. The binding capacity of human albumin for bilirubin and its significance in the significance in the pathogenesis of kernicterus. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 May;25(3):257–261. doi: 10.3109/00365517009046203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratlid D. The effect of free fatty acids, bile acids, and hematin on bilirubin binding by human erythrocytes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Sep;30(1):107–112. doi: 10.3109/00365517209081098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen R., Theilgaard J. Bilirubin colloid formation in neutral aqueous solution. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Dec;24(4):395–398. doi: 10.3109/00365516909080178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOG J. Determination of bilirubin in serum as alkaline azobilirubin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(3):241–245. doi: 10.1080/00365515809087173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner L. M., Snyder R. N., Chabon R. S., Bernstein J. Kernicterus: high incidence in premature infants with low serum bilirubin concentrations. Pediatrics. 1970 Jun;45(6):906–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS R. C., LUCEY J. F., MACLEAN J. R. Kernicterus in premature infants associated with low concentrations of bilirubin in the plasma. Pediatrics. 1958 Jun;21(6):875–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howorth P. J. Determination of serum albumin in neonatal jaundice. The albumin saturation index. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Apr;32(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. Binding of bilirubin to human serum albumin - determination of the dissociation constants. FEBS Lett. 1969 Oct 21;5(2):112–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann N. A., Simcha A. J., Blondheim S. H. The uptake of bilirubin by blood cells from plasma and its relationship to the criteria for exchange transfusion. Clin Sci. 1967 Aug;33(1):201–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie S. O., Bratlid D. The protective effect of albumin on bilirubin toxicity on human fibroblasts. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 Aug;26(1):37–41. doi: 10.3109/00365517009049211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey J. F., Valaes T., Doxiadis S. A. Serum albumin reserve PSP dye binding capacity in infants with kernicterus. Pediatrics. 1967 Jun;39(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODELL G. B. The dissociation of bilirubin from albumin and its clinical implications. J Pediatr. 1959 Sep;55:268–279. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(59)80223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSKI F. A., NAIMAN J. L. RED CELL BINDING OF BILIRUBIN. J Pediatr. 1963 Nov;63:1034–1037. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell G. B., Cohen S. N., Kelly P. C. Studies in kernicterus. II. The determination of the saturation of serum albumin with bilirubin. J Pediatr. 1969 Feb;74(2):214–230. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell G. B. Influence of pH on distribution of bilirubin between albumin and mitochondria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):352–354. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priolisi A., Ziino L. Comparative analysis between the reserve albumin-binding capacity (HBABA method) and the saturation index of hyperbilirubinemic sera. Biol Neonate. 1971;19(4):258–271. doi: 10.1159/000240421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. The absorption of bilirubin by erythrocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Sep;7:733–734. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


