Abstract
Eighteen premature infants were studied. 9 were fed with human milk and 9 with a modified cow's milk. Subsequent to a 72-hour fat balance, a duodenal intubation was performed on the 14th day of life. Total bile acids were determined in serial duodenal aspirates before and after a milk feed. Bile acid excretion in the faeces during a 72-hour period was also measured.
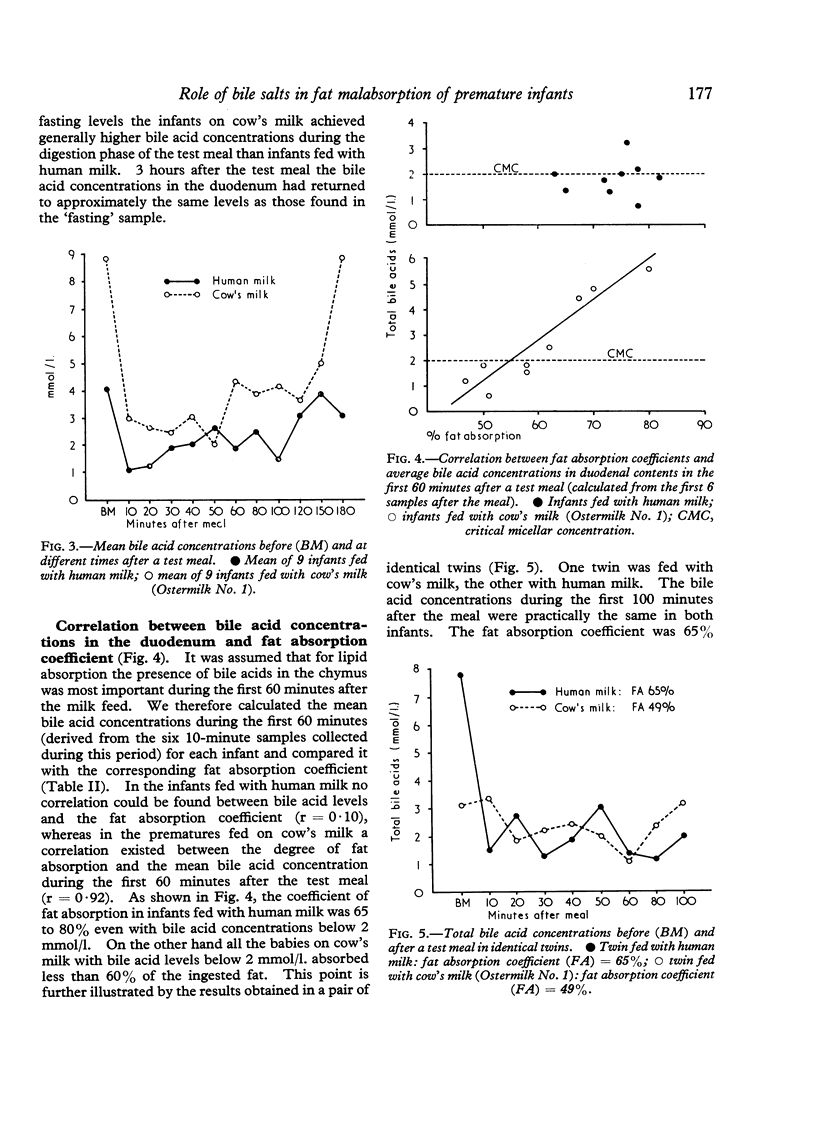
Infants fed with human milk absorbed fat better (mean fat absorption coefficient, 75%) than those receiving a cow's milk formula (mean fat absorption coefficient, 60%). In both groups the bile acid concentrations after a meal were often less than that required for the formation of micellar solutions and solubilization of fat (i.e. <2 mmol/l.). With human milk, a reasonable fat absorption occurred even with bile acid levels below the critical micellar concentration. In the infants fed with the cow's milk formula, impaired fat absorption was correlated with low bile acid levels.
Infants on human milk excreted less bile acids in the stool (mean, 41·9 μmol/kg per 24 hr) than did infants fed with the cow's milk formula (mean, 72·4 μmol/kg per 24 hr). In both groups the faecal loss of bile acids was increased compared with that in older infants and children.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON C. M., FRENCH J. M., SAMMONS H. G., FRAZER A. C., GERRARD J. W., SMELLIE J. M. Coeliac disease; gastrointestinal studies and the effect of dietary wheat flour. Lancet. 1952 Apr 26;1(6713):836–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)90795-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONGIOVANNI A. M. BILE ACID CONTENT OF GALLBLADDER OF INFANTS, CHILDREN AND ADULTS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 May;25:678–685. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-5-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B. Effect of tauro-cholic acid on the pH/activity curve of rat pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Jan;13(1):149–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley B. W., Murphy G. M., Bouchier I. A. Intraluminal bile-salt deficiency in the pathogenesis of steatorrhoea. Lancet. 1969 Aug 23;2(7617):400–402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgström B., Erlanson C. Pancreatic juice co-lipase: physiological importance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 20;242(2):509–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON M., BAUER C. H. Patterns of fat excretion in feces of premature infants fed various preparations of milk. Pediatrics. 1960 Mar;25:375–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESNUELLE P. Pancreatic lipase. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1961;23:129–161. doi: 10.1002/9780470122686.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C., Schulman J. H., Stewart H. C. Emulsification of fat in the intestine of the rat and its relationship to absorption. J Physiol. 1944 Dec 15;103(3):306–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1944.sp004079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F. THE FUNCTION OF BILE SALTS IN FAT ABSORPTION. THE SOLVENT PROPERTIES OF DILUTE MICELLAR SOLUTIONS OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:57–68. doi: 10.1042/bj0890057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. S., Frank D., Hitzig W. H. Vitamin E and haemolytic anaemia in premature infants. Arch Dis Child. 1973 May;48(5):360–365. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.5.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. G., Hoffman N. E. The interaction of lipase, lipase cofactor and bile salts in triglyceride hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 5;248(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. M., Billing B. H., Baron D. N. A fluorimetric and enzymatic method for the estimation of serum total bile acids. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Oct;23(7):594–598. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.7.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A., Strandvik B., Ojamäe O. Bile acids and pancreatic enzymes during absorption in the newborn. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 Sep;61(5):571–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb15947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLEY J. R., DOWER J. C., OWEN C. A., Jr, STICKLER G. B. BILE ACIDS IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 May;63:838–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJOVALL J. On the concentration of bile acids in the human intestine during absorption. Bile acids and sterioids 74. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Aug 31;46:339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate D. A., Widdowson E. M., Smits B. J., Cooke W. T., Walker C. H., Mathers N. P. Absorption and excretion of calcium and fat by young infants. Lancet. 1969 Mar 8;1(7593):487–489. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91589-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Deest B. W., Fordtran J. S., Morawski S. G., Wilson J. D. Bile salt and micellar fat concentration in proximal small bowel contents of ileectomy patients. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1314–1324. doi: 10.1172/JCI105823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. B., Ingall D., Szczepanik P., Klein P. D., Lester R. Bile-salt metabolism in the newborn. Measurement of pool size and synthesis by stable isotope technic. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 1;288(9):431–434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303012880902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A. M., Chartrand L., Doyon G., Gordon S., Roy C. C. The quantitative determination of fecal bile acids in children by the enzymatic method. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Jul;39(2):524–531. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90082-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsch H., Heinz F., Lagally G., Stuhlfauth K. Fettresorption auf Frauenmilch bei Neugeborenen. Klin Wochenschr. 1965 Aug 15;43(16):902–904. doi: 10.1007/BF01711257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson E. M. Absorption and excretion of fat, nitrogen, and minerals from "filled" milks by babies one week old. Lancet. 1965 Nov 27;2(7422):1099–1105. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoppi G., Andreotti G., Pajno-Ferrara F., Njai D. M., Gaburro D. Exocrine pancreas function in premature and full term neonates. Pediatr Res. 1972 Dec;6(12):880–886. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197212000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


