Abstract
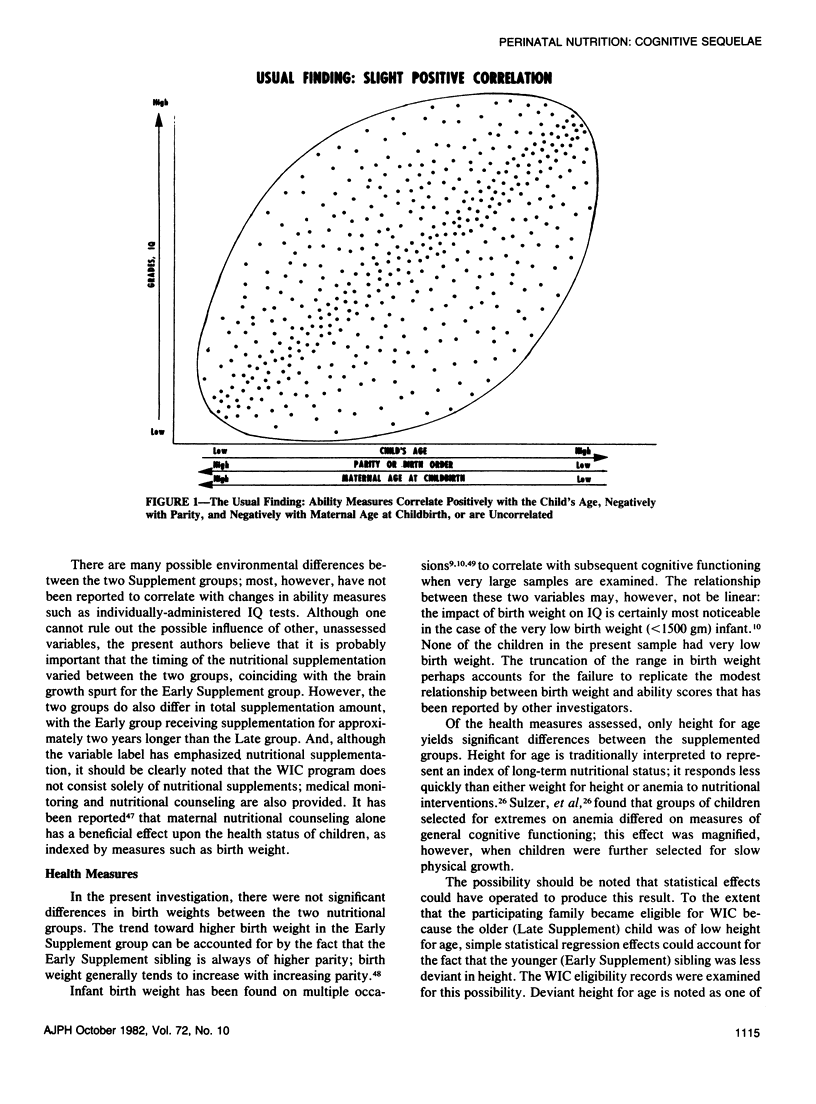
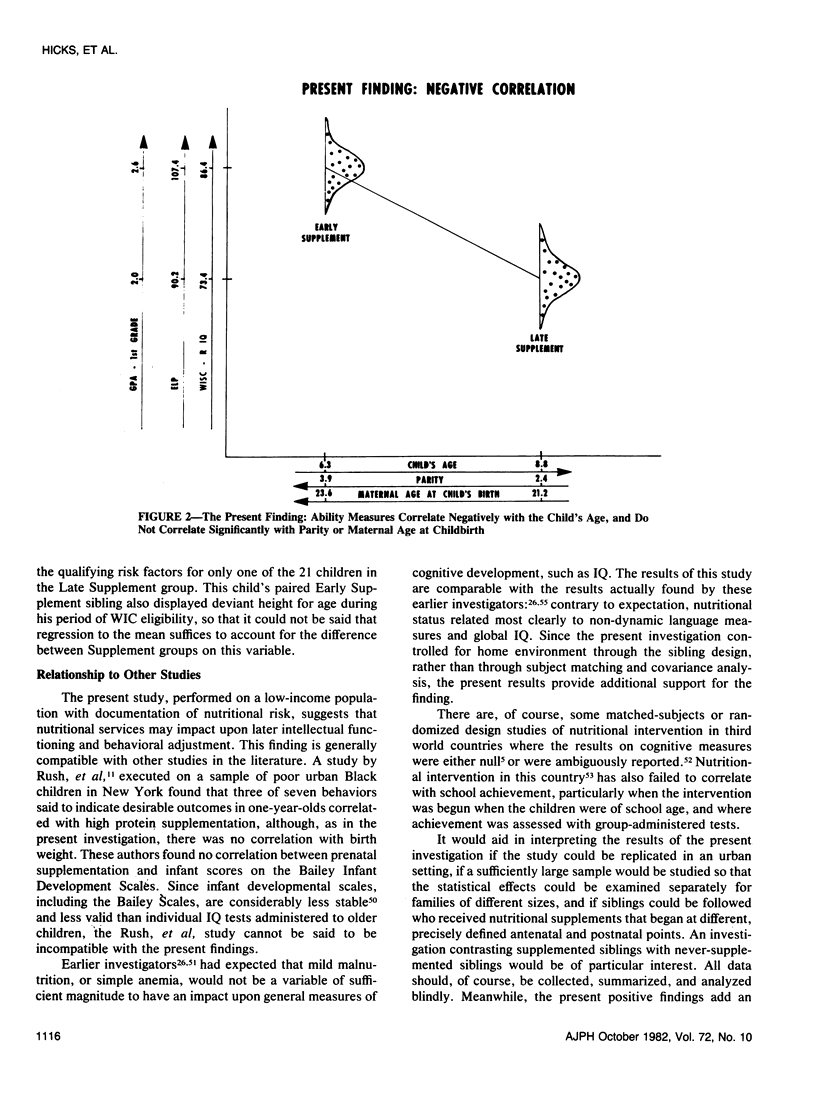
A battery of cognitive measures, an adjustment measure, and multiple health indices were obtained for sibling pairs who differed in the timing of their participation in the Special Supplemental Food Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) several years earlier, with participation during the perinatal period occurring for one sibling, but after one year of age for the other. Results indicated that the perinatally supplemented group showed significant enhancement of most intellectual and behavioral measures in the current home and school setting, including IQ, attention span, visual-motor synthesis, and school grade-point average when compared with the group supplemented later. Of the health assessments, most trends were in the expected direction, but only height for age values were significantly different for the two groups.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belmont L., Marolla F. A. Birth order, family size, and intelligence. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1096–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenfield J., Schwartz J. B. Nutrition intervention in the community -- the "WIC" program. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 6;302(10):579–581. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198003063021013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. W. Birth order and school-related behavior: a heuristic review. Psychol Bull. 1968 Jul;70(1):45–51. doi: 10.1037/h0026023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breland H. M. Birth order, family size, and intelligence. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):114–114. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. Birth order and intelligence. J Soc Psychol. 1968 Dec;76(2):199–206. doi: 10.1080/00224545.1968.9933613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragg B. G. The development of cortical synapses during starvation in the rat. Brain. 1972;95(1):143–150. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. N. The biochemistry of brain development and mental retardation. Br J Psychiatry. 1977 Dec;131:565–574. doi: 10.1192/bjp.131.6.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing J., Sands J. Quantitative growth and development of human brain. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Oct;48(10):757–767. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.10.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien C. M., Thomson A. J., Burgoyne K. Low-birthweight children at early school-age: a longitudinal study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1980 Feb;22(1):26–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1980.tb04303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edozien J. C., Switzer B. R., Bryan R. B. Medical evaluation of the special supplemental food program for women, infants, and children. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Mar;32(3):677–692. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.3.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. E., Moodie A. D., Hansen J. D. Kwashiorkor and intellectual development. S Afr Med J. 1971 Dec 25;45(49):1413–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen D., Vermeersch J. A. Health status and school achievement of children from Head Start and Free School Lunch Programs. Public Health Rep. 1980 Jul-Aug;95(4):362–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman V. B., Guthrie H. A., Guthrie G. M. Physical and intellectual development in Philippine children fed five different dietary staples. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Nov;29(11):1242–1251. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.11.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzig M. E., Birch H. G., Richardson S. A., Tizard J. Intellectual levels of school children severely malnourished during the first two years of life. Pediatrics. 1972 Jun;49(6):814–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAWI A. A., PASAMANICK B. Association of factors of pregnancy with reading disorders in childhood. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Mar 22;166(12):1420–1423. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.02990120012003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH H. L. The relation of primary mental abilities in five- and six-year-olds to sex of child and characteristics of his sibling. Child Dev. 1954 Sep;25(3):209–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1954.tb04756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. T., Gershoff S., Reed R., Austin J. E. Evaluation of the effect of WIC supplemental feeding on birth weight. J Am Diet Assoc. 1982 Mar;80(3):220–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipper E., Lee K., Gartner L. M., Grellong B. Determinants of neurobehavioral outcome in low-birth-weights infants. Pediatrics. 1981 Apr;67(4):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipper E., Lee K., Gartner L. M., Grellong B. Determinants of neurobehavioral outcome in low-birth-weights infants. Pediatrics. 1981 Apr;67(4):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunneborg P. W. Birth order, aptitude, and achievement. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1968 Feb;32(1):101–101. doi: 10.1037/h0025425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L., Blanc W., Paul C. Effects of maternal nutrition on the human fetus. Pediatrics. 1973 Oct;52(4):494–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman H. L., Gunnoe C., Leviton A., Reed R., Peresie H., Maher C., Barrett P. Deficits in psychologic and classroom performance of children with elevated dentine lead levels. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 29;300(13):689–695. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903293001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primrose T., Higgins A. A study in human antepartum nutrition. J Reprod Med. 1971 Dec;7(6):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record R. G., McKeown T., Edwards J. H. The relation of measured intelligence to birth order and maternal age. Ann Hum Genet. 1969 Jul;33(1):61–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1969.tb01630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush D., Stein Z., Susser M. A randomized controlled trial of prenatal nutritional supplementation in New York City. Pediatrics. 1980 Apr;65(4):683–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush D., Stein Z., Susser M. Controlled trial of prenatal nutrition supplementation defended. Pediatrics. 1980 Oct;66(4):656–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


