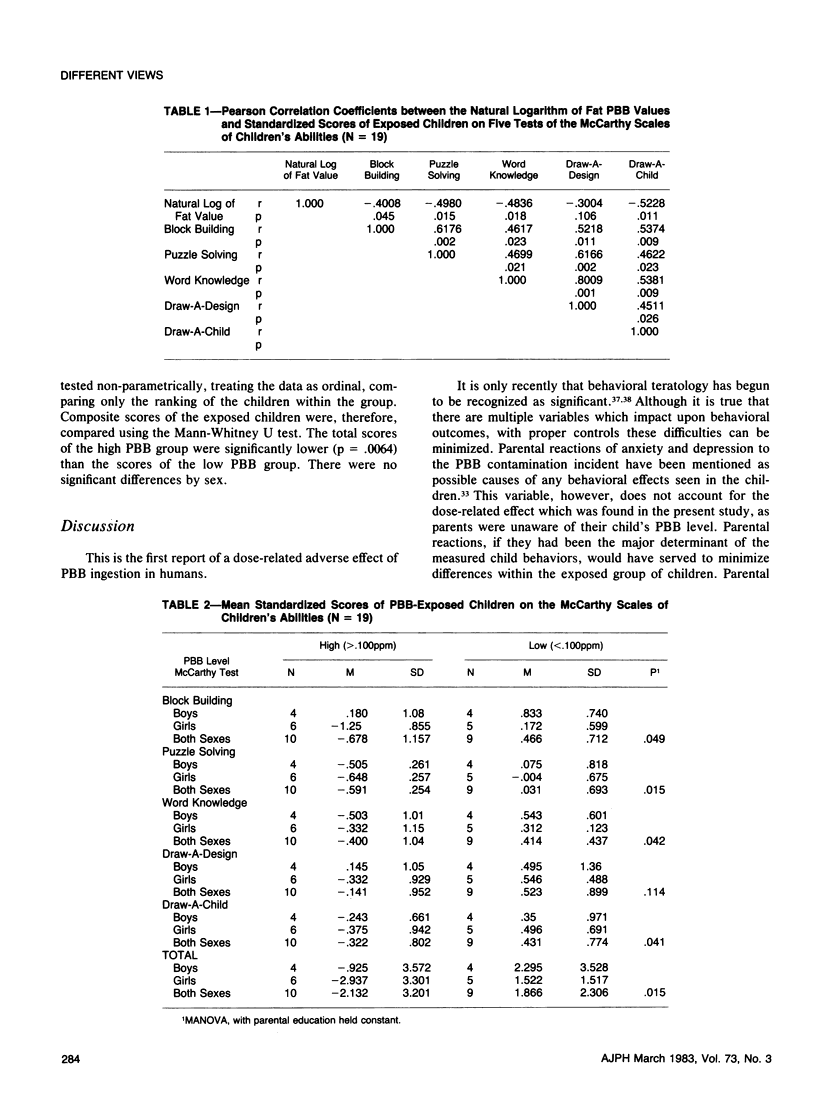
Abstract
To investigate whether ingestion of polybrominated biphenyls has an adverse effect on the neuropsychological development of young children exposed in utero and in infancy, five tests of the McCarthy Scales of Children's Abilities were administered to a group of 19 PBB-exposed Michigan children. When the data for the exposed group were analyzed according to body burden of PBB as determined by fat biopsy, correlations ranging from -.5228 to -.3004 were found between the natural logarithms of the children's fat PBB values and their standardized scores on the developmental scales. Four of the five correlations were significant at p less than .05. Multivariate analysis of covariance confirmed the existence of a significant main effect for fat PBB level, with parental education held constant. Children with higher body burdens of PBB (greater than .100 ppm) scored significantly lower than exposed children with lower body burdens on the same four tests, and on a composite score representing overall performance. These results suggest the existence of an inverse relationship between body levels of PBB and some developmental abilities in young children.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. R., Barsotti D. A., Lambrecht L. K., Van Miller J. P. Reproductive effects of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons on nonhuman primates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:419–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. A., Holstein E. C., Daum S. M., Sarkozi L., Selikoff I. J. Liver function tests among Michigan and Wisconsin dairy farmers. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:333–339. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. A., Lilis R., Selikoff I. J., Rosenman K. D., Valciukas J. A., Freedman S. Unanticipated prevalence of symptoms among dairy farmers in Michigan and Wisconsin. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:217–226. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahn A. K., Mills J. L., Snyder P. J., Gann P. H., Houten L., Bialik O., Hollmann L., Utiger R. D. Hypothyroidism in workers exposed to polybrominated biphenyls. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 3;302(1):31–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001033020105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr M., Jr Pediatric aspects of the Michigan polybrominated biphenyl contamination. Environ Res. 1980 Apr;21(2):255–274. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(80)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr M., Jr Pediatric health aspects of PBBs. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:291–294. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekesi J. G., Anderson H. A., Roboz J. P., Roboz J., Fischbein A., Selikoff I. J., Holland J. F. Immunologic dysfunction among PBB-exposed Michigan dairy farmers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:717–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekesi J. G., Holland J. F., Anderson H. A., Fischbein A. S., Rom W., Wolff M. S., Selikoff I. J. Lymphocyte function of Michigan dairy farmers exposed to polybrominated biphenyls. Science. 1978 Mar 17;199(4334):1207–1209. doi: 10.1126/science.204005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman R. E., Heironimus M. P., Allen J. R. Correlation of PCB body burden with behavioral toxicology in monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1978 Jul;9(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(78)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. G., Nixon R. Exposure to polybrominated biphenyls. Some effects on personality and cognitive functioning. JAMA. 1979 Aug 10;242(6):523–527. doi: 10.1001/jama.242.6.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter L. J. Michigan's PBB Incident: Chemical Mix-Up Leads to Disaster. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):240–243. doi: 10.1126/science.192.4236.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. G., Netter K. J., Gibson J. E. Effects of chronic administration of polybrominated biphenyls on parameters associated with hepatic drug metabolism. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;13(1):75–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Carlo F. J., Seifter J., DeCarlo V. J. Assessment of the hazards of polybrominated biphenyls. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:351–365. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunckel A. E. An updating on the polybrominated biphenyl disaster in Michigan. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1975 Nov 1;167(9):838–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller I., Hartmann R. J., Garcia C., Seifter J. Effects of polybrominated biphenyl on a discrimination task in rats. Neurobehav Toxicol. 1979 Winter;1(4):263–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay K. Polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) environmental contamination in Michigan, 1973-1976. Environ Res. 1977 Feb;13(1):74–93. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(77)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. D., Burse V. W., Liddle J. A. Toxicity of polybrominated biphenyl. Lancet. 1977 Sep 17;2(8038):602–603. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickert D. E., Dent J. G., Cagen S. Z., McCormack K. M., Melrose P., Gibson J. E. Distribution of polybrominated biphenyls after dietary exposure in pregnant and lactating rats and their offspring. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:63–66. doi: 10.1289/ehp.782363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight S. D., Sanger V. L. Pathologic features of polybrominated biphenyl toxicosis in the rat and guinea pig. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Dec 1;169(11):1231–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stross J. K., Nixon R. K., Anderson M. D. Neuropsychiatric findings in patients exposed to polybrominated biphenyls. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:368–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilson H. A., Cabe P. A., Mitchell C. L. Behavioral and neurological toxicity of polybrominated biphenyls in rats and mice. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:257–263. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilson H. A., Cabe P. A. Studies on the neurobehavioral effects of polybrominated biphenyls in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:325–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valciukas J. A., Lilis R., Anderson H. A., Wolff M. S., Petrocci M. The neurotoxicity of polybrominated biphenyls: results of a medical field survey. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:337–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valciukas J. A., Lilis R., Wolff M. S., Anderson H. A. Comparative neurobehavioral study of a polybrominated biphenyl-exposed population in Michigan and a nonexposed group in Wisconsin. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:199–210. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil W. B., Spencer M., Benjamin D., Seagull E. The effect of polybrominated biphenyl on infants and young children. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


