Abstract
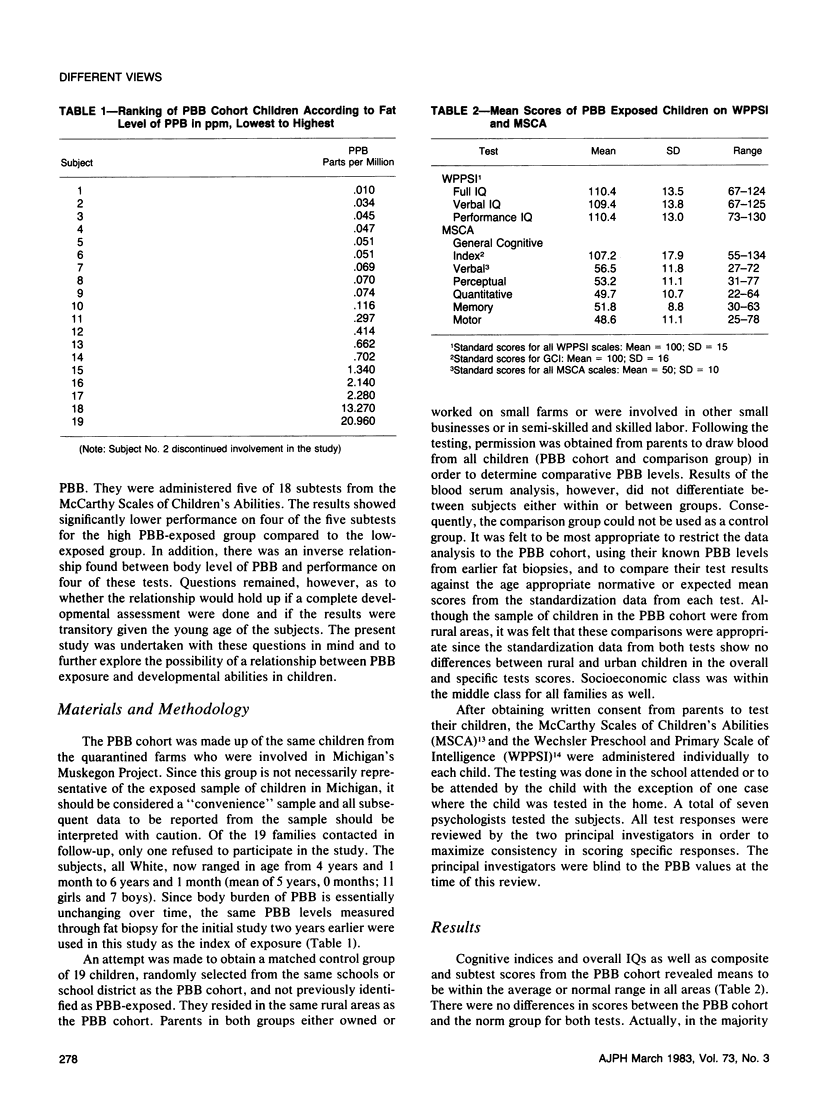
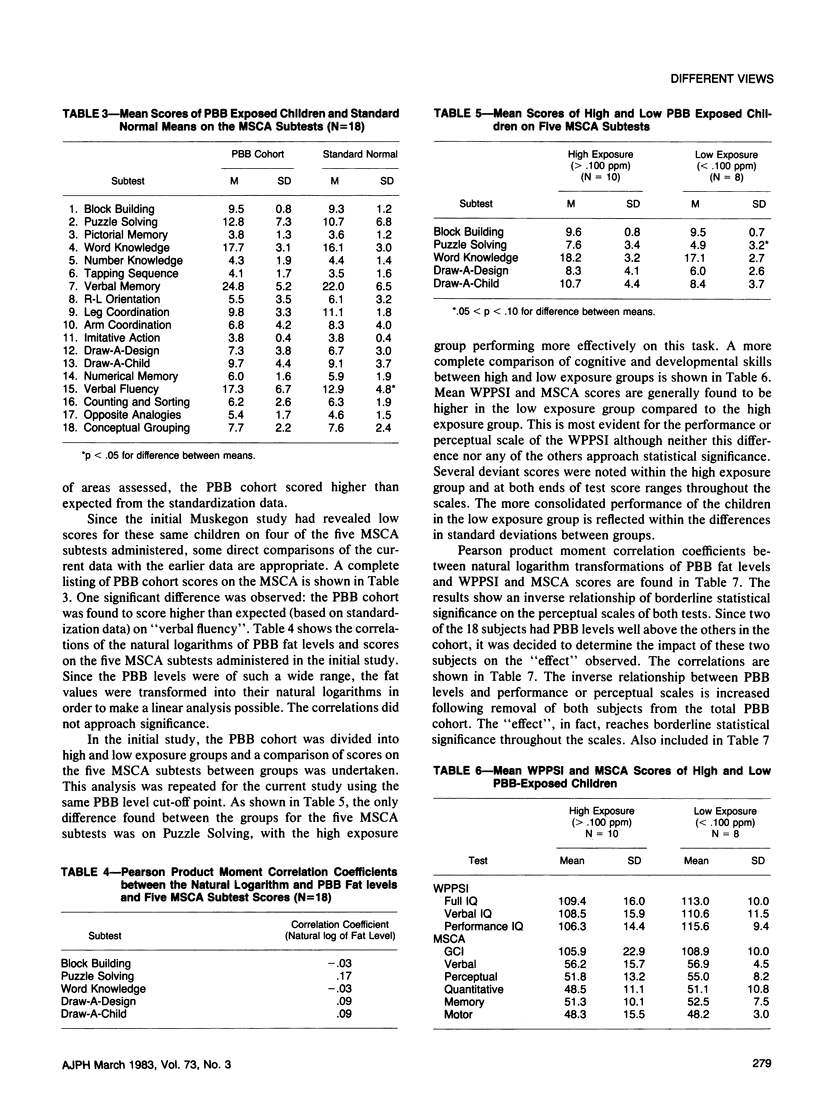
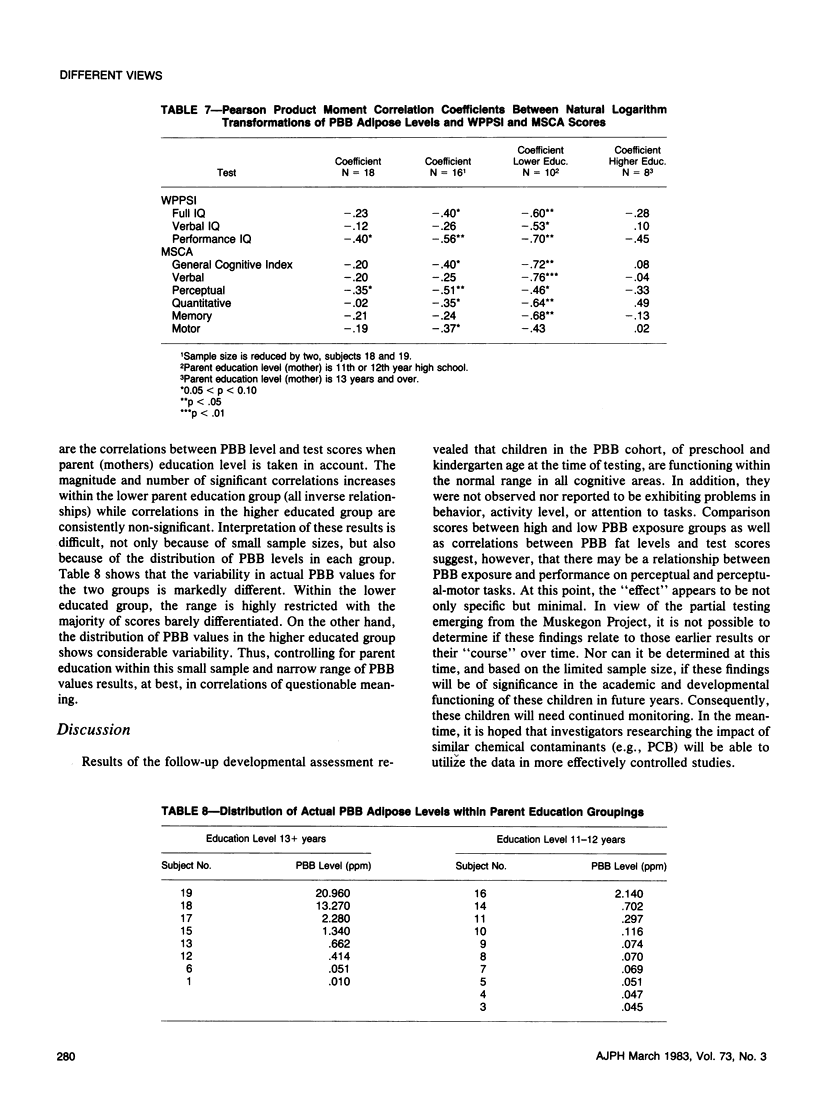
Eighteen children, ages 4 to 6 years, with known exposure to polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) in utero and/or through breast milk were administered developmental tests. These same children had exhibited low scores on a partial developmental assessment two years earlier. Current results were compared to normative test data. Findings showed: 1) PBB cohort children are within the normal range in all areas assessed; 2) An inverse relationship is noted between PBB fat level and scores on some developmental tasks. The importance of this finding for later development is unclear and, thus will bear future monitoring.
Full text
PDF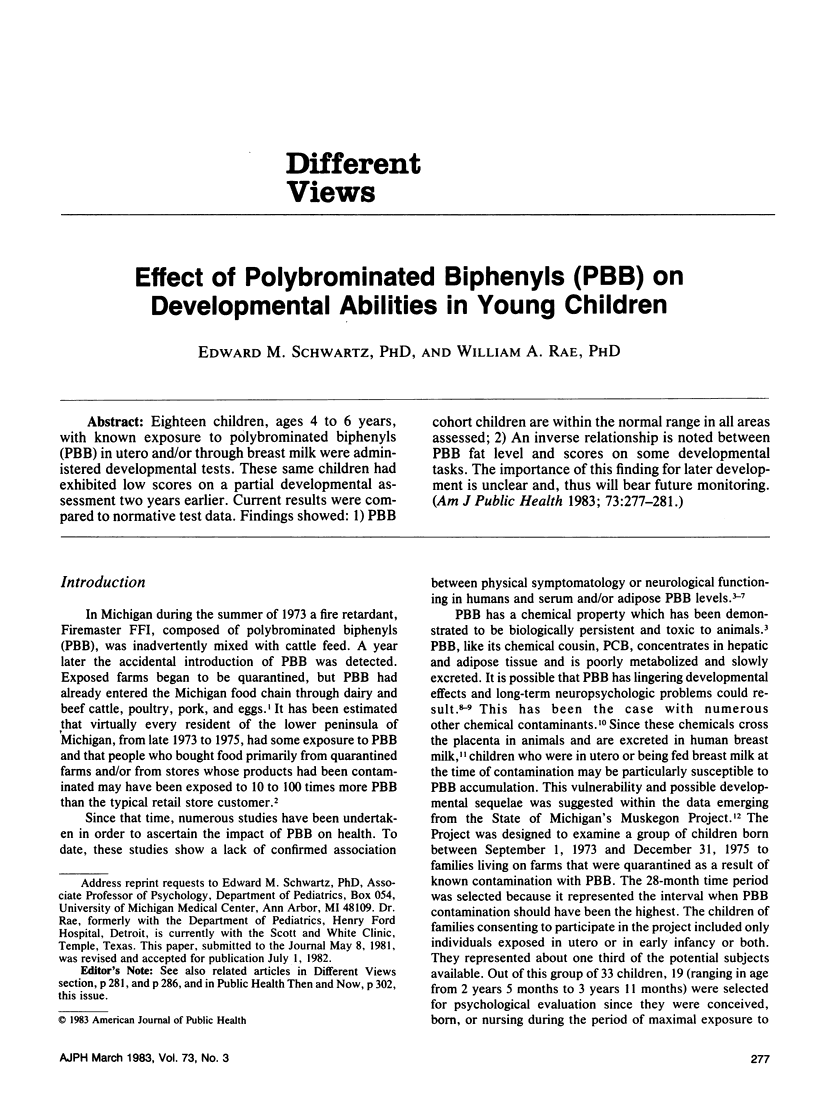

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. A., Lilis R., Selikoff I. J., Rosenman K. D., Valciukas J. A., Freedman S. Unanticipated prevalence of symptoms among dairy farmers in Michigan and Wisconsin. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Apr;23:217–226. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7823217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. A., Wolff M. S., Lilis R., Holstein E. C., Valciukas J. A., Anderson K. E., Petrocci M., Sarkozi L., Selikoff I. J. Symptoms and clinical abnormalities following ingestion of polybrominated-biphenyl-contaminated food products. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:684–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekesi J. G., Holland J. F., Anderson H. A., Fischbein A. S., Rom W., Wolff M. S., Selikoff I. J. Lymphocyte function of Michigan dairy farmers exposed to polybrominated biphenyls. Science. 1978 Mar 17;199(4334):1207–1209. doi: 10.1126/science.204005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. G., Nixon R. Exposure to polybrominated biphenyls. Some effects on personality and cognitive functioning. JAMA. 1979 Aug 10;242(6):523–527. doi: 10.1001/jama.242.6.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter L. J. Michigan's PBB Incident: Chemical Mix-Up Leads to Disaster. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):240–243. doi: 10.1126/science.192.4236.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. G., Netter K. J., Gibson J. E. Effects of chronic administration of polybrominated biphenyls on parameters associated with hepatic drug metabolism. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;13(1):75–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. D., Burse V. W., Liddle J. A. Toxicity of polybrominated biphenyl. Lancet. 1977 Sep 17;2(8038):602–603. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landrigan P. J., Wilcox K. R., Jr, Silva J., Jr, Humphrey H. E., Kauffman C., Heath C. W., Jr Cohort study of Michigan residents exposed to polybrominated biphenyls: epidemiologic and immunologic findings. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:284–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summary of the workshop on perinatal and postnatal defects and neurologic abnormalities from chemical exposures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:458–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil W. B., Spencer M., Benjamin D., Seagull E. The effect of polybrominated biphenyl on infants and young children. J Pediatr. 1981 Jan;98(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


