Abstract
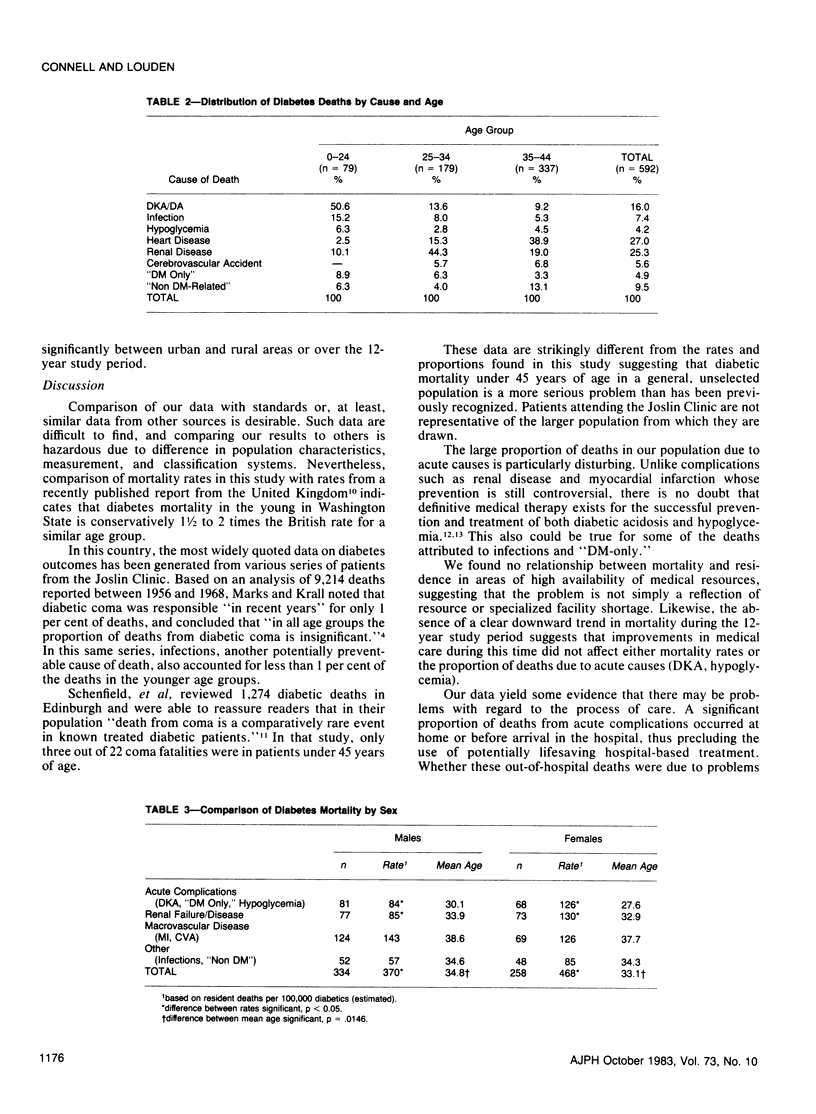
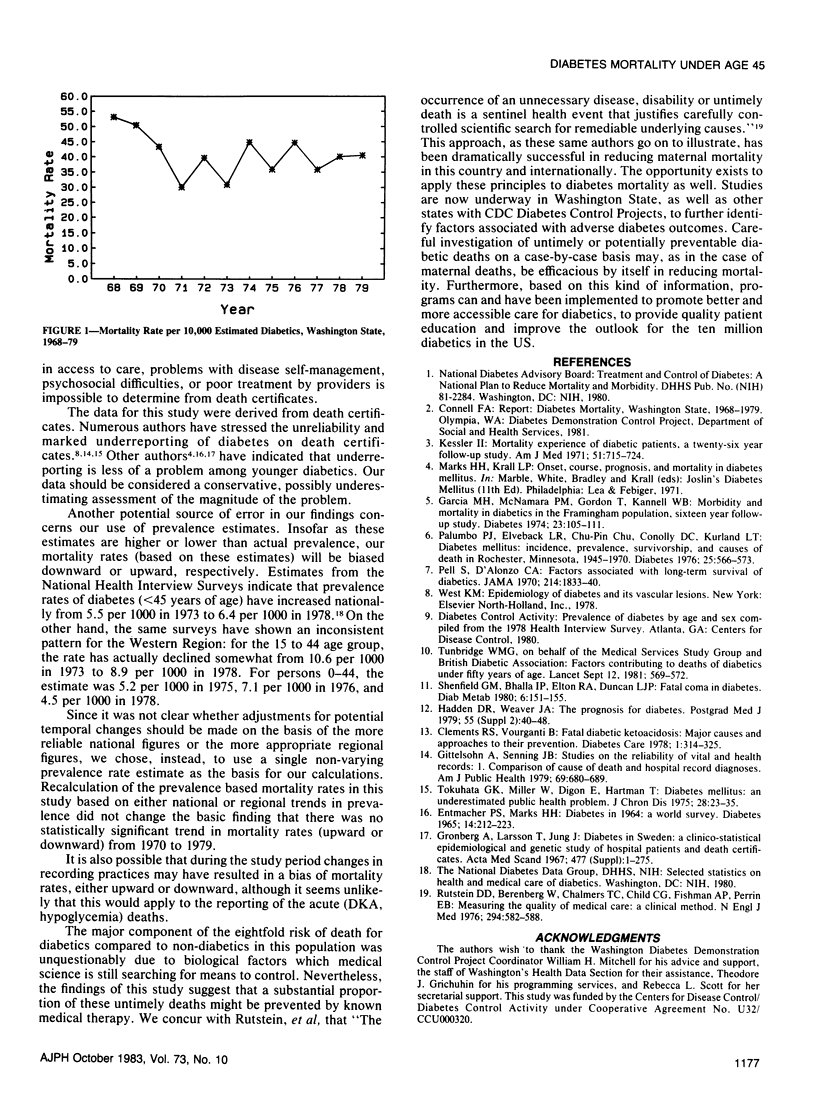
A detailed review of death certificates in Washington State for the years 1968-1979 was undertaken to analyze diabetes mortality for persons under 45 years of age. Diabetics in this age group had a mortality rate from medical causes eight times higher than that of the comparable general population. Almost one-third of the deaths were due to acute complications for which there is definitive medical therapy. Over the 12-year period there was no consistent decline in mortality rates or in deaths from acute complications, nor was there evidence of increased survivorship as reflected in the average age at death. Although residence in areas of sparse medical resources was not associated with high mortality rates, a significant proportion of deaths in all geographical areas occurred at home or before arrival at a hospital. Mortality rates and the proportion of deaths from acute, potentially preventable causes were higher in this study than in other recently published series, suggesting that early diabetes mortality may be a more serious problem than has been previously recognized. Diabetes mortality in this age group can be considered a "sentinel health event" and should call attention to potential problems in health care delivery.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clements R. S., Jr, Vourganti B. Fatal diabetic ketoacidosis: major causes and approaches to their prevention. Diabetes Care. 1978 Sep-Oct;1(5):314–325. doi: 10.2337/diacare.1.5.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENTMACHER P. S., MARKS H. H. DIABETES IN 1964; A WORLD SURVEY. Diabetes. 1965 Apr;14:212–223. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.4.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. J., McNamara P. M., Gordon T., Kannel W. B. Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes. 1974 Feb;23(2):105–111. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittelsohn A., Senning J. Studies on the reliability of vital and health records: I. Comparison of cause of death and hospital record diagnoses. Am J Public Health. 1979 Jul;69(7):680–689. doi: 10.2105/ajph.69.7.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönberg A., Larsson T., Jung J. Diabetes in Sweden. A clinico-statistical, epidemiological and genetic study of hospital patients and death certificates. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1967;477:1–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden D. R., Weaver J. A. The prognosis for diabetes. Postgrad Med J. 1979;55 (Suppl 2):40–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler I. I. Mortality experience of diabetic patients. A twenty-six-year follow-up study. Am J Med. 1971 Dec;51(6):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo P. J., Elveback L. R., Chu C. P., Connolly D. C., Kurland L. T. Diabetes mellitus: incidence, prevalence, survivorship, and causes of death in Rochester, Minnesota, 1945-1970. Diabetes. 1976 Jul;25(7):566–573. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.7.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pell S., D'Alonzo C. A. Factors associated with long-term survival of diabetics. JAMA. 1970 Dec 7;214(10):1833–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutstein D. D., Berenberg W., Chalmers T. C., Child C. G., 3rd, Fishman A. P., Perrin E. B. Measuring the quality of medical care. A clinical method. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 11;294(11):582–588. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603112941104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenfield G. M., Bhalla I. P., Elton R. A., Duncan L. J. Fatal coma in diabetes. Diabete Metab. 1980 Jun;6(2):151–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuhata G. K., Miller W., Digon E., Hartman T. Diabetes mellitus: an underestimated public health program. J Chronic Dis. 1975 Jan;28(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(75)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunbridge W. M. Factors contributing to deaths of diabetics under fifty years of age. On behalf of the Medical Services Study Group and British Diabetic Association. Lancet. 1981 Sep 12;2(8246):569–572. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90950-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


