Abstract
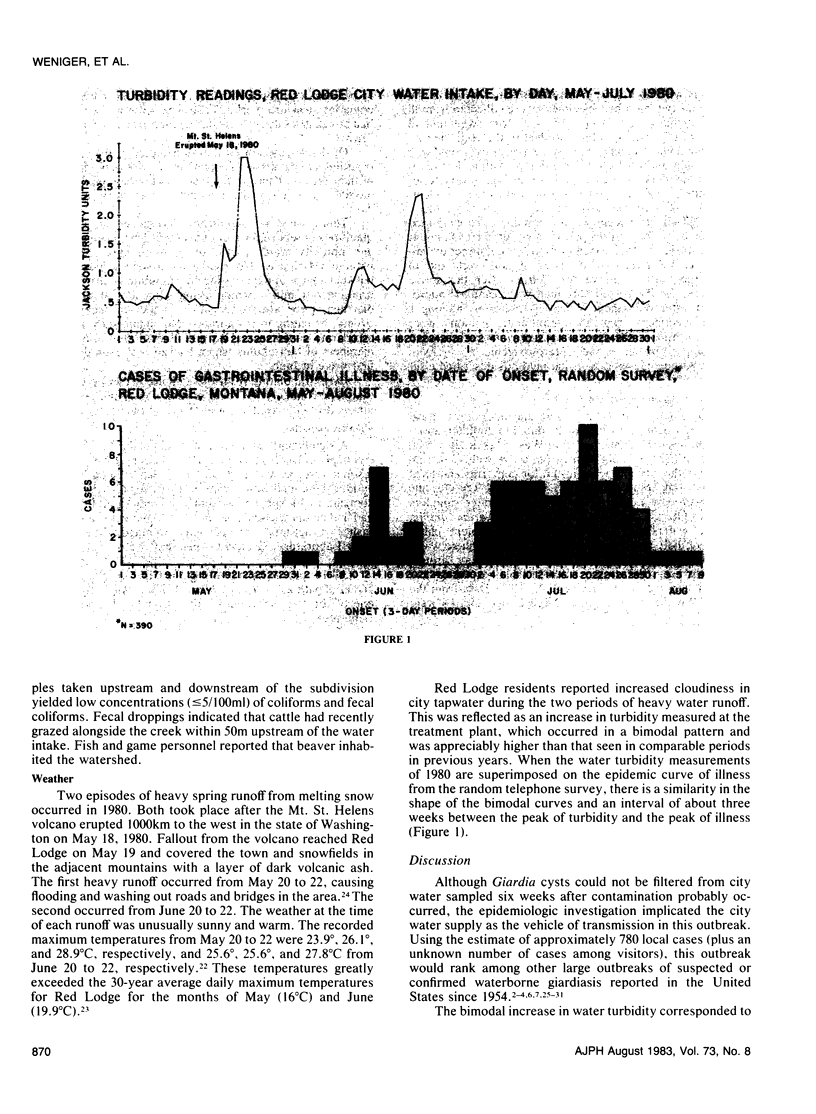
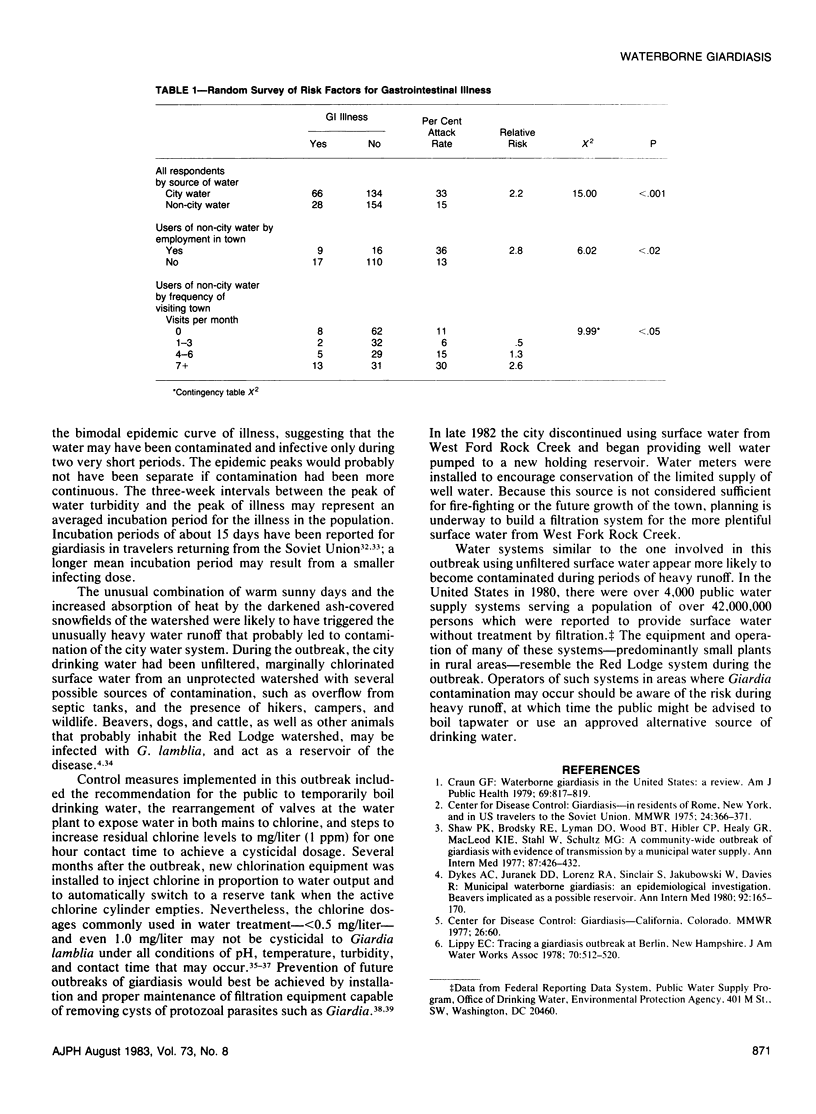
From mid-June through early August 1980, an outbreak of gastrointestinal illness in Red Lodge, Montana affected approximately 780 persons, as estimated from attack rates of 33 per cent and 15 per cent in urban and rural residents, respectively. Giardia lamblia was identified in stool specimens from 51 per cent of 47 persons with a history of untreated gastrointestinal illness and in 13 per cent of 24 specimens from asymptomatic persons (p = .00045, Fisher's Exact Test). The epidemic curve was bimodal with peaks in mid-June and mid-July. Each peak occurred about three weeks after an episode of very heavy water runoff resulting from warm sunny weather and snow darkened by ashfall from the Mt. St. Helens volcanic eruption of May 18, 1980. Unfiltered and inadequately chlorinated surface water was supplied by the city water system, which was implicated as the vehicle of transmission in the outbreak. Water systems providing unfiltered surface water are more likely to become contaminated during periods of heavy water runoff.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craun G. F. Waterborne giardiasis in the United States: a review. Am J Public Health. 1979 Aug;69(8):817–819. doi: 10.2105/ajph.69.8.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes A. C., Juranek D. D., Lorenz R. A., Sinclair S., Jakubowski W., Davies R. Municipal waterborne giardiasis: an epidemilogic investigation. Beavers implicated as a possible reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):165–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarroll E. L., Bingham A. K., Meyer E. A. Effect of chlorine on Giardia lamblia cyst viability. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):483–487. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.483-487.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarroll E. L., Jr, Bingham A. K., Meyer E. A. Giardia cyst destruction: effectiveness of six small-quantity water disinfection methods. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jan;29(1):8–11. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López C. E., Dykes A. C., Juranek D. D., Sinclair S. P., Conn J. M., Christie R. W., Lippy E. C., Schultz M. G., Mires M. H. Waterborne giardiasis: a communitywide outbreak of disease and a high rate of asymptomatic infection. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Oct;112(4):495–507. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S. D., Fox D., Brown D. Identifying school children with behavior disorders. Community Ment Health J. 1982 Winter;18(4):249–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00754539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer W. T. Epidemic giardiasis. A continued elusive entity. Rocky Mt Med J. 1973 Oct;70(10):48–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice E. W., Hoff J. C., Schaefer F. W., 3rd Inactivation of Giardia cysts by chlorine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):250–251. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.250-251.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. K., Brodsky R. E., Lyman D. O., Wood B. T., Hibler C. P., Healy G. R., Macleod K. I., Stahl W., Schultz M. G. A communitywide outbreak of giardiasis with evidence of transmission by a municipal water supply. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Oct;87(4):426–432. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-4-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veazie L. Epidemic giardiasis. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 9;281(15):853–853. doi: 10.1056/nejm196910092811521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEATLEY W. B. A rapid staining procedure for intestinal amoebae and flagellates. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Oct;21(10):990–991. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/21.10_ts.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Wolfe M. S., Schultz M. G. Giardiasis in travelers. J Infect Dis. 1971 Aug;124(2):235–237. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]