Abstract
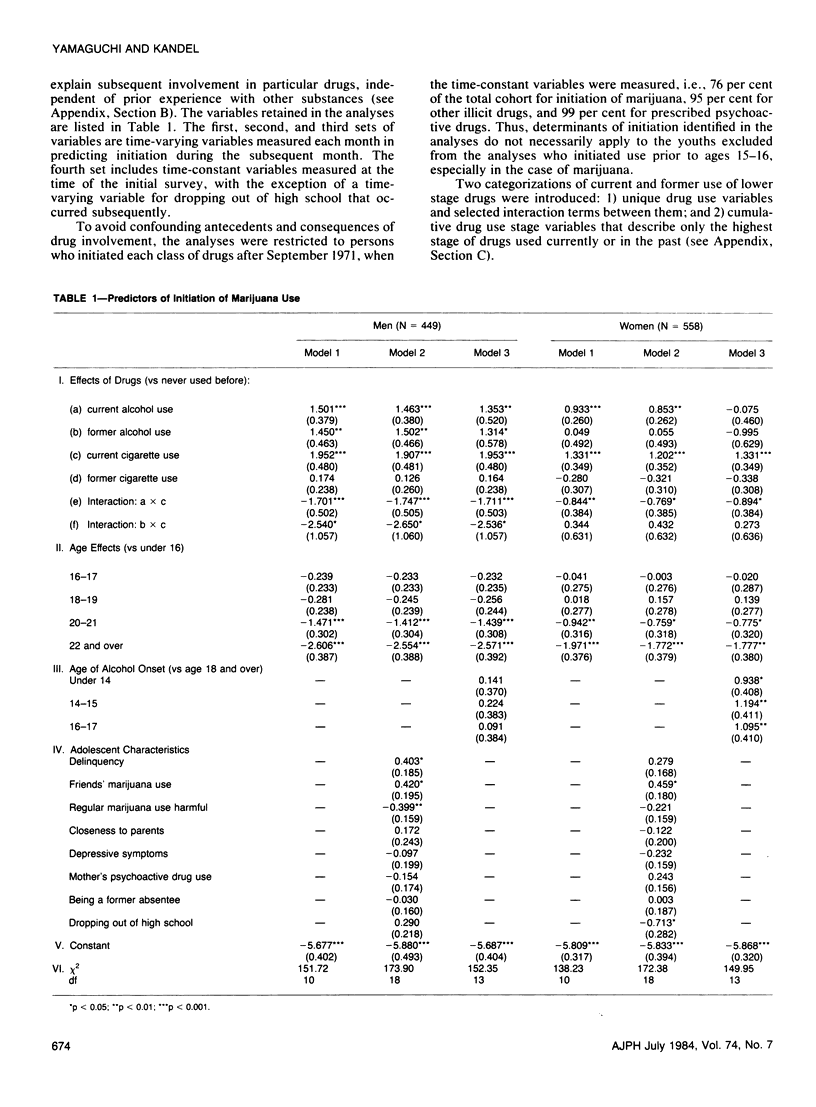
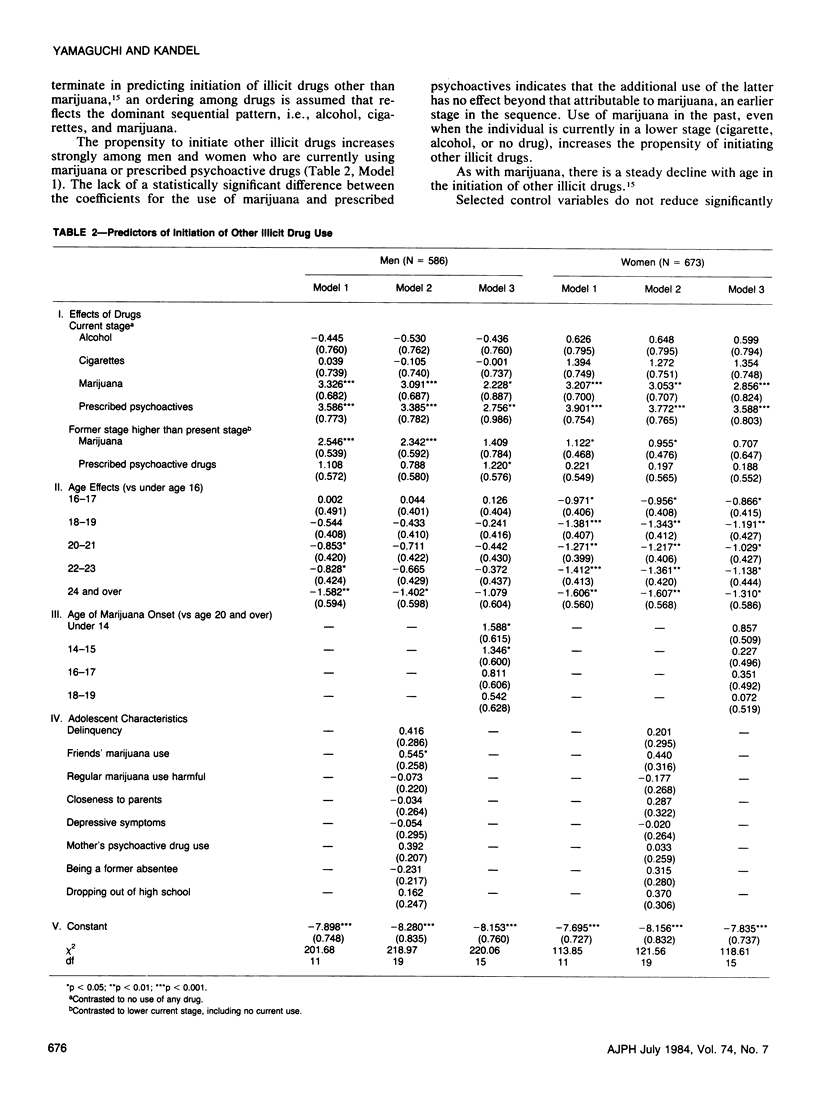
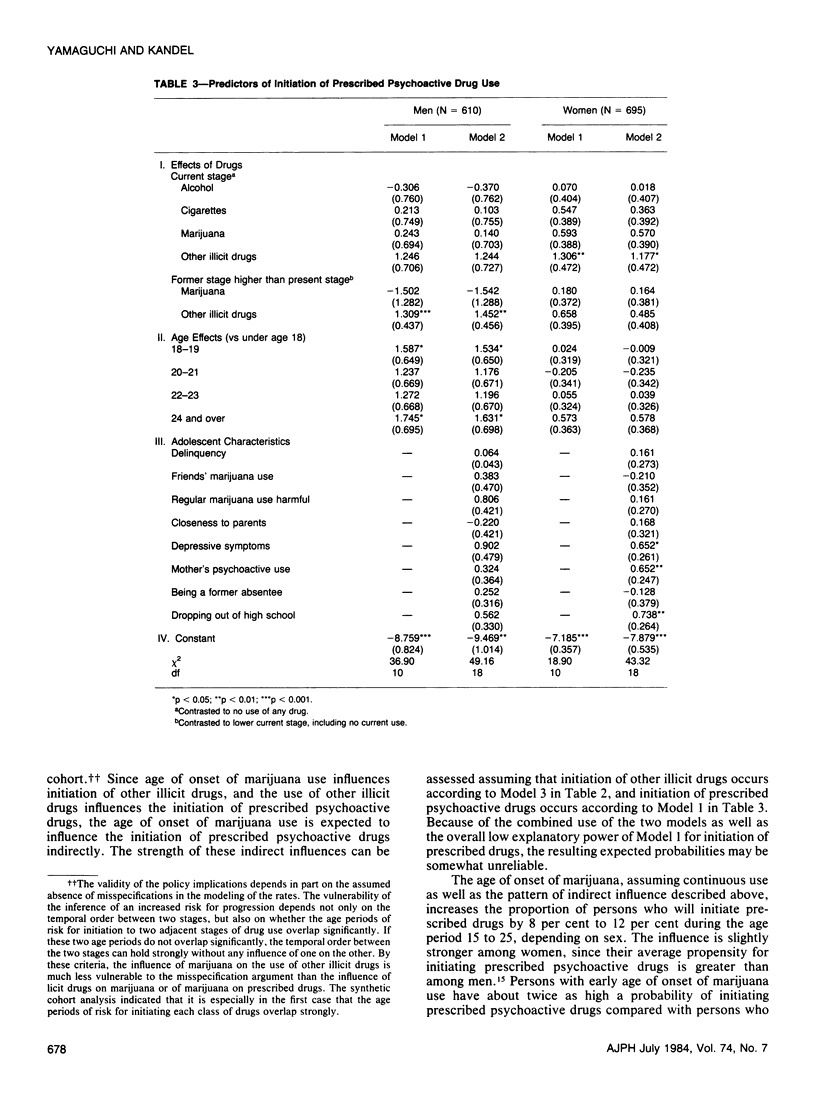
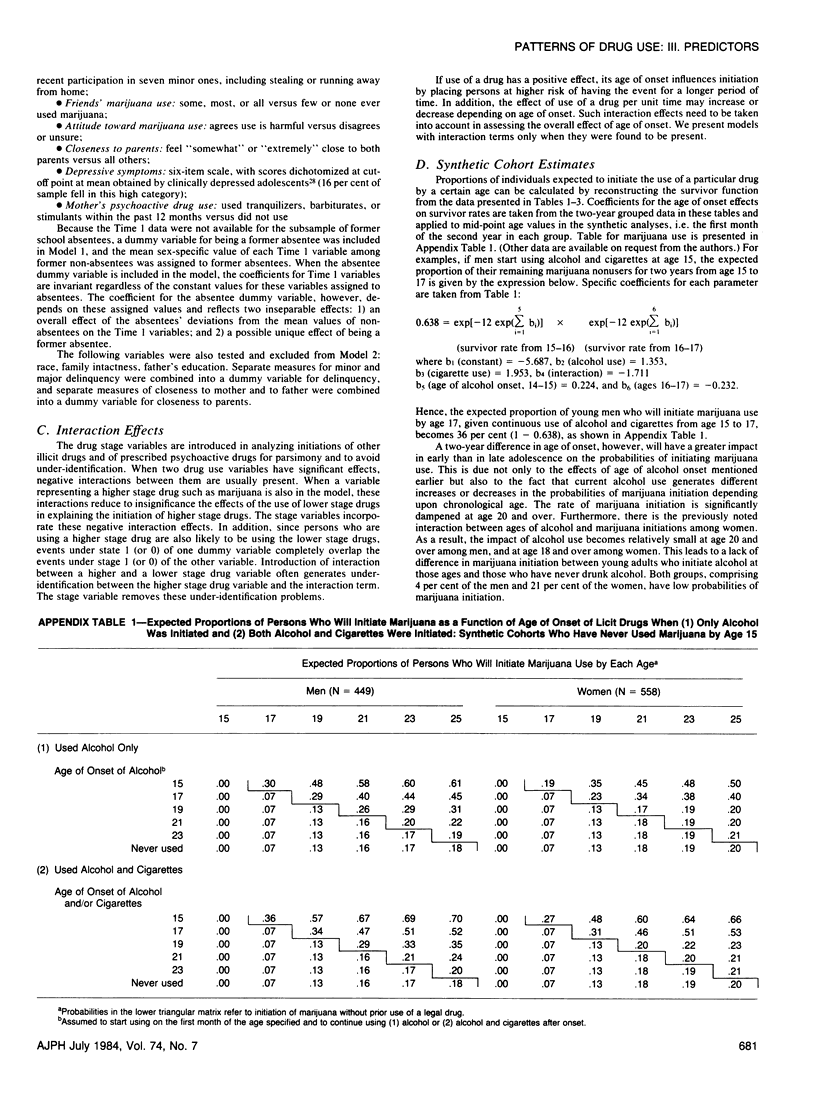
Possible linkages of influence among classes of drugs in the observed sequential progression from adolescence to young adulthood are investigated through event history analyses. Three stages are examined: initiation to marijuana, to the use of other illicit drugs, and to prescribed psychoactive drugs. The data are based on a follow-up cohort of former adolescents representative of high school students in grade 10 and 11 in New York State who were reinterviewed nine years later at ages 24-25. The sequential order between alcohol and/or cigarettes and marijuana reflects not only the effect of the use of legal drugs on marijuana initiation, but also age effects on onset of these drugs, controlling for individual characteristics measured in adolescence; marijuana use by one's friends in adolescence is an additional important predictor of marijuana initiation. Prior use of marijuana is necessary for progression to other illicit drugs. Multiple factors are involved in the progression to prescribed drugs, with adolescent depressive symptomatology and use of other illicit drugs important for both sexes, and maternal use of psychoactive drugs, dropping out of school, and prior use of marijuana of additional importance for women. Although licit drugs influence initiation into marijuana independently of age effects, it is especially for the progression from marijuana to other illicit drugs that the earlier drug is associated with the progression to a higher stage drug.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler I., Kandel D. B. Cross-cultural perspectives on developmental stages in adolescent drug use. J Stud Alcohol. 1981 Sep;42(9):701–715. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1981.42.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. S., Lukoff I. F., Whiteman M. Peer, family, and personality domains as related to adolescents drug behavior. Psychol Rep. 1977 Dec;41(3 Pt 2):1095–1102. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1977.41.3f.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. E., Jessor R. Problem drinking and the dimension of involvement with drugs: a Guttman scalogram analysis of adolescent drug use. Am J Public Health. 1983 May;73(5):543–552. doi: 10.2105/ajph.73.5.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huba G. J., Wingard J. A., Bentler P. M. A comparison of two latent variable causal models for adolescent drug use. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1981 Jan;40(1):180–193. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.40.1.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel D. B., Davies M. Epidemiology of depressive mood in adolescents: an empirical study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982 Oct;39(10):1205–1212. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290100065011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel D. B. Marijuana users in young adulthood. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Feb;41(2):200–209. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790130096013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel D., Single E., Kessler R. C. The epidemiology of drug use among New York State high school students: Distribution, trends, and change in rates of use. Am J Public Health. 1976 Jan;66(1):43–53. doi: 10.2105/ajph.66.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell J. A., Clayton R. R. The stepping-stone hypothesis--marijuana, heroin, and causality. Chem Depend. 1982;4(3):229–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton S., Kessler R., Kandel D. Depressive mood and adolescent illicit drug use: a longitudinal analysis. J Genet Psychol. 1977 Dec;131(2D):267–289. doi: 10.1080/00221325.1977.10533299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Kandel D. B. Patterns of drug use from adolescence to young adulthood: II. Sequences of progression. Am J Public Health. 1984 Jul;74(7):668–672. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.7.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


