Abstract
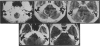
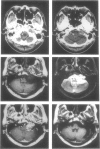
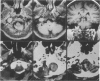
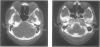
Twelve patients with jugular foramen neurinoma were operated on at our clinic between 1974 and 1990. The initial signs and symptoms were variable; dysfunctions of the 7th, 8th, 9th, 10th, and 11th nerves were frequently observed. Among these, involvement of the eighth nerve was most frequent, and three patients were given a misdiagnosis of acoustic neurinoma. Computed tomography scan and magnetic resonance imaging were useful not only for the correct diagnosis, but also for planning the surgical treatment and postoperative followup. Surgical resection was accomplished with four different approaches: (1) suboccipital approach without opening the jugular foramen, (2) suboccipital approach with opening the jugular foramen, (3) suboccipital approach with opening the jugular foramen combined with infralabyrinthine approach, (4) infralabyrinthine approach. The surgical approach depended on the presence of intracranial tumor and on the extent of extracranial involvement. There was no operative mortality. Dysfunction of the 8th, 9th, 10th, or 11th nerve did not improve in any patient after tumor removal. In contrast, 12th nerve palsy improved in two of three patients after tumor removal. The nerve of origin was identified in five cases; those were from the ninth nerve in three and from the 11th nerve in two.
Full text
PDF
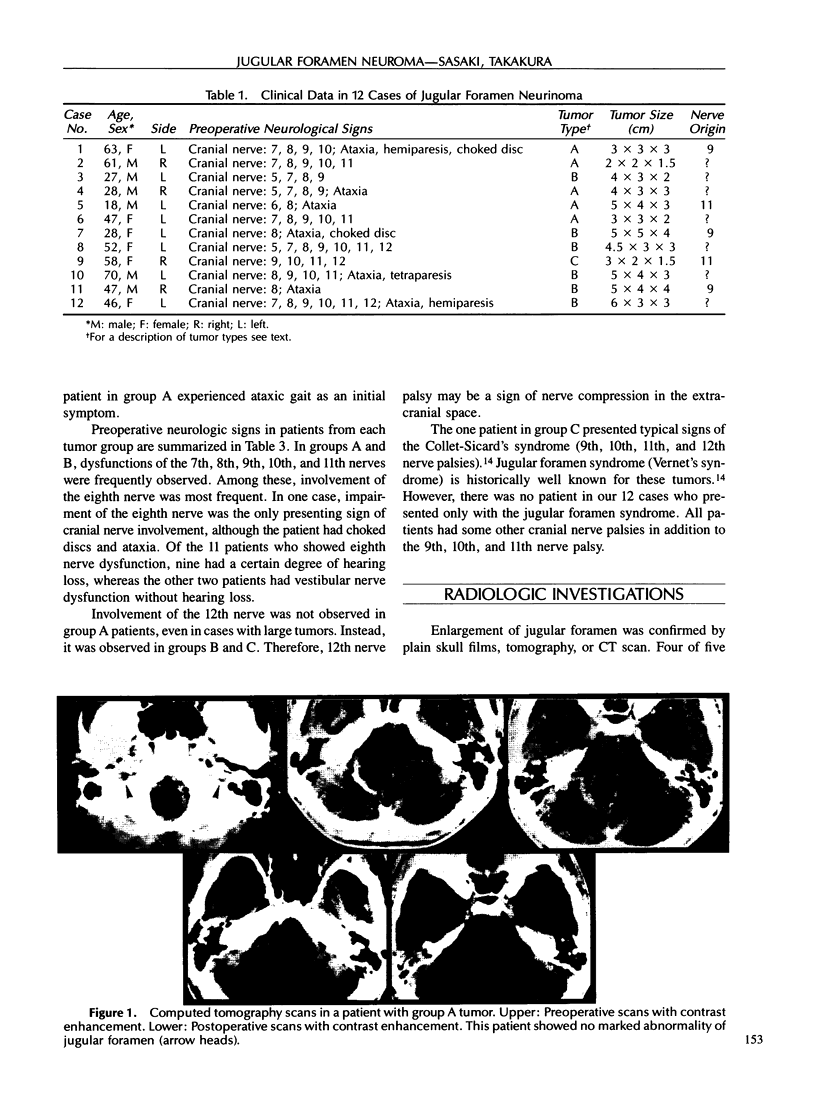
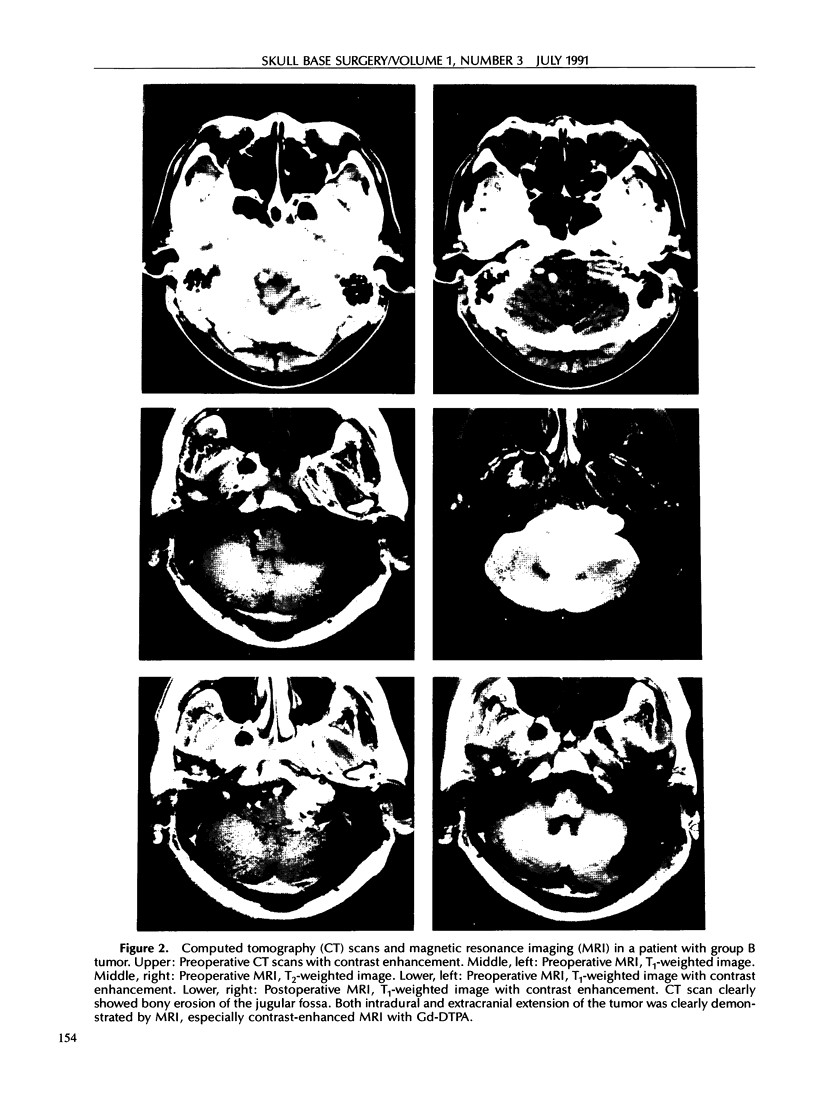

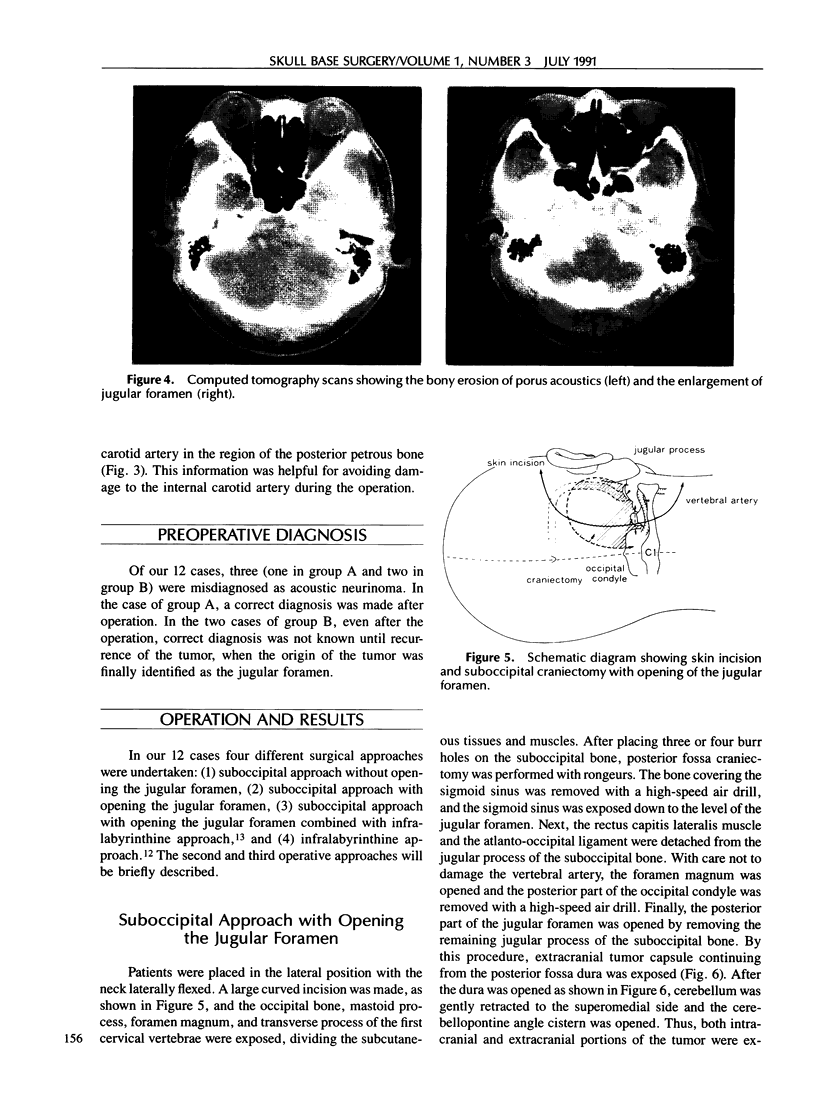

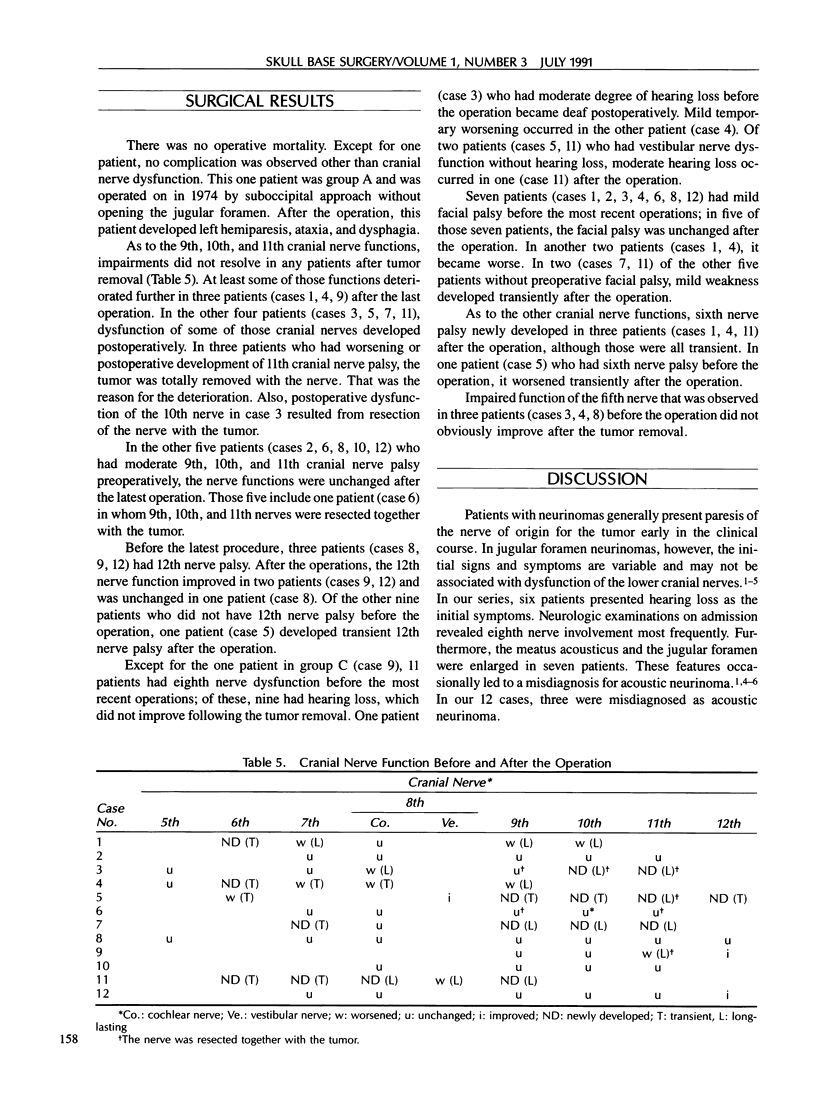


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clemis J. D., Noffsinger D., Derlacki E. L. A jugular foramen schwannoma simulating an acoustic tumor with recovery of retrolabyrinthine cochleovestibular function. Trans Sect Otolaryngol Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1977 Jul-Aug;84(4 Pt 1):ORL–687-96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumley R. L., Wilson C. Schwannomas of the jugular foramen. Laryngoscope. 1984 Jun;94(6):772–778. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198406000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch U., Pillsbury H. C. Infratemporal fossa approach to lesions in the temporal bone and base of the skull. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979 Feb;105(2):99–107. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1979.00790140045008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin D. J., Moore G. F., Fisch U. Jugular foramen peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Laryngoscope. 1989 Oct;99(10 Pt 1):1081–1087. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198210000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gacek R. R. Schwannoma of the jugular foramen. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976 Mar-Apr;85(2 PT1):215–224. doi: 10.1177/000348947608500206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakuba A., Hashi K., Fujitani K., Ikuno H., Nakamura T., Inoue Y. Jugular foramen neurinomas. Surg Neurol. 1979 Feb;11(2):83–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn K. L., House W. F., Hitselberger W. E. Schwannomas of the jugular foramen. Laryngoscope. 1985 Jul;95(7 Pt 1):761–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye A. H., Hahn J. F., Kinney S. E., Hardy R. W., Jr, Bay J. W. Jugular foramen schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 1984 May;60(5):1045–1053. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.5.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. R., Johns M. E., Winn R. H. Infralabyrinthine approach to skull-base lesions. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985 Apr;93(2):250–258. doi: 10.1177/019459988509300224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniglia A. J., Chandler J. R., Goodwin W. J., Jr, Parker J. C., Jr Schwannomas of the parapharyngeal space and jugular foramen. Laryngoscope. 1979 Sep;89(9 Pt 1):1405–1414. doi: 10.1002/lary.5540890905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima T., Hasuo K., Yasumori K., Yoshida K., Hirakata R., Fukui M., Masuda K. Magnetic resonance imaging of jugular foramen neurinomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1989;96(3-4):83–87. doi: 10.1007/BF01456163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountjoy J. R., Dolan K. D., McCabe B. F. Neurilemmoma of the ninth cranial nerve masquerading as an acoustic neuroma. Arch Otolaryngol. 1974 Jul;100(1):65–67. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1974.00780040069015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely J. G. Reversible compression neuropathy of the eighth cranial nerve from a large jugular foramen schwannoma. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979 Sep;105(9):555–560. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1979.00790210053012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluchino F., Crivelli G., Vaghi M. A. Intracranial neurinomas of the nerves of the jugular foramen. Report of 12 personal cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1975;31(3-4):201–221. doi: 10.1007/BF01406293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVIEN H. J., BAKER H. L., RIVERS M. H. JUGULAR FORAMEN SYNDROME AND ALLIED SYNDROMES. Neurology. 1963 Sep;13:797–809. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.9.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamataki A., Fujitsu K., Fujii S., Mochimatsu Y., Kuwabara T. [Surgical approach for jugular foramen neurinoma--combined suboccipital and infralabyrinthine approach using a rotatable head holder]. No Shinkei Geka. 1986 Jun;14(7):887–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]