Abstract
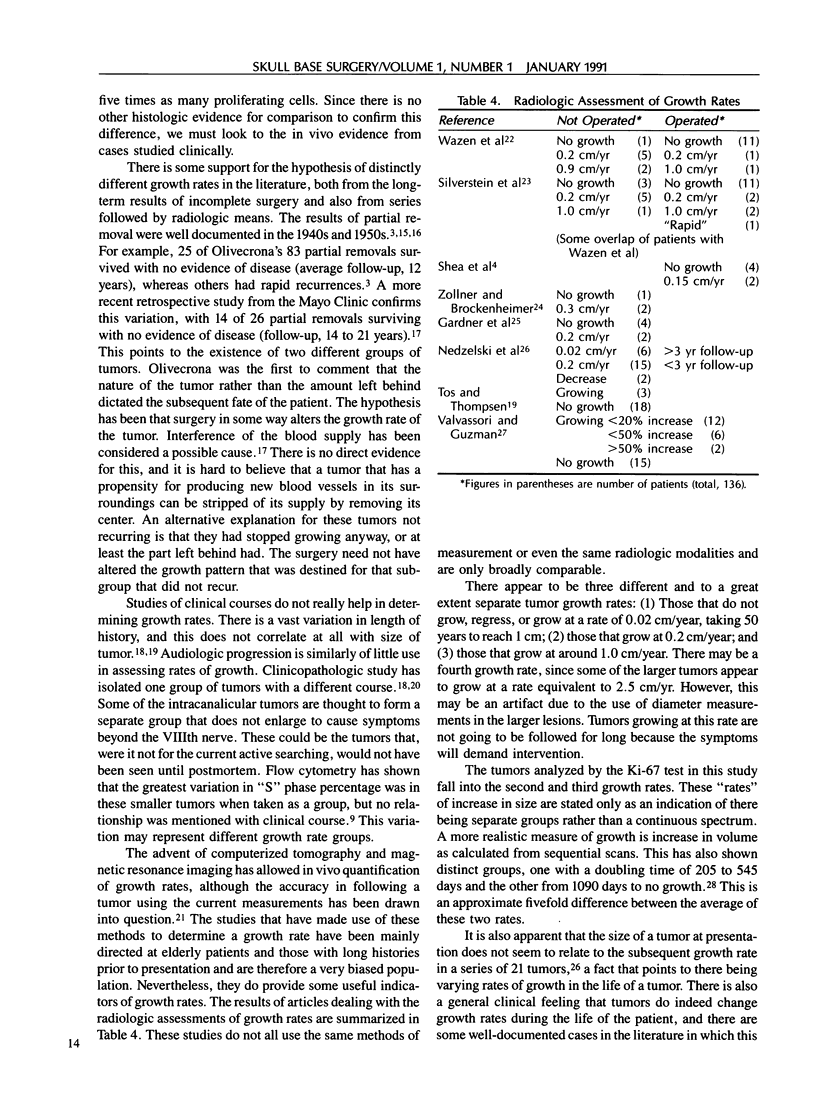
The growth rate of acoustic tumors, although slow, varies widely. There may be a continuous spectrum or distinct groups of tumor growth rates. Clinical, audiologic, and conventional histologic tests have failed to shed any light on this problem. Modern immunohistochemical methods may stand a better chance. The Ki-67 monoclonal antibody stains proliferating cells and is used in this study to investigate the growth fraction of 13 skull base schwannomas. The acoustic tumors can be divided into two different growth groups, one with a rate five times the other. The literature is reviewed to see if this differentiation is borne out by the radiologic studies. Distinct growth rates have been reported: one very slow, taking 50 years to reach 1 cm in diameter, a second rate with a diameter increase of 0.2 cm/year, and a third rate five times the second, with a 1.0 cm increase in diameter per year. A fourth group growing at 2.5 cm/year is postulated, but these tumors cannot be followed for long radiologically, since symptoms demand surgical intervention. The clinical implications of these separate growth rates are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burger P. C., Shibata T., Kleihues P. The use of the monoclonal antibody Ki-67 in the identification of proliferating cells: application to surgical neuropathology. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Sep;10(9):611–617. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198609000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross J. P., Jr Unilateral neurilemmomas of the eighth cranial nerve: then and now. Am J Otol. 1981 Jul;3(1):28–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargason R. D., Jacques S., Rand R. W., Shelden C. H. A three-dimensional and volume determination of tumors of the cerebellopontine angle. Surg Neurol. 1982 Aug;18(2):112–115. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(82)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner G., Moretz W. H., Jr, Robertson J. H., Clark C., Shea J. J., Jr Nonsurgical management of small and intracanalicular acoustic tumors. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986 Mar;94(3):328–333. doi: 10.1177/019459988609400312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J. An immunohistological method for estimating cell growth fractions in rapid histopathological diagnosis during surgery. Int J Cancer. 1985 Feb 15;35(2):169–171. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Schwab U., Lemke H., Stein H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;31(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSCHEN F., LUNDBORG T. The relation between the clinical course and the morphologic picture in acoustic tumors. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1954;116:121–126. doi: 10.3109/00016485409130285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasantikul V., Netsky M. G., Glasscock M. E., 3rd, Hayes J. W. Intracanalicular neurilemmomas: clinicopathologic study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1980 Jan-Feb;89(1 Pt 1):29–32. doi: 10.1177/000348948008900108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasantikul V., Netsky M. G., Glasscock M. E., 3rd, Hays J. W. Acoustic neurilemmoma. Clinicoanatomical study of 103 patients. J Neurosurg. 1980 Jan;52(1):28–35. doi: 10.3171/jns.1980.52.1.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laasonen E. M., Troupp H. Volume growth rate of acoustic neurinomas. Neuroradiology. 1986;28(3):203–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00548193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolt A. M., Shibata T., Kleihues P. Growth rate of human pituitary adenomas. J Neurosurg. 1987 Dec;67(6):803–806. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.6.0803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetje C. M., Whittaker C. K., Davidson K. C., Vergara G. G. Spontaneous acoustic tumor involution: a case report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1988 Jan;98(1):95–97. doi: 10.1177/019459988809800118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTHFIELD D. W. C. Acoustic neurinoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1950 Nov;13(4):277–278. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.13.4.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nager G. T. Acoustic neurinomas. Acta Otolaryngol. 1985 Mar-Apr;99(3-4):245–261. doi: 10.3109/00016488509108905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedzelski J. M., Canter R. J., Kassel E. E., Rowed D. W., Tator C. H. Is no treatment good treatment in the management of acoustic neuromas in the elderly? Laryngoscope. 1986 Aug;96(8):825–829. doi: 10.1002/lary.1986.96.8.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVECRONA H. Analysis of results of complete and partial removal of acoustic neuromas. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1950 Nov;13(4):271–272. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.13.4.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNYBACKER J. B., CAIRNS H. Results in 130 cases of acoustic neurinoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1950 Nov;13(4):272–277. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.13.4.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen N., Tribukait B., Thomsen J., Holm L. E., Tos M. Implications of DNA characterization of human acoustic neuromas. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1984;406:278–281. doi: 10.3109/00016488309123050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea J. J., 3rd, Hitselberger W. E., Benecke J. E., Jr, Brackmann D. E. Recurrence rate of partially resected acoustic tumors. Am J Otol. 1985 Nov;Suppl:107–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen J., Tos M. Acoustic neuromas. Diagnostic delay, growth rate and possible non-surgical treatment. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1988;452:26–33. doi: 10.3109/00016488809124991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tos M., Thomsen J. Epidemiology of acoustic neuromas. J Laryngol Otol. 1984 Jul;98(7):685–692. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100147292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valvassori G. E., Guzman M. Growth rate of acoustic neuromas. Am J Otol. 1989 May;10(3):174–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wazen J., Silverstein H., Norrell H., Besse B. Preoperative and postoperative growth rates in acoustic neuromas documented with CT scanning. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985 Apr;93(2):151–155. doi: 10.1177/019459988509300204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennerberg J., Mercke U. Growth potential of acoustic neuromas. Am J Otol. 1989 Jul;10(4):293–296. doi: 10.1097/00129492-198907000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zöllner C., Bockenheimer S. The growth rate of acoustic neuromas: a report of three cases. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1985;241(3):259–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00453697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



