Abstract
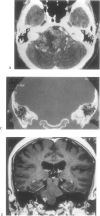
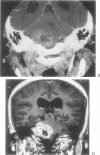
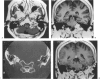
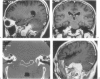
Twelve cases of schwannomas of the jugular foramen that involved surgery in our department between 1983 and 1997 are described. Eight were women and 4 were men (mean age, 40 years), and the duration of their symptoms, the most predominant of which were hearing loss and tinnitus, ranged from 1 month to 20 years (median, 8.5 months). Depending on their radiological and surgical features, tumors were classified as type A, a tumor primarily at the cerebellopontine angle with minimal enlargement of the jugular foramen (n = 5); type B, a tumor primarily at the jugular foramen with or without intracranial extension (n = 4); type C, a primarily extracranial tumor with extension into the jugular foramen (n = 0); or type D, a dumbbell tumor with both intracranial and extracranial components (n = 3). A retrosigmoid suboccipital craniectomy (RSSOC) was performed for type A tumors; for types B and D, the RSSOC or staged infratemporal fossa approach (ITFA)/RSSOC was used. Total removal was achieved in 6 cases, near total removal in 3, and subtotal removal in 3. The most common complication was lower cranial nerve dysfunction (n = 5). The follow-up period ranged from 6 to 173 (mean, 48) months, and there was no recurrence. Two patients showed regrowth of the tumor after subtotal resection, however. In 1 of these, the residual tumor had progressed within 12 months of initial surgery, it was again resected and linac radiosurgery was successful. In the other, the residual mass had progressed within 8 months of initial surgery, and the pathological report indicated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. Conclusively, type A tumors could be totally resected with the retrosigmoid approach alone. For type B and D tumors, however, combined ITFA and retrosigmoid approach showed the better results. In spite of our limited data, cases showing adhesion to critical structures can be managed by subtotal or near total resection followed by radiosurgery to reduce postoperative complications.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenberg I. K., McCreary H. S. Neurilemmoma of the jugular foramen. Laryngoscope. 1971 Apr;81(4):544–557. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197104000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call W. H., Pulec J. L. Neurilemoma of the jugular foramen. Transmastoid removal. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1978 May-Jun;87(3 Pt 1):313–317. doi: 10.1177/000348947808700303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesen P., Plets C., Goffin J., Van den Bergh R., Baert A., Wilms G. The glossopharyngeal neurinoma. Case reports and literature review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1989;91(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/s0303-8467(89)80010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumley R. L., Wilson C. Schwannomas of the jugular foramen. Laryngoscope. 1984 Jun;94(6):772–778. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198406000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch U., Pillsbury H. C. Infratemporal fossa approach to lesions in the temporal bone and base of the skull. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979 Feb;105(2):99–107. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1979.00790140045008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin D. J., Moore G. F., Fisch U. Jugular foramen peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Laryngoscope. 1989 Oct;99(10 Pt 1):1081–1087. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198210000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gacek R. R. Schwannoma of the jugular foramen. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976 Mar-Apr;85(2 PT1):215–224. doi: 10.1177/000348947608500206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn K. L., House W. F., Hitselberger W. E. Schwannomas of the jugular foramen. Laryngoscope. 1985 Jul;95(7 Pt 1):761–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani H., Masuzawa H., Kanazawa I., Kubo T., Tokuyama Y. A combined extradural-posterior petrous and suboccipital approach to the jugular foramen tumours. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1994;126(2-4):179–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01476430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura Y., Sze G. Totally cystic schwannoma of the tenth cranial nerve mimicking an epidermoid. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992 Sep-Oct;13(5):1333–1334. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye A. H., Hahn J. F., Kinney S. E., Hardy R. W., Jr, Bay J. W. Jugular foramen schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 1984 May;60(5):1045–1053. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.5.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida Y., Kobayashi T., Tanaka T., Oyama H., Niwa M. [A new strategy for the treatment of jugular foramen tumors using radiosurgery]. No Shinkei Geka. 1995 Aug;23(8):671–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. B., Kim S. H., Kim H. T., Kim J. H., Kim M. H., Ko Y. Jugular foramen neurilemmoma mimicking an intra-axial brainstem tumor--a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 1996 Jun;11(3):282–284. doi: 10.3346/jkms.1996.11.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magliulo G., Ronzoni R., Cristofari P. Unilateral acoustic neuroma associated with a tenth cranial nerve schwannoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1993 Oct;102(10):818–819. doi: 10.1177/000348949310201016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoni A., Sanna M., Saleh E., Achilli V. Lower cranial nerve schwannomas involving the jugular foramen. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1997 May;106(5):370–379. doi: 10.1177/000348949710600503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naunton R. F., Proctor L., Elpern B. S. The audiologic signs of ninth nerve neurinoma. Arch Otolaryngol. 1968 Mar;87(3):222–227. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1968.00760060224002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely J. G. Reversible compression neuropathy of the eighth cranial nerve from a large jugular foramen schwannoma. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979 Sep;105(9):555–560. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1979.00790210053012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz O., Reed L. Spinal accessory nerve schwannoma involving the jugular foramen. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995 Apr;16(4 Suppl):986–989. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellet W., Cannoni M., Pech A. The widened transcochlear approach to jugular foramen tumors. J Neurosurg. 1988 Dec;69(6):887–894. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.69.6.0887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluchino F., Crivelli G., Vaghi M. A. Intracranial neurinomas of the nerves of the jugular foramen. Report of 12 personal cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1975;31(3-4):201–221. doi: 10.1007/BF01406293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock B. E., Kondziolka D., Flickinger J. C., Maitz A., Lunsford L. D. Preservation of cranial nerve function after radiosurgery for nonacoustic schwannomas. Neurosurgery. 1993 Oct;33(4):597–601. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199310000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samii M., Babu R. P., Tatagiba M., Sepehrnia A. Surgical treatment of jugular foramen schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 1995 Jun;82(6):924–932. doi: 10.3171/jns.1995.82.6.0924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmall R. J., Dolan K. D. Vagal schwannoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1992 Apr;101(4):360–362. doi: 10.1177/000348949210100413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal R., d'Anthouard F., David P., Halimi P., Zerah M., Bely N., Doyon D., Hurth M. Cystic schwannoma mimicking a brain stem tumor: MR features. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):662–664. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199007000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki F., Handa J., Todo G. Intracranial glossopharyngeal neurinomas. Report of two cases with special emphasis on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Surg Neurol. 1989 May;31(5):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(89)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan L. C., Bordi L., Symon L., Cheesman A. D. Jugular foramen neuromas: a review of 14 cases. Surg Neurol. 1990 Oct;34(4):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(90)90130-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner K. E., Pitts L. H., Davis R. L., Sheline G. E. Radiation therapy for the treatment of non-eight nerve intracranial neurilemmoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988 Feb;14(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(88)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner K. E., Sheline G. E., Pitts L. H., Wara W. M., Davis R. L., Boldrey E. B. Efficacy of irradiation for incompletely excised acoustic neurilemomas. J Neurosurg. 1987 Dec;67(6):858–863. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.6.0858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]